
Volume contraction
Encyclopedia
Volume contraction is a decrease in body fluid volume, also including any concomitant loss of osmolyte
s. The loss of the water component of body fluid is specifically termed dehydration
.
(ECF) and/or intracellular fluid (ICF).
, which is termed hypovolemia
. Thus, it primarily affects the circulatory system
, potentially causing hypovolemic shock.
ECF volume contraction or hypovolemia is usually the type of volume contraction of primary concern in emergency, since ECF is approximately half the volume of ICF and is the first to be affected in e.g. bleeding
. Volume contraction is sometimes even used synonymously with hypovolemia.
(K+) see section below.
ICF volume contraction may cause disturbances in various organs throughout the body.
.
of sodium
(Na+) and potassium
(K+) in the lost fluid, as well as estimating the body composition of the person.
1. To calculate an estimation, the total amount of substance in the body before the loss is first estimated:
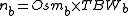
where:
2. The total amount of substance in the body after the loss is then estimated:
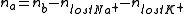
where:
3. The new osmolarity becomes:
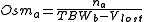
where:
4. This osmolarity is evenly distributed in the body, and is used to estimate the new volumes of ICF and ECF, respectively:
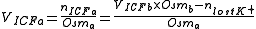
where:
In homologous manner:
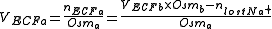
where:
5. The volume of lost fluid from each compartment:
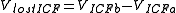
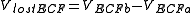
where:
Osmolyte
Osmolytes are compounds affecting osmosis. They are soluble in the solution within a cell, or in the surrounding fluid, e.g. as plasma osmolytes. They play a role in maintaining cell volume and fluid balance. For example, when a cell swells due to external osmotic pressure, membrane channels open...
s. The loss of the water component of body fluid is specifically termed dehydration
Dehydration
In physiology and medicine, dehydration is defined as the excessive loss of body fluid. It is literally the removal of water from an object; however, in physiological terms, it entails a deficiency of fluid within an organism...
.
By body fluid compartment
Volume contraction is more or less a loss of extracellular fluidExtracellular fluid
Extracellular fluid usually denotes all body fluid outside of cells. The remainder is called intracellular fluid.In some animals, including mammals, the extracellular fluid can be divided into two major subcompartments, interstitial fluid and blood plasma...
(ECF) and/or intracellular fluid (ICF).
ECF volume contraction
Volume contraction of extracellular fluid is directly coupled to and almost proportional to volume contraction of blood plasmaBlood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
, which is termed hypovolemia
Hypovolemia
In physiology and medicine, hypovolemia is a state of decreased blood volume; more specifically, decrease in volume of blood plasma...
. Thus, it primarily affects the circulatory system
Circulatory system
The circulatory system is an organ system that passes nutrients , gases, hormones, blood cells, etc...
, potentially causing hypovolemic shock.
ECF volume contraction or hypovolemia is usually the type of volume contraction of primary concern in emergency, since ECF is approximately half the volume of ICF and is the first to be affected in e.g. bleeding
Bleeding
Bleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
. Volume contraction is sometimes even used synonymously with hypovolemia.
ICF volume contraction
Volume contraction of intracellular fluid may occur after substantial fluid loss, since it is much larger than ECF volume, or loss of potassiumPotassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
(K+) see section below.
ICF volume contraction may cause disturbances in various organs throughout the body.
Dependence on lost solutes
Na+ loss approximately correlates with fluid loss from ECF, since Na+ has a much higher concentration in ECF than ICF. In contrast, K+ has a much higher concentration in ICF than ECF, and therefore its loss rather correlates with fluid loss from ICF, since K+ loss from ECF causes the K+ in ICF to diffuse out of the cells, dragging water with it by osmosisOsmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
.
Estimation
When the body loses fluids, the amount lost from ICF and ECF, respectively, can be estimated by measuring volume and amount of substanceAmount of substance
Amount of substance is a standards-defined quantity that measures the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. It is sometimes referred to as chemical amount. The International System of Units defines the amount of substance to be...
of sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
(Na+) and potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
(K+) in the lost fluid, as well as estimating the body composition of the person.
1. To calculate an estimation, the total amount of substance in the body before the loss is first estimated:
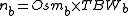
where:
- nb = Total amount of substance before fluid loss
- Osmb = Body osmolarity before loss (almost equal to plasma osmolalityPlasma osmolality-Measured osmolality :Osmolality can be measured on an analytical instrument called an osmometer. It works on the method of depression of freezing point.Plasma osmolality is affected by changes in water content...
of 275-299 milli-osmoles per kilogram) - TBWb = Total body water before loss (approximately 60% of body weight, or using tritiated water or deuterium)
2. The total amount of substance in the body after the loss is then estimated:
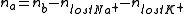
where:
- na = Total amount of substance after fluid loss
- nb = Total amount of substance before fluid loss
- nlost Na+ = Amount of substance of lost sodium
- nlost K+ = Amount of substance of lost potassium
3. The new osmolarity becomes:
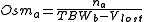
where:
- Osma = Body osmolarity after loss
- na = Total amount of substance after fluid loss
- TBWb = Total body water before loss
- Vlost = Volume of lost fluid
4. This osmolarity is evenly distributed in the body, and is used to estimate the new volumes of ICF and ECF, respectively:
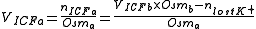
where:
- VICF a = Intracellular fluid volume after fluid loss
- nICF a = Amount of substance in ICF after fluid loss
- Osma = Body osmolarity after loss
- VICF b = Intracellular fluid volume before fluid loss (approximately 40% of body weight, or subtracting ECF from TBW)
- Osmb = Body osmolarity before loss (almost equal to plasma osmolalityPlasma osmolality-Measured osmolality :Osmolality can be measured on an analytical instrument called an osmometer. It works on the method of depression of freezing point.Plasma osmolality is affected by changes in water content...
of 275-299 milli-osmoles per kilogram) - nlost K+ = Amount of substance of lost potassium
In homologous manner:
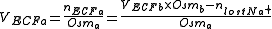
where:
- VECF a = Extracellular fluid volume after fluid loss
- nECF a = Amount of substance in ECF after fluid loss
- VECF b = Extracellular fluid volume before fluid loss (approximately 20% of body weight, or by using inulin)
- Osmb = Body osmolarity before loss (almost equal to plasma osmolalityPlasma osmolality-Measured osmolality :Osmolality can be measured on an analytical instrument called an osmometer. It works on the method of depression of freezing point.Plasma osmolality is affected by changes in water content...
of 275-299 milli-osmoles per kilogram) - nlost K+ = Amount of substance of lost potassium
5. The volume of lost fluid from each compartment:
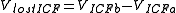
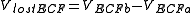
where:
- VI/ECF b = Intra/Extra-cellular fluid volume before fluid loss
- VI/ECF a = Intra/Extra-cellular fluid volume after fluid loss

