
Tutte matrix
Encyclopedia
In graph theory
, the Tutte matrix A of a graph
G = (V, E) is a matrix used to determine the existence of a perfect matching: that is, a set of edges which is incident with each vertex exactly once.
If the set of vertices V has n elements then the Tutte matrix is an n × n matrix A with entries
Graph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of graphs, mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects from a certain collection. A "graph" in this context refers to a collection of vertices or 'nodes' and a collection of edges that connect pairs of...
, the Tutte matrix A of a graph
Graph (mathematics)
In mathematics, a graph is an abstract representation of a set of objects where some pairs of the objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by mathematical abstractions called vertices, and the links that connect some pairs of vertices are called edges...
G = (V, E) is a matrix used to determine the existence of a perfect matching: that is, a set of edges which is incident with each vertex exactly once.
If the set of vertices V has n elements then the Tutte matrix is an n × n matrix A with entries
-
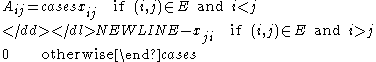
where the xij are indeterminates. The determinantDeterminantIn linear algebra, the determinant is a value associated with a square matrix. It can be computed from the entries of the matrix by a specific arithmetic expression, while other ways to determine its value exist as well...
of this skew-symmetric matrix is then a polynomial (in the variables xij, i < j ): this coincides with the square of the pfaffianPfaffianIn mathematics, the determinant of a skew-symmetric matrix can always be written as the square of a polynomial in the matrix entries. This polynomial is called the Pfaffian of the matrix, The term Pfaffian was introduced by who named them after Johann Friedrich Pfaff...
of the matrix A and is non-zero (as a polynomial) if and only if a perfect matching exists. (It should be noted that this is not the Tutte polynomialTutte polynomialThe Tutte polynomial, also called the dichromate or the Tutte–Whitney polynomial, is a polynomial in two variables which plays an important role in graph theory, a branch of mathematics and theoretical computer science...
of G.)
The Tutte matrix is a generalisation of the Edmonds matrix for a balanced bipartite graphBipartite graphIn the mathematical field of graph theory, a bipartite graph is a graph whose vertices can be divided into two disjoint sets U and V such that every edge connects a vertex in U to one in V; that is, U and V are independent sets...
.

