
VOC Opperhoofden in Japan
Encyclopedia

Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
(Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie or VOC in old-spelling
Spelling reform
Many languages have undergone spelling reform, where a deliberate, often officially sanctioned or mandated, change to spelling takes place. Proposals for such reform are also common....
Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
, literally "United East Indian
Indies
The Indies is a term that has been used to describe the lands of South and Southeast Asia, occupying all of the present India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and also Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam, Brunei, Singapore, the Philippines, East Timor, Malaysia and...
Company") in Japan during the period of the Tokugawa shogunate
Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the and the , was a feudal regime of Japan established by Tokugawa Ieyasu and ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family. This period is known as the Edo period and gets its name from the capital city, Edo, which is now called Tokyo, after the name was...
, also known as the Edo period
Edo period
The , or , is a division of Japanese history which was ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family, running from 1603 to 1868. The political entity of this period was the Tokugawa shogunate....
.
Opperhoofd
Opperhoofd
Opperhoofd is a Dutch word which literally means 'supreme head'.The Danish equivalent Overhoved, which is derived from a Danish pronunciation of the Dutch word, is also treated here....
is a Dutch word (plural Opperhoofden) which literally means 'supreme head[man]'. In its historical usage, the word is a gubernatorial title, comparable to the English chief factor, for the chief executive officer of a Dutch factory
Factory (trading post)
Factory was the English term for the trading posts system originally established by Europeans in foreign territories, first within different states of medieval Europe, and later in their colonial possessions...
in the sense of trading post, as led by a factor, i.e. agent.
The Dutch East India Company was established in 1602 by the States-General of the Netherlands
States-General of the Netherlands
The States-General of the Netherlands is the bicameral legislature of the Netherlands, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The parliament meets in at the Binnenhof in The Hague. The archaic Dutch word "staten" originally related to the feudal classes in which medieval...
to carry out colonial activities in Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
. The VOC enjoyed unique success in Japan, in part because of the ways in which the character and other qualities of its Opperhoofden were perceived to differ from other competitors.
Trading posts or factories

Hirado, 1609-1639
The first VOC trading outpost in Japan was on the island of Hirado off the coast of KyūshūKyushu
is the third largest island of Japan and most southwesterly of its four main islands. Its alternate ancient names include , , and . The historical regional name is referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands....
. Permission for establishing this permanent facility was granted in 1609; but the right to make use of this convenient location was revoked in 1639.
Dejima, 1639-1860
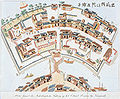
.jpg)
Sakoku
was the foreign relations policy of Japan under which no foreigner could enter nor could any Japanese leave the country on penalty of death. The policy was enacted by the Tokugawa shogunate under Tokugawa Iemitsu through a number of edicts and policies from 1633–39 and remained in effect until...
("closed door" policy) was ordered by the Tokugawa shogunate
Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the and the , was a feudal regime of Japan established by Tokugawa Ieyasu and ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family. This period is known as the Edo period and gets its name from the capital city, Edo, which is now called Tokyo, after the name was...
; and by 1641, the VOC had to transfer all of its mercantile operations to the small man-made island of Dejima
Dejima
was a small fan-shaped artificial island built in the bay of Nagasaki in 1634. This island, which was formed by digging a canal through a small peninsula, remained as the single place of direct trade and exchange between Japan and the outside world during the Edo period. Dejima was built to...
in Nagasaki harbor. The island had been built for the Portuguese, but they had been forced to abandon it and all contacts with Japan. Only the Dutch were permitted to remain after all other Westerners had been excluded.
The Dutch presence in Japan was closely monitored and controlled. For example, each year the VOC had to transfer the opperhoofd. Each opperhoofd was expected to travel to Edo to offer tribute to the shogun. The VOC traders had to be careful not to import anything religious; and they were not allowed to bring any females, nor to bury their dead ashore. They were largely free to do as they pleased on the island; but they were explicitly ordered to work on Sunday.
For nearly 250 years a series of VOC traders lived, worked and seemed to thrive in this confined location.
List of chief traders at Hirado
is a small island just off the western shore of the Japanese island of Kyūshū. In the early 17th century, Hirado was a major center of foreign trade and included British, Chinese, and other trading stations along with the Dutch one, maintained and operated by the VOC after 1609. The serial leaders of this VOC trading enclave or "factory" at Hirado were:- Jacques SpecxJacques SpecxJacques Specx was a Dutch merchant, who founded the trade on Japan and Korea in 1609. Jacques Specx received the support of William Adams to obtain extensive trading rights from the Shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu on August 24, 1609, which allowed him to establish a trading factory in Hirado on September...
: 20.9.1609 - 28.8.1612 - Hendrick Brouwer: 28.8.1612 - 6.8.1614
- Jacques SpecxJacques SpecxJacques Specx was a Dutch merchant, who founded the trade on Japan and Korea in 1609. Jacques Specx received the support of William Adams to obtain extensive trading rights from the Shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu on August 24, 1609, which allowed him to establish a trading factory in Hirado on September...
: 6.8.1614 - 29.10.1621 - Leonardt Camps: 29.10.1621 - 21.11.1623
- Cornelis van Nijenroode: 21.11.1623 - _._.1631
- Pieter Stamper: 1631
- Cornelis van NijenrodeCornelis van NijenrodeCornelis van Nijenrode, also Cornelis van Nieuwroode was Governor of the VOC-trading post in Hirado, Japan from 1623 to 1633....
: _._.1631 - 31.1.1633 - Pieter van Sante or Pieter van Santen: 31.1.1633 - 6.9.1633
- Nicolaes CouckebackerNicolaes CouckebackerNicolaes Coeckebacker or Couckebacker was twice Chief of the Dutch trading factory at Hirado, the Japanese trading post of the Dutch East India Company. He arrived in 1633 and stayed till fall 1635...
: 6.9.1633 - _._.1635 - Maerten Wesselingh or Hendrick Hagenaer (?): _._.1635-_._.1637
- Nicolaes CouckebackerNicolaes CouckebackerNicolaes Coeckebacker or Couckebacker was twice Chief of the Dutch trading factory at Hirado, the Japanese trading post of the Dutch East India Company. He arrived in 1633 and stayed till fall 1635...
: _._.1637 - 3.2.1639 - François CaronFrançois CaronFrançois Caron was a French Huguenot refugee to the Netherlands who served the Dutch East India Company for 30 years, rising from cabin boy to Director-General at Batavia , only one grade below Governor-General...
: 3.2.1639 - 13.2.1641 Caron was last Opperhoofd at Hirado.
List of chief traders at Dejima

Artificial island
An artificial island or man-made island is an island or archipelago that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means...
in the bay of Nagasaki. This island was a Dutch trading post during Japan's period of maritime restrictions (海禁, kaikin
Sakoku
was the foreign relations policy of Japan under which no foreigner could enter nor could any Japanese leave the country on penalty of death. The policy was enacted by the Tokugawa shogunate under Tokugawa Iemitsu through a number of edicts and policies from 1633–39 and remained in effect until...
, 1641–1853) during the Edo period
Edo period
The , or , is a division of Japanese history which was ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family, running from 1603 to 1868. The political entity of this period was the Tokugawa shogunate....
. The serial leaders of this VOC trading enclave or "factory" at Dejima were:

- Janus Henricus Donker CurtiusJanus Henricus Donker CurtiusJanus Henricus Donker Curtius was the last Dutch commissioner for the island of Dejima in Japan. He studied law at Leiden University....
: 2.11.1852 - 28.2.1860 [Donker Curtius became the last in a long list of hardy Dutch Opperhoofden who were stationed at Dejima; and fortuitously, Curtius also became the first of many Dutch diplomatic and trade representatives in Japan during the burgeoning pre-Meiji years.]
Sources
- Blomhoff, J.C. (2000). The Court Journey to the Shogun of Japan: From a Private Account by Jan Cock Blomhoff. Amsterdam
- Blussé, L. et al., eds. (1995–2001) The Deshima [sic] Dagregisters: Their Original Tables of Content. Leiden.
- Blussé, L. et al., eds. (2004). The Deshima Diaries Marginalia 1740-1800. Tokyo.
- Boxer. C.R. (1950). Jan Compagnie in Japan, 1600-1850: An Essay on the Cultural, Aristic, and Scientific Influence Exercised by the Hollanders in Japan from the Seventeenth to the Nineteenth Centuries. Den Haag.
- Caron, F. (1671). A True Description of the Mighty Kingdoms of Japan and Siam. London. de Winter, Michiel. (2006). "VOC in Japan: Betrekkingen tussen Hollanders en Japanners in de Edo-periode, tussen 1602-1795" ("VOC in Japan: Relations between the Dutch and Japanese in the Edo-period, between 1602-1795").
- Doeff, H. (1633). Herinneringen uit Japan. Amsterdam. [Doeff, H. "Recollections of Japan" ISBN 1-55395-849-7]
- Edo-Tokyo Museum exhibition catalog. (2000). A Very Unique Collection of Historical Significance: The Kapitan (the Dutch Chief) Collection from the Edo Period—The Dutch Fascination with Japan. Catalog of "400th Anniversary Exhibition Regarding Relations between Japan and the Netherlands," a joint project of the Edo-Tokyo Museum, the City of Nagasaki, the National Museum of Ethnology, the National Natuurhistorisch Museum" and the National Herbarium of the Netherlands in Leiden, the Netherlands. Tokyo.
- Leguin, F. (2002). Isaac Titsingh (1745-1812): Een passie voor Japan, leven en werk van de grondlegger van de Europese Japanologie. Leiden.
- Nederland's Patriciaat, Vol. 13 (1923). Den Haag.
- Screech, Timon. (2006). Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779-1822. London.
- Siebold, P.F.v. (1897). Nippon. Würzburg e Leipzig.
- Titsingh, I. (1820). Mémoires et Anecdotes sur la Dynastie régnante des Djogouns, Souverains du Japon. Paris.
- Titsingh, I. (1822). Illustrations of Japan; consisting of Private Memoirs and Anecdotes of the reigning dynasty of The Djogouns, or Sovereigns of Japan. London.

