Ullage motor
Encyclopedia
Ullage motors are relatively small, independently-fueled rocket engine
s that may be fired to accelerate the rocket
prior to main engine ignition, when the vehicle is in a zero-g situation.
 Liquid, cryogenic rockets keep their propellant in tanks. These tanks are never completely filled, to allow for expansion of the cold liquid propellant. In micro-gravity
Liquid, cryogenic rockets keep their propellant in tanks. These tanks are never completely filled, to allow for expansion of the cold liquid propellant. In micro-gravity
conditions the ullage
gas may float around and threaten to be sucked into the engines, which is very undesirable. Small rocket engines, called ullage motors, are sometimes used to settle the propellant prior to the main engine ignition. These motors provide acceleration that moves the main engine liquid propellants to the bottom of their tanks, so they can be pumped into the engine plumbing. Meanwhile the ullage gas floats to the top, away from the engine inlets. Such motors were first invented by Soviet engineers for the Molniya
interplanetary launch vehicle
in 1960.
The firing of the ullage motors is used during stage separation of rocket and/or stabilization of a rocket when there are brief reductions in acceleration which could allow the liquid propellant to float away from the engine intakes. Ullage motors are also commonly employed on deep-space missions where a liquid rocket
needs to start a burn after traveling in micro-gravity.
Ullage motors are typically very small; research shows that accelerations of the order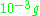 are needed to avoid excessive gas intake. Some vehicles use other techniques to hold liquid at the inlet, as once the main engines are ignited, ullage motors are no longer required.
are needed to avoid excessive gas intake. Some vehicles use other techniques to hold liquid at the inlet, as once the main engines are ignited, ullage motors are no longer required.
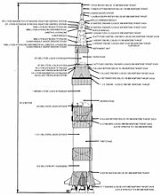
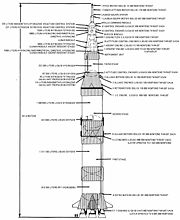
The four ullage motors of the Saturn V rocket used in the American Apollo program were located on the second stage. In the third stage (known as S-IVB
), there was a more general Auxiliary Propulsion System that also had ullage functions.
Rocket engine
A rocket engine, or simply "rocket", is a jet engineRocket Propulsion Elements; 7th edition- chapter 1 that uses only propellant mass for forming its high speed propulsive jet. Rocket engines are reaction engines and obtain thrust in accordance with Newton's third law...
s that may be fired to accelerate the rocket
Rocket
A rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle which obtains thrust from a rocket engine. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellants carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction...
prior to main engine ignition, when the vehicle is in a zero-g situation.
Description

Weightlessness
Weightlessness is the condition that exists for an object or person when they experience little or no acceleration except the acceleration that defines their inertial trajectory, or the trajectory of pure free-fall...
conditions the ullage
Ullage
Ullage or Headspace refers to the unfilled space in a container, particularly with a liquid.-Etymology:The word comes ultimately from the Latin oculus, “eye”, which was used in a figurative sense by the Romans for the bung hole of a barrel...
gas may float around and threaten to be sucked into the engines, which is very undesirable. Small rocket engines, called ullage motors, are sometimes used to settle the propellant prior to the main engine ignition. These motors provide acceleration that moves the main engine liquid propellants to the bottom of their tanks, so they can be pumped into the engine plumbing. Meanwhile the ullage gas floats to the top, away from the engine inlets. Such motors were first invented by Soviet engineers for the Molniya
Molniya (rocket)
Molniya 8K78 was a modification of the well-known R-7 Semyorka rocket and had four stages.This derivative of the original three stage Vostok rocket was especially designed to bring high flying satellites into orbit or to launch probes to other planets. The first launch of this rocket was on...
interplanetary launch vehicle
Launch vehicle
In spaceflight, a launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket used to carry a payload from the Earth's surface into outer space. A launch system includes the launch vehicle, the launch pad and other infrastructure....
in 1960.
The firing of the ullage motors is used during stage separation of rocket and/or stabilization of a rocket when there are brief reductions in acceleration which could allow the liquid propellant to float away from the engine intakes. Ullage motors are also commonly employed on deep-space missions where a liquid rocket
Liquid rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or a liquid rocket is a rocket engine that uses propellants in liquid form. Liquids are desirable because their reasonably high density allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low, and it is possible to use lightweight pumps to pump the propellant from...
needs to start a burn after traveling in micro-gravity.
Ullage motors are typically very small; research shows that accelerations of the order
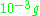 are needed to avoid excessive gas intake. Some vehicles use other techniques to hold liquid at the inlet, as once the main engines are ignited, ullage motors are no longer required.
are needed to avoid excessive gas intake. Some vehicles use other techniques to hold liquid at the inlet, as once the main engines are ignited, ullage motors are no longer required.The four ullage motors of the Saturn V rocket used in the American Apollo program were located on the second stage. In the third stage (known as S-IVB
S-IVB
The S-IVB was built by the Douglas Aircraft Company and served as the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB. It had one J-2 engine...
), there was a more general Auxiliary Propulsion System that also had ullage functions.

