Transposition of the great vessels
Encyclopedia
Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects
(CHDs) involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the primary blood vessel
s: superior
and/or inferior
vena cavae (SVC, IVC), pulmonary artery
, pulmonary vein
s, and aorta
. CHDs involving only the primary arteries
(pulmonary artery and aorta) belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA).
.
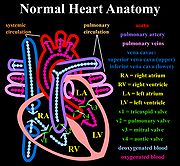
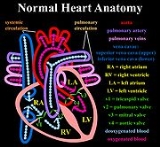
 In a normal heart
In a normal heart
, oxygen
-depleted blood
is pumped from the right side of the heart, through the pulmonary artery, to the lung
s where it is oxygenated. The oxygen-rich red blood then returns to the left heart
, via the pulmonary veins, and is pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body, including the heart muscle
itself.
Congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect is a defect in the structure of the heart and great vessels which is present at birth. Many types of heart defects exist, most of which either obstruct blood flow in the heart or vessels near it, or cause blood to flow through the heart in an abnormal pattern. Other...
(CHDs) involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the primary blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s: superior
Superior vena cava
The superior vena cava is truly superior, a large diameter, yet short, vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the heart's right atrium...
and/or inferior
Inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava , also known as the posterior vena cava, is the large vein that carries de-oxygenated blood from the lower half of the body into the right atrium of the heart....
vena cavae (SVC, IVC), pulmonary artery
Pulmonary artery
The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood....
, pulmonary vein
Pulmonary vein
The pulmonary veins are large blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. In humans there are four pulmonary veins, two from each lung...
s, and aorta
Aorta
The aorta is the largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it branches off into two smaller arteries...
. CHDs involving only the primary arteries
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
(pulmonary artery and aorta) belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA).
Etiologies
Preexisting diabetes mellitus of an expectant mother is a risk factor that has been described for the fetus having TGV. Additionally, the children of diabetic mothers are more likely to have aortic coarctationAortic coarctation
Coarctation of the aorta, or aortic coarctation, is a congenital condition whereby the aorta narrows in the area where the ductus arteriosus inserts.-Types:There are three types:...
.
Description




Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
-depleted blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
is pumped from the right side of the heart, through the pulmonary artery, to the lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s where it is oxygenated. The oxygen-rich red blood then returns to the left heart
Left heart
Left heart is a term used to refer collectively to the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart; occasionally, this term is intended to reference the left atrium, left ventricle, and the aorta collectively....
, via the pulmonary veins, and is pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body, including the heart muscle
Coronary circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels of the heart muscle . The vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood to the myocardium are known as coronary arteries...
itself.

