
Ventricular pressure
Encyclopedia
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
within the ventricles
Ventricle (heart)
In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
of the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
.
Left ventricular pressure
During most of the cardiac cycleCardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is a term referring to all or any of the events related to the flow or blood pressure that occurs from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. The frequency of the cardiac cycle is described by the heart rate. Each beat of the heart involves five major stages...
, ventricular pressure is less than the pressure in the aorta
Aorta
The aorta is the largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it branches off into two smaller arteries...
, but during systole
Systole (medicine)
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
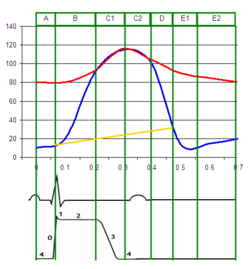
, the ventricular pressure rapidly increases, and the two pressures become equal to each other (represented by the junction of the blue and red lines on the diagram on this page), the aortic valve
Aortic valve
The aortic valve is one of the valves of the heart. It is normally tricuspid , although in 1% of the population it is found to be congenitally bicuspid . It lies between the left ventricle and the aorta....
opens, and blood is pumped to the body.
Elevated left ventricular end-diastolic pressure has been described as a risk factor in cardiac surgery.
Noninvasive approximations have been described.
An elevated pressure difference between the aortic pressure and the left ventricular pressure may be indicative of aortic stenosis.

