Viable System Model
Encyclopedia
The viable systems model, or VSM is a model of the organisational structure of any viable or autonomous system
. A viable system is any system organised in such a way as to meet the demands of surviving in the changing environment. One of the prime features of systems that survive is that they are adaptable. The VSM expresses a model for a viable system, which is an abstracted cybernetic (regulation theory) description that is applicable to any organisation that is a viable system and capable of autonomy.
theorist and cybernetician
Stafford Beer
in his book Brain of the Firm (1972). Together with Beer's earlier works on cybernetics applied to management, this book effectively founded management cybernetics
.
The first thing to note about the cybernetic theory of organizations encapsulated in the VSM is that viable systems are recursive
; viable systems contain viable systems that can be modeled using an identical cybernetic description as the higher (and lower) level systems in the containment hierarchy (Beer expresses this property of viable systems as cybernetic isomorphism).
A development of this model has originated the theoretical proposal called Viable systems approach
.
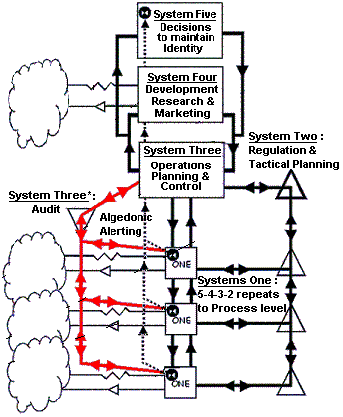 A viable system is composed of five interacting subsystems which may be mapped onto aspects of organizational structure. In broad terms Systems 1–3. are concerned with the 'here and now' of the organization's operations, System 4 is concerned with the 'there and then' – strategical responses to the effects of external, environmental and future demands on the organization. System 5 is concerned with balancing the 'here and now' and the 'there and then' to give policy directives which maintain the organization as a viable entity.
A viable system is composed of five interacting subsystems which may be mapped onto aspects of organizational structure. In broad terms Systems 1–3. are concerned with the 'here and now' of the organization's operations, System 4 is concerned with the 'there and then' – strategical responses to the effects of external, environmental and future demands on the organization. System 5 is concerned with balancing the 'here and now' and the 'there and then' to give policy directives which maintain the organization as a viable entity.
In addition to the subsystems that make up the first level of recursion, the environment is represented in the model. The presence of the environment in the model is necessary as the domain of action of the system and without it there is no way in the model to contextualize or ground the internal interactions of the organization.
The model is derived from the architecture of the brain and nervous system. Systems 3-2-1 are identified with the ancient brain or autonomic nervous system
. System 4 embodies cognition and conversation. System 5, the higher brain functions, include introspection and decision making.
concept of (Requisite) Variety
: the number of possible states of a system or of an element of the system. There are two aphorisms that permit observers to calculate Variety; four Principles of Organization; the Recursive System Theorem; three Axioms of Management and a Law of Cohesion. These rules ensure the Requisite Variety condition is satisfied, in effect that resources are matched to requirement.
These principles are:
These axioms are:
actuality: "What we are managing to do now, with existing resources, under existing constraints."
capability: "This is what we could be doing (still right now) with existing resources, under existing constraints, if we really worked at it."
potentiality: "This is what we ought to be doing by developing our resources and removing constraints, although still operating within the bounds of what is already known to be feasible."
Beer adds "It would help a lot to fix these definitions clearly in the mind." System 4's job is essentially to realize potential.
He then defines productivity: is the ratio of actuality and capability;
latency: is the ratio of capability and potentiality;
performance: is the ratio of actuality and potentiality, and also the product of latency and productivity.
Consider the management of a process with cash earnings or savings for a company or government: potentially £100,000 but aiming to make £ 60,000. Actually sales, savings or taxes of £40,000 are realized.
So potentiality = £100,000; capability = £60,000; actuality = £40,000.
Thus latency = 60/100 = 0.6;
productivity = 40/60 = 0.67;
performance = 0.6 × 0.67 = 0.4 (or actuality/potential 40/100).
These methods (also known as normalisations) can be similarly applied in general e.g. to hours worked in the performance of tasks or products in a production process of some kind.
When actuality deviates from capability, because someone did something well or something badly, an algedonic alert is sent to management. If corrective action, adoption of a good technique or correction of an error, is not taken in a timely manner the alert is escalated. Because the criteria are applied in an ordered
hierarchy the management itself need not be, but the routine response functions must be ordered to reflect best known heuristic
practice. These heuristics are constantly monitored for improvement by the organization's System 4s.
Pay structures reflect these constraints on performance when capability or potential is realized with, for example, productivity bonuses
, stakeholder agreements and intellectual property
rights.
.
This defines a metalanguage
stack of increasing capability to resolve undecidability
in the autonomous lower levels. If someone near process level needs to innovate to achieve potential, or restore capability, help can be secured from management of higher variety.
An algedonic alert, sent when actuality deviates by some statistically significant
amount from capability, makes this process automatic.
The notion of adding more variety or states to resolve ambiguity
or undecidability (also known as the decision problem
) is the subject of Chaitin's metamathematical
conjecture algorithmic information theory
and provides a potentially rigorous theoretical basis for a general management heuristic. If a process is not producing the agreed product more information, if applicable, will correct this, resolve ambiguity, conflict
or undecidability.
In "Platform for Change" (Beer 1975) the thesis is developed via a collection of papers to learned bodies, including UK Police and Hospitals, to produce a visualization of the "Total System". Here a "Relevant ethic" evolves from "Experimental ethics" and the "Ethic with a busted gut" to produce a sustainable earth with reformed "old institutions" becoming "new institutions" driven by approval (eudemonic criteria "Questions of Metric" in Platform... pp 163– 179) from the "software milieu" while culture adopts the systems approach and "Homo Faber
" (man the maker) becomes "Homo Gubernator" (self-steering).
measures are used to match people, machines and money to jobs that produce products or services. In a set of processes some jobs are done by one person. Some are done by many and often many processes are done by the same person. Throughout the working day a participant, in completing a task, may find the focus shifts between internal and external Systems 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 from moment to moment.
The choices, or decisions discriminated, and their cost (or effort) defines the variety and hence resources needed for the job. The processes (Systems 1) are operationally managed by System 3 by monitoring performance and assuring (System 2) the flow of product between System 1s and out to users.
System 3 is able to audit (via 3*) past performance so "bad times" for production can be compared to "good times". If things go wrong and levels of risk
increase the System 3 asks for help or puts it to colleagues for a remedy. This is the pain of an algedonic alert, which can be automatic when performance fails to achieve capability targets. The autonomic 3-2-1 homeostatic loop's problem is absorbed for solution within the autonomy of its metasystem. Development (the System 4 role of research and marketing) is asked for recommendations.
If more resources are required System 5 has to make the decision on which is the best option from System 4. Escalation to higher management (up the metalinguistic levels of recursion) will be needed if the remedy requires more resources than the current level of capability or variety can sustain. The pleasure of an algedonic alert which are performance improving innovation
s can also be handled in this way.
In a small business all these functions might be done by one person or shared between the participants. In larger enterprises roles can differentiate and become more specialized emphasizing one or more aspects of the VSM. Local conditions, the environment and nature of the service or product, determines where warehousing, sales, advertising, promotion, dispatch, taxation, finance, salaries etc., fit into this picture. Not all enterprises charge for their transactions (e.g. some schools and medical services, policing) and voluntary staff may not be paid. Advertising or shipping might not be part of the business or they might be the principal activity. Whatever the circumstances, all enterprises are required to be useful to their users if they are to remain viable. For all participants the central question remains: "Do I do what I always do for this transaction or do I innovate?" It is embodied in the calls on System 4. The VSM describes the constraints: a knowledge of past performance and how it may be improved.
Beer dedicated "Brain of the Firm" to his colleagues past and present with the words "Absolutum Obsoletum" which he translated "If it works it’s out of date".
Organizations:
System
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
. A viable system is any system organised in such a way as to meet the demands of surviving in the changing environment. One of the prime features of systems that survive is that they are adaptable. The VSM expresses a model for a viable system, which is an abstracted cybernetic (regulation theory) description that is applicable to any organisation that is a viable system and capable of autonomy.
Overview
The model was developed by operations researchOperations research
Operations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
theorist and cybernetician
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the interdisciplinary study of the structure of regulatory systems. Cybernetics is closely related to information theory, control theory and systems theory, at least in its first-order form...
Stafford Beer
Anthony Stafford Beer
Anthony Stafford Beer was a British theorist, consultant and professor at the Manchester Business School. He is best known for his work in the fields of operational research and management cybernetics.- Biography :...
in his book Brain of the Firm (1972). Together with Beer's earlier works on cybernetics applied to management, this book effectively founded management cybernetics
Management cybernetics
Management cybernetics is the field of cybernetics concerned with management and organizations. The notion of cybernetics and management was first introduced by Stafford Beer in the late 1950s-Cybernetics and Complexity:...
.
The first thing to note about the cybernetic theory of organizations encapsulated in the VSM is that viable systems are recursive
Recursion
Recursion is the process of repeating items in a self-similar way. For instance, when the surfaces of two mirrors are exactly parallel with each other the nested images that occur are a form of infinite recursion. The term has a variety of meanings specific to a variety of disciplines ranging from...
; viable systems contain viable systems that can be modeled using an identical cybernetic description as the higher (and lower) level systems in the containment hierarchy (Beer expresses this property of viable systems as cybernetic isomorphism).
A development of this model has originated the theoretical proposal called Viable systems approach
Viable systems approach
The Viable Systems Approach is a system theory in which the observed entities and their environment are interpreted through a systemic viewpoint, starting with the analysis of fundamental elements and finally considering more complex related systems...
.
Components of the viable system model
Here we give a brief introduction to the cybernetic description of the organization encapsulated in a single level of the VSM.
- System 1 in a viable system contains several primary activities. Each System 1 primary activity is itself a viable system due to the recursive nature of systems as described above. These are concerned with performing a function that implements at least part of the key transformation of the organization.
- System 2 represents the information channels and bodies that allow the primary activities in System 1 to communicate between each other and which allow System 3 to monitor and co-ordinate the activities within System 1.
- System 3 represents the structures and controls that are put into place to establish the rules, resources, rights and responsibilities of System 1 and to provide an interface with Systems 4/5.
- System 4 – The bodies that make up System 4 are responsible for looking outwards to the environment to monitor how the organization needs to adapt to remain viable.
- System 5 is responsible for policy decisions within the organization as a whole to balance demands from different parts of the organization and steer the organization as a whole.
In addition to the subsystems that make up the first level of recursion, the environment is represented in the model. The presence of the environment in the model is necessary as the domain of action of the system and without it there is no way in the model to contextualize or ground the internal interactions of the organization.
- Algedonic alerts (from the Greek αλγος, pain and ηδος, pleasure) are alarms and rewards that escalate through the levels of recursion when actual performance fails or exceeds capability, typically after a timeoutTimeout (telecommunication)In telecommunication and related engineering , the term timeout or time-out has several meanings, including...
.
The model is derived from the architecture of the brain and nervous system. Systems 3-2-1 are identified with the ancient brain or autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
. System 4 embodies cognition and conversation. System 5, the higher brain functions, include introspection and decision making.
Rules for the viable system
In "Heart of Enterprise" a companion volume to "Brain...", Beer applies Ashby'sWilliam Ross Ashby
W. Ross Ashby was an English psychiatrist and a pioneer in cybernetics, the study of complex systems. His first name was not used: he was known as Ross Ashby....
concept of (Requisite) Variety
Variety (cybernetics)
In cybernetics the term variety denotes the total number of distinct states of a system.- Overview :The term Variety was introduced by W. Ross Ashby to denote the count of the total number of states of a system. The condition for dynamic stability under perturbation was described by his Law of...
: the number of possible states of a system or of an element of the system. There are two aphorisms that permit observers to calculate Variety; four Principles of Organization; the Recursive System Theorem; three Axioms of Management and a Law of Cohesion. These rules ensure the Requisite Variety condition is satisfied, in effect that resources are matched to requirement.
Regulatory aphorisms
These aphorisms are:- It is not necessary to enter the black box to understand the nature of the function it performs.
- It is not necessary to enter the black box to calculate the variety that it potentially may generate.
Principles of organization
(Principles are 'primary sources of particular outcome')These principles are:
- Managerial, operational and environmental varieties diffusing through an institutional system, tend to equate; they should be designed to do so with minimum damage to people and cost.
- The four directional channels carrying information between the management unit, the operation, and the environment must each have a higher capacity to transmit a given amount of information relevant to variety selection in a given time than the originating subsystem has to generate it in that time.
- Wherever the information carried on a channel capable of distinguishing a given variety crosses a boundary, it undergoes transductionTransducerA transducer is a device that converts one type of energy to another. Energy types include electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic , chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a...
(converting energy from one form to another); the variety of the transducer must be at least equivalent to the variety of the channel. - The operation of the first three principles must be cyclically maintained through time without hiatus or lags.
Recursive system theorem
This theorem states:- In a recursiveRecursionRecursion is the process of repeating items in a self-similar way. For instance, when the surfaces of two mirrors are exactly parallel with each other the nested images that occur are a form of infinite recursion. The term has a variety of meanings specific to a variety of disciplines ranging from...
organizational structure any viable system contains, and is contained in, a viable system.
Axioms
(Axioms are statements 'worthy of belief')These axioms are:
- The sum of horizontal variety disposed by n operational elements (systems one) equals the sum of the vertical variety disposed by the six vertical components of corporate cohesion (5, 4, 3, 3*, 2, 1).
- The variety disposed by System Three resulting from the operation of the First Axiom equals the variety disposed by System Four.
- The variety disposed by System Five equals the residual variety generated by the operation of the Second Axiom.
The law of cohesion for multiple recursions of the viable system
This law ('something invariant in nature') states:- The System One variety accessible to System Three of recursion x equals the variety disposed by the sum of the metasystems of recursion y for every recursive pair.
Measuring performance
In "Brain..." (p. 163) Beer describes a triple vector to characterize activity in a System 1. The components are:actuality: "What we are managing to do now, with existing resources, under existing constraints."
capability: "This is what we could be doing (still right now) with existing resources, under existing constraints, if we really worked at it."
potentiality: "This is what we ought to be doing by developing our resources and removing constraints, although still operating within the bounds of what is already known to be feasible."
Beer adds "It would help a lot to fix these definitions clearly in the mind." System 4's job is essentially to realize potential.
He then defines productivity: is the ratio of actuality and capability;
latency: is the ratio of capability and potentiality;
performance: is the ratio of actuality and potentiality, and also the product of latency and productivity.
Consider the management of a process with cash earnings or savings for a company or government: potentially £100,000 but aiming to make £ 60,000. Actually sales, savings or taxes of £40,000 are realized.
So potentiality = £100,000; capability = £60,000; actuality = £40,000.
Thus latency = 60/100 = 0.6;
productivity = 40/60 = 0.67;
performance = 0.6 × 0.67 = 0.4 (or actuality/potential 40/100).
These methods (also known as normalisations) can be similarly applied in general e.g. to hours worked in the performance of tasks or products in a production process of some kind.
When actuality deviates from capability, because someone did something well or something badly, an algedonic alert is sent to management. If corrective action, adoption of a good technique or correction of an error, is not taken in a timely manner the alert is escalated. Because the criteria are applied in an ordered
Order theory
Order theory is a branch of mathematics which investigates our intuitive notion of order using binary relations. It provides a formal framework for describing statements such as "this is less than that" or "this precedes that". This article introduces the field and gives some basic definitions...
hierarchy the management itself need not be, but the routine response functions must be ordered to reflect best known heuristic
Heuristic
Heuristic refers to experience-based techniques for problem solving, learning, and discovery. Heuristic methods are used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution, where an exhaustive search is impractical...
practice. These heuristics are constantly monitored for improvement by the organization's System 4s.
Pay structures reflect these constraints on performance when capability or potential is realized with, for example, productivity bonuses
Performance-related pay
Performance-related pay is money paid to someone relating to how well one works. Car salesmen, production line workers, for example, may be paid in this way, or through commission....
, stakeholder agreements and intellectual property
Intellectual property
Intellectual property is a term referring to a number of distinct types of creations of the mind for which a set of exclusive rights are recognized—and the corresponding fields of law...
rights.
Metalanguage
In ascending the recursions of the viable system the context of each autonomous 5-4-3-2 metasystem enlarges and acquires more varietyVariety (cybernetics)
In cybernetics the term variety denotes the total number of distinct states of a system.- Overview :The term Variety was introduced by W. Ross Ashby to denote the count of the total number of states of a system. The condition for dynamic stability under perturbation was described by his Law of...
.
This defines a metalanguage
Metalanguage
Broadly, any metalanguage is language or symbols used when language itself is being discussed or examined. In logic and linguistics, a metalanguage is a language used to make statements about statements in another language...
stack of increasing capability to resolve undecidability
Undecidable problem
In computability theory and computational complexity theory, an undecidable problem is a decision problem for which it is impossible to construct a single algorithm that always leads to a correct yes-or-no answer....
in the autonomous lower levels. If someone near process level needs to innovate to achieve potential, or restore capability, help can be secured from management of higher variety.
An algedonic alert, sent when actuality deviates by some statistically significant
Statistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
amount from capability, makes this process automatic.
The notion of adding more variety or states to resolve ambiguity
Ambiguity
Ambiguity of words or phrases is the ability to express more than one interpretation. It is distinct from vagueness, which is a statement about the lack of precision contained or available in the information.Context may play a role in resolving ambiguity...
or undecidability (also known as the decision problem
Decision problem
In computability theory and computational complexity theory, a decision problem is a question in some formal system with a yes-or-no answer, depending on the values of some input parameters. For example, the problem "given two numbers x and y, does x evenly divide y?" is a decision problem...
) is the subject of Chaitin's metamathematical
Metamathematics
Metamathematics is the study of mathematics itself using mathematical methods. This study produces metatheories, which are mathematical theories about other mathematical theories...
conjecture algorithmic information theory
Algorithmic information theory
Algorithmic information theory is a subfield of information theory and computer science that concerns itself with the relationship between computation and information...
and provides a potentially rigorous theoretical basis for a general management heuristic. If a process is not producing the agreed product more information, if applicable, will correct this, resolve ambiguity, conflict
Conflict resolution
Conflict resolution is conceptualized as the methods and processes involved in facilitating the peaceful ending of some social conflict. Often, committed group members attempt to resolve group conflicts by actively communicating information about their conflicting motives or ideologies to the rest...
or undecidability.
In "Platform for Change" (Beer 1975) the thesis is developed via a collection of papers to learned bodies, including UK Police and Hospitals, to produce a visualization of the "Total System". Here a "Relevant ethic" evolves from "Experimental ethics" and the "Ethic with a busted gut" to produce a sustainable earth with reformed "old institutions" becoming "new institutions" driven by approval (eudemonic criteria "Questions of Metric" in Platform... pp 163– 179) from the "software milieu" while culture adopts the systems approach and "Homo Faber
Homo faber
Homo faber is a philosophical concept articulated by Hannah Arendt and Max Scheler that refers to humans as controlling the environment through tools...
" (man the maker) becomes "Homo Gubernator" (self-steering).
Applying VSM
In applying the VSM varietyVariety (cybernetics)
In cybernetics the term variety denotes the total number of distinct states of a system.- Overview :The term Variety was introduced by W. Ross Ashby to denote the count of the total number of states of a system. The condition for dynamic stability under perturbation was described by his Law of...
measures are used to match people, machines and money to jobs that produce products or services. In a set of processes some jobs are done by one person. Some are done by many and often many processes are done by the same person. Throughout the working day a participant, in completing a task, may find the focus shifts between internal and external Systems 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 from moment to moment.
The choices, or decisions discriminated, and their cost (or effort) defines the variety and hence resources needed for the job. The processes (Systems 1) are operationally managed by System 3 by monitoring performance and assuring (System 2) the flow of product between System 1s and out to users.
System 3 is able to audit (via 3*) past performance so "bad times" for production can be compared to "good times". If things go wrong and levels of risk
Risk
Risk is the potential that a chosen action or activity will lead to a loss . The notion implies that a choice having an influence on the outcome exists . Potential losses themselves may also be called "risks"...
increase the System 3 asks for help or puts it to colleagues for a remedy. This is the pain of an algedonic alert, which can be automatic when performance fails to achieve capability targets. The autonomic 3-2-1 homeostatic loop's problem is absorbed for solution within the autonomy of its metasystem. Development (the System 4 role of research and marketing) is asked for recommendations.
If more resources are required System 5 has to make the decision on which is the best option from System 4. Escalation to higher management (up the metalinguistic levels of recursion) will be needed if the remedy requires more resources than the current level of capability or variety can sustain. The pleasure of an algedonic alert which are performance improving innovation
Innovation
Innovation is the creation of better or more effective products, processes, technologies, or ideas that are accepted by markets, governments, and society...
s can also be handled in this way.
In a small business all these functions might be done by one person or shared between the participants. In larger enterprises roles can differentiate and become more specialized emphasizing one or more aspects of the VSM. Local conditions, the environment and nature of the service or product, determines where warehousing, sales, advertising, promotion, dispatch, taxation, finance, salaries etc., fit into this picture. Not all enterprises charge for their transactions (e.g. some schools and medical services, policing) and voluntary staff may not be paid. Advertising or shipping might not be part of the business or they might be the principal activity. Whatever the circumstances, all enterprises are required to be useful to their users if they are to remain viable. For all participants the central question remains: "Do I do what I always do for this transaction or do I innovate?" It is embodied in the calls on System 4. The VSM describes the constraints: a knowledge of past performance and how it may be improved.
Beer dedicated "Brain of the Firm" to his colleagues past and present with the words "Absolutum Obsoletum" which he translated "If it works it’s out of date".
See also
- American Society for CyberneticsAmerican Society for CyberneticsThe American Society for Cybernetics is an American non-profit scholastic organization for organization for the advancement of cybernetics as a science and the interdisciplinary collaboration and synthesis of cybernetics. The society contributes to the cooperation around the research and...
- Cybernetics SocietyCybernetics SocietyThe Cybernetics Society is the UK based learned society that exists to promote the understanding of cybernetics. The core activity of the Cybernetics Society is the organization and facilitation of scientific meetings, conferences, and social events...
- World Organisation of Systems and CyberneticsTransducerA transducer is a device that converts one type of energy to another. Energy types include electrical, mechanical, electromagnetic , chemical, acoustic or thermal energy. While the term transducer commonly implies the use of a sensor/detector, any device which converts energy can be considered a...
Further reading
- 1972, Stafford Beer, Brain of the Firm; Allen Lane, The Penguin Press, London, Herder and Herder, USA. Translated into German, Italian, Swedish and French (The founding work)
- 1975, Stafford Beer, Platform for Change; John Wiley, London and New York. (Lectures, talks and papers)
- 1979, Stafford Beer, The Heart of Enterprise; John Wiley, London and New York. (Discussion of VSM applied)
- 1985, Stafford Beer, Diagnosing the System for Organizations; John Wiley, London and New York. Translated into Italian and Japanese. (Handbook of organizational structure, design and fault diagnosis)
- 1989, Ed. Espejo and Harnden The Viable System Model; John Wiley, London and New York.
- 2007, William F. Christopher Holistic Management; John Wiley, London and New York.
- 2008, Türke, Ralf-Eckhard: Governance – Systemic Foundation and Framework (Contributions to Management Science, Physica of Springer, September 2008).Link
- 2008, Patrick Hoverstadt: The Fractal Organization: Creating sustainable organizations with the Viable System Model Wiley
- 2008, José Pérez Ríos, Diseño y diagnóstico de organizaciones viables: un enfoque sistémico, Universidad de Valladolid ReadOnTime
- 2010, Golinelli Gaetano M, "Viable Systems Approach (VSA): Governing business dynamics", CEDAM, Padova.
- 2010, George Hobbs and Rens Scheepers, "Cybernetics and the Agility Question," Proceedings of IFIP 8.2/Organizations and Society in Information Systems (OASIS). Sprouts: Working Papers on Information Systems, 10(114).Link
External links
- Metaphorum: researching and developing VSM applications
- ASVSA: Research Association on Viable Systems
- The VSM on a memorial website of Stafford Beer
- Video from Manchester Business School (1974) of Stafford Beer talking about VSM applied in Chile. Menu at bottom of page
- VSM diagnosis and design for co-operatives and social economy enterprises
- The Systems Perspective: Methods and Models for the Future by Allenna LeonardAllenna LeonardAllenna Leonard is an American cyberneticist, consultant and Director of Team Syntegrity Inc. of Toronto, Canada, internationally, specializing in the application of Stafford Beer's Viable System Model and Syntegration.- Biography :...
with Stafford Beer - Stafford Beer and the Humankind Future
- To Change Ourselves: A Personal VSM Application by Allenna Leonard
- Viable Software
- Modelling Organisations Using the Viable Systems Model by Patrick Hoverstadt
- VSM oriented Enterprise Architecture from Tetradian Consulting
- The Viable System Model Livas short introductory videos on YouTubeYouTubeYouTube is a video-sharing website, created by three former PayPal employees in February 2005, on which users can upload, view and share videos....
- Management Cybernetics Portal in Russia
- The reasoning behind the Viable System Model
- The Viable Systems Approach (Italian)
- The Viable System Agent A Smalltalk implementation of the VSM.
Organizations:

