
UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase
Encyclopedia
UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are UDP-glucose and sulfite
, whereas its two products
are UDP-6-sulfoquinovose and H2O
.
In a subsequent reaction catalyzed by sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol synthase, the sulfoquinovose portion of UDP-sulfoquinovose is combined with diacyglycerol to produced the sulfolipid
sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol
(SQDG).
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
s, specifically those acting on carbon-sulfur bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is UDP-6-sulfo-6-deoxyglucose sulfohydrolase. Other names in common use include sulfite:UDP-glucose sulfotransferase, and UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase. This enzyme participates in nucleotide sugars metabolism
and glycerolipid metabolism.
The 3-dimensional structure of the enzyme is known from Protein Data Bank
entries 1qrr (Mulichak et al., 1999), 1i24, 1i2b and 1i2c.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- UDP-glucose + sulfite
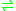 UDP-6-sulfoquinovose + H2O
UDP-6-sulfoquinovose + H2O
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are UDP-glucose and sulfite
Sulfite
Sulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are UDP-6-sulfoquinovose and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
.
In a subsequent reaction catalyzed by sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol synthase, the sulfoquinovose portion of UDP-sulfoquinovose is combined with diacyglycerol to produced the sulfolipid
Sulfolipid
Sulfolipids are a class of lipids which possess a sulfur-containing functional group. One of the most common consituents of sulfolipids is sulfoquinovose, which is acylated to form sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerols. In plants, sulfolipids are important intermediates in the sulfur cycle....
sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol
SQDG
Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerols, abbreviated SQDG, are a class of sulfur-containing but phosphorus-free lipids found in many photosynthetic organisms.- Discovery, structure and chemical properties :...
(SQDG).
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolase
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. For example, an enzyme that catalyzed the following reaction is a hydrolase:-Nomenclature:...
s, specifically those acting on carbon-sulfur bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is UDP-6-sulfo-6-deoxyglucose sulfohydrolase. Other names in common use include sulfite:UDP-glucose sulfotransferase, and UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase. This enzyme participates in nucleotide sugars metabolism
Nucleotide sugars metabolism
In nucleotide sugar metabolism a group of biochemicals known as nucleotide sugars act as donors for sugar residues in the glycosylation reactions that produce polysaccharides. They are substrates for glycosyltransferases. The nucleotide sugars are also intermediates in nucleotide sugar...
and glycerolipid metabolism.
The 3-dimensional structure of the enzyme is known from Protein Data Bank
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
entries 1qrr (Mulichak et al., 1999), 1i24, 1i2b and 1i2c.

