
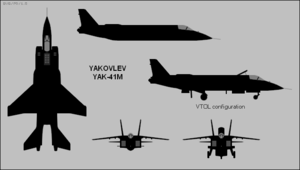
Yakovlev Yak-141
Encyclopedia
The Yakovlev Yak-141 (NATO reporting name
Freestyle), also known as the Yak-41, is a supersonic
vertical takeoff/landing
(VTOL) fighter aircraft
designed by Yakolev. It did not enter production.
to be an interim aircraft, developed to gain experience designing and developing military VTOL aircraft. Even before the Yak-38's introduction, the Soviet Navy desired a more comprehensive aircraft, with greater capabilities than the Yak-38 offered. The result was a design contract offered to Yakovlev in 1975
without any competition. The requirement was for an aircraft with only one mission: air defense of the fleet. Unlike the Yak-38, this aircraft was to have sustained supersonic speed. Maneuverability, radar and weapons loads were expected to be similar to those of current front-line fighters. For the Soviet Navy this aircraft was to be their next generation VTOL fighter. For Yakovlev the aircraft was viewed as a way of returning to designing Soviet fighter aircraft.
Because of the importance and complexity of the project, Alexander Sergeyevich Yakovlev
assigned a large portion of his OKB
to the development of the new VTOL fighter, with no fewer than ten chief engineers working simultaneously on what was called "Product 48" (the military had designated it Yak-41). Over fifty designs were studied. One key problem was designing an aircraft with both vectoring thrust and an afterburner, which was essential for sustained supersonic speeds. A twin-engine design was considered, but abandoned as the loss of an engine on landing would result in an immediate roll to the side. Eventually it was decided that the best arrangement was a single vectoring nozzle located just behind the center of gravity, as well as dedicated vertical thrust jets positioned just behind the cockpit. A considerable amount of time was spent in the development of a flat, rectangular nozzle similar to that later employed on the American F-22 Raptor
. Such a nozzle proved well-suited for the changes in configuration needed for both thrust vectoring and supersonic flight, and allowed for a thin, shallow tail. Ultimately, a circular nozzle was used, located between twin booms supporting the twin-finned tail.
Parts that were to be subjected to excessive heat from the engines during landing were manufactured of titanium
, and no less than 26% of the overall aircraft was to be manufactured of graphite
or composite material
. Because of heat build-up, hovering was restricted to no more than 2½ minutes.
All three engines were controlled through an interlinked digital system, which was capable of controlling both engine start-up as well as modulating the thrust of all three engines during landing and hovering flight. Twin tandem reaction control jets were positioned at the wingtips, while a swiveling yaw jet was positioned under the nose.
The cockpit was pressurized and air-conditioned. The small canopy was bulletproof in front. It hinged to the right, but because of a long dorsal spine it had no rear vision. The ejection seat was automatically armed as soon as the engine duct was rotated past 30 degrees with an airspeed of less than 300 km/h (186 mph). The instrumentation in the prototypes was simple and similar to that planned for the earlier Yak-36M. The production version was to have been fitted with an extensive avionics and weapons suite including doppler radar, laser-TV ranging and aiming, as well as a heads-up multifunction display (HUD) which worked in connection with a helmet-mounted missile aiming system as found on the Mikoyan MiG-29
. This system allows the pilot to lock onto an enemy aircraft by turning his head as far as 80 degrees from front.
The undercarriage was tricycle, and equipped with the latest multi-disc, anti-skid brakes. The steerable nose wheel retracted to the rear, while the main gear retracted forward.
The top-mounted wing was similar to that of the Yakovlev Yak-36, though the outer panel swept back, and could be folded up for shipboard storage. The main engine was served by four side-mounted ducts as well as a row of large louvers along the upper surface to allow air to enter the engine during full power hovering. This engine was the R-79V-300, a two-shaft augmented turbofan with a bypass ratio of 1. Maximum thrust was 14,000 kg (30,864 lb). The rear nozzle could rotate from 0 degrees to 95 degrees for VTOL landing and hovering. The two lift engines were the RD-41 design, a simple single-shaft engine made mostly of titanium. Each had a thrust of 4,100 kg (9,040 lb). The engines were installed behind the cockpit at an angle of 85 degrees. Like the Yak-38, the engines received their air through eight spring-operated dorsal flaps, and the exhaust exited through a belly opening covered by two ventral doors.
The first conventional flight, using 48-2, took place at Zhukovskii on 9 March 1987, with chief test pilot Sinitsyn at the controls. He made the first hovering flight on 29 December 1989 flying 48-3, and used the same aircraft to make the first complete transition from vertical to high-speed flight and vertical landing on 13 June 1990. From April 1991, various kinds of rolling take-off and run-on landings were performed on normal runways and also "ski-jump" ramps at the lift jet center at Saky
. Throughout testing the aircraft was found to demonstrate excellent combat maneuvers. Chief test pilot Sinitsyn went on to set twelve new world class records, but as the Yak-41 designation was classified, the records were submitted under the fictitious name "Yak-141". As a result, the previously unknown aircraft came to be known in the west as the "Yak-141". In 1992, Yakovlev repainted both flying aircraft in olive/grey camouflage, with the Russian tricolor insignia, and painted a white "141" on both aircraft in place of their previous call signs, "75" and 77".
On 26 September 1991, Sinitsyn made the first vertical landing on the Soviet aircraft carrier Admiral Gorshkov
(ex-Baku) in 48-2. An hour later, Vladimir A. Yakimov landed 48-3 on the same deck. The pilots would go on to make eight flights from the ship until Yakimov made a hard landing on 5 October. The undercarriage ruptured a fuel tank, causing a serious fire. After almost 30 seconds, Yakimov ejected successfully, and was rescued from the sea. The aircraft was later repaired and placed on display (see "Survivors"). That same month the Soviet Navy
announced that no further funds were available to continue the program. The factory at Smolensk
had anticipated this and had not constructed the tooling for production.
trainer, which was eventually developed in partnership with Aermacchi
of Italy
). Lockheed Martin
, which was in the process of developing the X-35
for the US Joint Strike Fighter program
, quickly stepped forward, and with their assistance 48-2 was displayed at the Farnborough Airshow in September 1992. Yakovlev announced that they had reached an agreement with Lockheed-Martin for funds of $385 to $400 million for three new prototypes and an additional static test aircraft to test improvements in design and avionics. Planned modifications for the proposed Yak-41M included an increase in STOL weight to 21,500 kg (47,400 lb). One of the prototypes would have been a dual-control trainer. Though no longer flyable, both 48-2 and 48-3 were exhibited at the 1993 Moscow airshow. The partnership began in late 1991, though it was not publicly revealed by Yakovlev until 6 September 1992, and was not revealed by Lockheed-Martin until June 1994.
Yak-41M
Yak-43 (Izdeliye 201)
Yak-141
NATO reporting name
NATO reporting names are classified code names for military equipment of the Eastern Bloc...
Freestyle), also known as the Yak-41, is a supersonic
Supersonic
Supersonic speed is a rate of travel of an object that exceeds the speed of sound . For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C this speed is approximately 343 m/s, 1,125 ft/s, 768 mph or 1,235 km/h. Speeds greater than five times the speed of sound are often...
vertical takeoff/landing
VTOL
A vertical take-off and landing aircraft is one that can hover, take off and land vertically. This classification includes fixed-wing aircraft as well as helicopters and other aircraft with powered rotors, such as cyclogyros/cyclocopters and tiltrotors...
(VTOL) fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft
A fighter aircraft is a military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat with other aircraft, as opposed to a bomber, which is designed primarily to attack ground targets...
designed by Yakolev. It did not enter production.
Design and development
Yakovlev always believed the Yak-38Yakovlev Yak-38
The Yakovlev Yak-38 was Soviet Naval Aviation's first and only operational VTOL strike fighter aircraft, in addition to being its first operational carrier-based fixed-wing aircraft...
to be an interim aircraft, developed to gain experience designing and developing military VTOL aircraft. Even before the Yak-38's introduction, the Soviet Navy desired a more comprehensive aircraft, with greater capabilities than the Yak-38 offered. The result was a design contract offered to Yakovlev in 1975
1975 in aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1975:-January:* A specially modified McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle sets eight time to climb records, including one of 3 minutes 27 seconds from standstill on the runway to a height of 30,000 metres ....
without any competition. The requirement was for an aircraft with only one mission: air defense of the fleet. Unlike the Yak-38, this aircraft was to have sustained supersonic speed. Maneuverability, radar and weapons loads were expected to be similar to those of current front-line fighters. For the Soviet Navy this aircraft was to be their next generation VTOL fighter. For Yakovlev the aircraft was viewed as a way of returning to designing Soviet fighter aircraft.
Because of the importance and complexity of the project, Alexander Sergeyevich Yakovlev
Alexander Sergeyevich Yakovlev
Alexander Sergeyevich Yakovlev was a Soviet aeronautical engineer. He designed the Yakovlev military aircraft and founded the Yakovlev Design Bureau. -Biography:...
assigned a large portion of his OKB
OKB
OKB is a transliteration of the Russian acronym for "Опытное конструкторское бюро" - Opytnoe Konstructorskoe Byuro, meaning Experimental Design Bureau...
to the development of the new VTOL fighter, with no fewer than ten chief engineers working simultaneously on what was called "Product 48" (the military had designated it Yak-41). Over fifty designs were studied. One key problem was designing an aircraft with both vectoring thrust and an afterburner, which was essential for sustained supersonic speeds. A twin-engine design was considered, but abandoned as the loss of an engine on landing would result in an immediate roll to the side. Eventually it was decided that the best arrangement was a single vectoring nozzle located just behind the center of gravity, as well as dedicated vertical thrust jets positioned just behind the cockpit. A considerable amount of time was spent in the development of a flat, rectangular nozzle similar to that later employed on the American F-22 Raptor
F-22 Raptor
The Lockheed Martin/Boeing F-22 Raptor is a single-seat, twin-engine fifth-generation supermaneuverable fighter aircraft that uses stealth technology. It was designed primarily as an air superiority fighter, but has additional capabilities that include ground attack, electronic warfare, and signals...
. Such a nozzle proved well-suited for the changes in configuration needed for both thrust vectoring and supersonic flight, and allowed for a thin, shallow tail. Ultimately, a circular nozzle was used, located between twin booms supporting the twin-finned tail.
Parts that were to be subjected to excessive heat from the engines during landing were manufactured of titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color....
, and no less than 26% of the overall aircraft was to be manufactured of graphite
Graphite
The mineral graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1789 from the Ancient Greek γράφω , "to draw/write", for its use in pencils, where it is commonly called lead . Unlike diamond , graphite is an electrical conductor, a semimetal...
or composite material
Composite material
Composite materials, often shortened to composites or called composition materials, are engineered or naturally occurring materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties which remain separate and distinct at the macroscopic or...
. Because of heat build-up, hovering was restricted to no more than 2½ minutes.
All three engines were controlled through an interlinked digital system, which was capable of controlling both engine start-up as well as modulating the thrust of all three engines during landing and hovering flight. Twin tandem reaction control jets were positioned at the wingtips, while a swiveling yaw jet was positioned under the nose.
The cockpit was pressurized and air-conditioned. The small canopy was bulletproof in front. It hinged to the right, but because of a long dorsal spine it had no rear vision. The ejection seat was automatically armed as soon as the engine duct was rotated past 30 degrees with an airspeed of less than 300 km/h (186 mph). The instrumentation in the prototypes was simple and similar to that planned for the earlier Yak-36M. The production version was to have been fitted with an extensive avionics and weapons suite including doppler radar, laser-TV ranging and aiming, as well as a heads-up multifunction display (HUD) which worked in connection with a helmet-mounted missile aiming system as found on the Mikoyan MiG-29
Mikoyan MiG-29
The Mikoyan MiG-29 is a fourth-generation jet fighter aircraft designed in the Soviet Union for an air superiority role. Developed in the 1970s by the Mikoyan design bureau, it entered service with the Soviet Air Force in 1983, and remains in use by the Russian Air Force as well as in many other...
. This system allows the pilot to lock onto an enemy aircraft by turning his head as far as 80 degrees from front.
The undercarriage was tricycle, and equipped with the latest multi-disc, anti-skid brakes. The steerable nose wheel retracted to the rear, while the main gear retracted forward.
The top-mounted wing was similar to that of the Yakovlev Yak-36, though the outer panel swept back, and could be folded up for shipboard storage. The main engine was served by four side-mounted ducts as well as a row of large louvers along the upper surface to allow air to enter the engine during full power hovering. This engine was the R-79V-300, a two-shaft augmented turbofan with a bypass ratio of 1. Maximum thrust was 14,000 kg (30,864 lb). The rear nozzle could rotate from 0 degrees to 95 degrees for VTOL landing and hovering. The two lift engines were the RD-41 design, a simple single-shaft engine made mostly of titanium. Each had a thrust of 4,100 kg (9,040 lb). The engines were installed behind the cockpit at an angle of 85 degrees. Like the Yak-38, the engines received their air through eight spring-operated dorsal flaps, and the exhaust exited through a belly opening covered by two ventral doors.
Operational history
Yakovlev obtained funding for four prototypes. The first (48-0, with no callsign) was a bare airframe for static and fatigue testing. The second (48-1, call sign "48") was a non-flying powerplant testbed. The third and fourth (48-2 and 48-3, call signs "75" and "77") were for flight testing. While 48-1 remained unpainted, 48-2 and 48-3 were painted in overall grey, with a black radome and fin cap antennas.The first conventional flight, using 48-2, took place at Zhukovskii on 9 March 1987, with chief test pilot Sinitsyn at the controls. He made the first hovering flight on 29 December 1989 flying 48-3, and used the same aircraft to make the first complete transition from vertical to high-speed flight and vertical landing on 13 June 1990. From April 1991, various kinds of rolling take-off and run-on landings were performed on normal runways and also "ski-jump" ramps at the lift jet center at Saky
Saky
Saky is a city in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, Ukraine. Population is 29,416 . The city has one of the major bases of the Ukrainian Navy. Other bases are at Odessa, Novoozerne, and Sebastopol....
. Throughout testing the aircraft was found to demonstrate excellent combat maneuvers. Chief test pilot Sinitsyn went on to set twelve new world class records, but as the Yak-41 designation was classified, the records were submitted under the fictitious name "Yak-141". As a result, the previously unknown aircraft came to be known in the west as the "Yak-141". In 1992, Yakovlev repainted both flying aircraft in olive/grey camouflage, with the Russian tricolor insignia, and painted a white "141" on both aircraft in place of their previous call signs, "75" and 77".
On 26 September 1991, Sinitsyn made the first vertical landing on the Soviet aircraft carrier Admiral Gorshkov
Soviet aircraft carrier Admiral Gorshkov
Admiral Gorshkov was a modified Kiev class aircraft carrier of the Russian Navy, originally named Baku. Sometimes Gorshkov is considered a separate class due to its improvements including a phased array radar, extensive electronic warfare installations, and an enlarged command and control suite...
(ex-Baku) in 48-2. An hour later, Vladimir A. Yakimov landed 48-3 on the same deck. The pilots would go on to make eight flights from the ship until Yakimov made a hard landing on 5 October. The undercarriage ruptured a fuel tank, causing a serious fire. After almost 30 seconds, Yakimov ejected successfully, and was rescued from the sea. The aircraft was later repaired and placed on display (see "Survivors"). That same month the Soviet Navy
Soviet Navy
The Soviet Navy was the naval arm of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy would have played an instrumental role in a Warsaw Pact war with NATO, where it would have attempted to prevent naval convoys from bringing reinforcements across the Atlantic Ocean...
announced that no further funds were available to continue the program. The factory at Smolensk
Smolensk
Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River. Situated west-southwest of Moscow, this walled city was destroyed several times throughout its long history since it was on the invasion routes of both Napoleon and Hitler. Today, Smolensk...
had anticipated this and had not constructed the tooling for production.
Yak-41 or Yak-141
The design was initially designated the Yak-41M by the Soviet military. Once testing commenced, and the two prototypes began accumulating numerous world class records, it became necessary to invent a designation for use in the west, as the name Yak-41M was classified. The designation Yak-141 was selected, and it was by this name that the aircraft became known to western allies, though officially the aircraft's designation remained Yak-41M within the Soviet military. In 1991 Lockheed-Martin entered into partnership with Yakovlev to further develop an aircraft they had always known as the Yak-141. Largely as a result of this agreement, by 1992 Yakovlev changed the aircraft's designation to Yak-141 for the two flyable prototypes. Series production in Russia could have resulted in additional modification to the designation.Lockheed Martin
Following the announcement by the CIS that it could no longer fund development of the Yak-41M, Yakovlev immediately entered into discussions with several foreign partners who could help fund the program (a tactic they were also pursuing for development of the Yak-130Yakovlev Yak-130
The Yakovlev Yak-130 is a subsonic two-seat advanced jet trainer/light attack aircraft or lead-in fighter trainer developed by the Yakovlev design bureau. Development of the plane began in 1991, and the maiden flight was conducted on 26 April 1996...
trainer, which was eventually developed in partnership with Aermacchi
Aermacchi
Alenia Aermacchi is an Italian company designing and producing trainer aircraft for military pilots.-Profile:Alenia Aermacchi has sold about 2,000 trainers to more than 40 countries and has collaborated in major international military programs....
of Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
). Lockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin is an American global aerospace, defense, security, and advanced technology company with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is headquartered in Bethesda, Maryland, in the Washington Metropolitan Area....
, which was in the process of developing the X-35
Lockheed Martin X-35
The Lockheed Martin X-35 was an experimental aircraft developed by Lockheed Martin for the Joint Strike Fighter Program. It was declared the winner over the Boeing X-32 and went on to enter production in the early 21st century as the F-35 Lightning II....
for the US Joint Strike Fighter program
Joint Strike Fighter Program
Joint Strike Fighter is a development and acquisition program intended to replace a wide range of existing fighter, strike, and ground attack aircraft for the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, and their allies. After a competition between the Boeing X-32 and the Lockheed Martin X-35, a...
, quickly stepped forward, and with their assistance 48-2 was displayed at the Farnborough Airshow in September 1992. Yakovlev announced that they had reached an agreement with Lockheed-Martin for funds of $385 to $400 million for three new prototypes and an additional static test aircraft to test improvements in design and avionics. Planned modifications for the proposed Yak-41M included an increase in STOL weight to 21,500 kg (47,400 lb). One of the prototypes would have been a dual-control trainer. Though no longer flyable, both 48-2 and 48-3 were exhibited at the 1993 Moscow airshow. The partnership began in late 1991, though it was not publicly revealed by Yakovlev until 6 September 1992, and was not revealed by Lockheed-Martin until June 1994.
Variants
Yak-41- The two flying prototypes and ground test article.
Yak-41M
- Proposed production aircraft with large LERXs (leading-edge root extensions) and other improvements, particularly in the avionic suite.
Yak-43 (Izdeliye 201)
- A proposed development of the Yak-41M 'Freehand' equipped with KuznetsovKuznetsov (aircraft engines)The Kuznetsov Design Bureau was a Soviet design bureau for aircraft engines, administrated by Nikolai Dmitriyevich Kuznetsov. It was created for developing German WW2 jet engine technology headed by a group of deported Junkers engineers under Ferdinand Brandner.The Kuznetzov Bureau first became...
NK-321 engines.
Yak-141
- Designation originally applied to a single Yak-41 for disinformation and propaganda purposes when registering records with the FAI (Fédération Aéronautique InternationaleFédération Aéronautique InternationaleThe Fédération Aéronautique Internationale is the world governing body for air sports and aeronautics and astronautics world records. Its head office is in Lausanne, Switzerland. This includes man-carrying aerospace vehicles from balloons to spacecraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles...
) and later for promotional purposes by Yakovlev.
Survivors
- Yak-41M (s/n 48-2, callsign "75") is on display at the Central Air Force MuseumCentral Air Force MuseumThe Central Air Force Museum in Monino at the site of Monino Airfield 40km east of Moscow, Russia, is one of the world's largest aviation museums, and the largest for Russian aircraft...
at MoninoMoninoMonino is an urban locality in Shchyolkovsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated east of Moscow. Population:...
. The aircraft is displayed in its 1992 livery with olive/grey camouflage markings and "141" painted in white in place of the former callsign. - Yak-41M (s/n 48-3, callsign "77") is on display at the Yakovlev OKB Museum. The aircraft is displayed in its 1992 livery with olive/grey camouflage markings and "141" painted in white in place of the former callsign.
Specifications (Yak-41)


