
US Standard Atmosphere
Encyclopedia
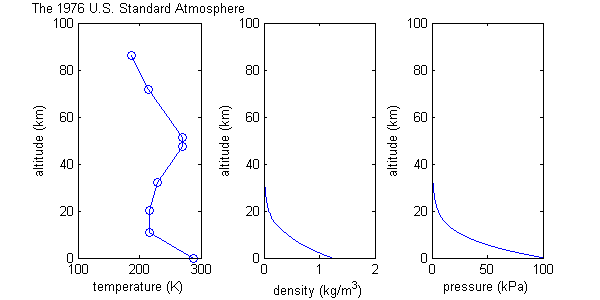
The U.S. Standard Atmosphere is a series of models that define values for atmospheric
temperature
, density
, pressure
and other properties over a wide range of altitude
s. The first model, based on an existing international standard, was published in 1958 by the U.S. Committee on Extension to the Standard Atmosphere, and was updated in 1962, 1966, and 1976.
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
, pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
and other properties over a wide range of altitude
Altitude
Altitude or height is defined based on the context in which it is used . As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context...
s. The first model, based on an existing international standard, was published in 1958 by the U.S. Committee on Extension to the Standard Atmosphere, and was updated in 1962, 1966, and 1976.
1962 version
The basic assumptions made for the 1962 version were:- air is a clean, dry, perfect gasPerfect gasIn physics, a perfect gas is a theoretical gas that differs from real gases in a way that makes certain calculations easier to handle. Its behavior is more simplified compared to an ideal gas...
mixture (cp/cvHeat capacityHeat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
= 1.40) - molecular weight to 90 km of 28.9644 (C-12 scale)
- principal sea-level constituents are assumed to be:
- N2NitrogenNitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
–78.084% - O2OxygenOxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
–20.9476% - ArArgonArgon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
–0.934% - CO2Carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
–0.0314% - NeNeonNeon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or...
–0.001818% - HeHeliumHelium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
–0.000524% - CH4MethaneMethane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
–0.0002%.
- N2
- assigned mean conditions at sea levelSea levelMean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
are as follows :- PPressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
= 101325 Pa = 0.1013250 MN/m2 = 2116.22 psf = 14.696 psiPounds per square inchThe pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch is a unit of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units... - TTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
= 288.15 K = 15 °C = 59 °F - ρDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
= 1.225 0 kg/m3 = 0.0764734 lbm/ft3 - gEarth's gravityThe gravity of Earth, denoted g, refers to the acceleration that the Earth imparts to objects on or near its surface. In SI units this acceleration is measured in metres per second per second or equivalently in newtons per kilogram...
= 9.80665 m/s2 = 32.174 1 ft/s2 - RGas constantThe gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
= 8.31432 J/mol-K = 1545.31 ft lb/lbmol-°R.
- P
1976 version
This is the most recent version and differs from previous versions only above 32 km:| Subscript b | Height above Sea Level | Static pressure | Standard temperature (K) |
Temperature Lapse Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (ft) | (pascals) | (inHg) | (K/m) | (K/ft) | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 101325 | 29.92126 | 288.15 | -0.0065 | -0.0019812 |
| 1 | 11,000 | 36,089 | 22632.1 | 6.683245 | 216.65 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 20,000 | 65,617 | 5474.89 | 1.616734 | 216.65 | 0.001 | 0.0003048 |
| 3 | 32,000 | 104,987 | 868.019 | 0.2563258 | 228.65 | 0.0028 | 0.00085344 |
| 4 | 47,000 | 154,199 | 110.906 | 0.0327506 | 270.65 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 5 | 51,000 | 167,323 | 66.9389 | 0.01976704 | 270.65 | -0.0028 | -0.00085344 |
| 6 | 71,000 | 232,940 | 3.95642 | 0.00116833 | 214.65 | -0.002 | -0.0006096 |

See also
- Atmospheric modelsAtmospheric modelsStatic atmospheric models describe how the ideal gas properties of an atmosphere change, primarily as a function of altitude....
- NRLMSISE-00NRLMSISE-00NRLMSISE-00 is an empirical, global model of the Earth's atmosphere from ground to space. It models the temperatures and densities of the atmosphere's components. A primary use of this model is to aid predictions of satellite orbital decay due to atmospheric drag...
- International Standard AtmosphereInternational Standard AtmosphereThe International Standard Atmosphere is an atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes. It has been established to provide a common reference for temperature and pressure and consists of tables of...
- Barometric formulaBarometric formulaThe barometric formula, sometimes called the exponential atmosphere or isothermal atmosphere, is a formula used to model how the pressure of the air changes with altitude.-Pressure equations:...

