
Time-of-flight
Encyclopedia
Time of flight describes a variety of methods that measure the time that it takes for an object, particle or acoustic, electromagnetic or other wave to travel a distance through a medium. This measurement can be used for a time standard (such as an atomic fountain), as a way to measure velocity or path length through a given medium, or as a way to learn about the particle or medium (such as composition or flow rate). The traveling object may be detected directly (e.g., ion detector in mass spectrometry) or indirectly (e.g., light scattered from an object in laser doppler velocimetry).
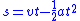
results in this equation

for the time of flight of a projectile.
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry
(TOFMS) is a method of mass spectrometry
in which ion
s are accelerated by an electric field
of known strength. This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy
as any other ion that has the same charge. The velocity of the ion depends on the mass-to-charge ratio
. The time that it subsequently takes for the particle to reach a detector at a known distance is measured. This time will depend on the mass-to-charge ratio
of the particle (heavier particles reach lower speeds). From this time and the known experimental parameters one can find the mass-to-charge ratio
of the ion. The elapsed time from the instant a particle leaves a source to the instant it reaches a detector.
measures the velocity of a liquid or gas through a pipe using acoustic sensors. This has some advantages over other measurement techniques. The results are slightly affected by temperature, density or conductivity. Maintenance is inexpensive because there are no moving parts
.
Ultrasonic flow meters come in three different types: transmission (contrapropagating transit time) flowmeters, reflection (Doppler) flowmeters, and open-channel flowmeters. Transit time flowmeters work by measuring the time difference between an ultrasonic pulse sent in the flow direction and an ultrasound pulse sent opposite the flow direction. Doppler flowmeters measure the doppler shift resulting in reflecting an ultrasonic beam off either small particles in the fluid, air bubbles in the fluid, or the flowing fluid's turbulence. Open channel flow meters measure upstream levels in front of flume
s or weir
s.
Optical time-of-flight sensors consist of two light beams projected into the fluid whose detection is either interrupted or instigated by the passage of small particles (which are assumed to be following the flow). This is not dissimilar from the optical beams used as safety devices in motorized garage doors or as triggers in alarm systems. The speed of the particles is calculated by knowing the spacing between the two beams. If there is only one detector, then the time difference can be measured via autocorrelation
. If there are two detectors, one for each beam, then direction can also be known. Since the location of the beams is relatively easy to determine, the precision of the measurement depends primarily on how small the setup can be made. If the beams are too far apart, the flow could change substantially between them, thus the measurement becomes an average over that space. Moreover, multiple particles could reside between them at any given time, and this would corrupt the signal since the particles are indistinguishable. For such a sensor to provide valid data, it must be small relative to the scale of the flow and the seeding density. MOEMS approaches yield extremely small packages, making such sensors applicable in a variety of situations.
The work function homogeneity of the tube can be controlled by a Kelvin probe
. The magnetic field can be measured by a fluxgate compass
. High frequencies are passively shielded and damped by radar absorbent material
. To generate arbitrary low frequencies field the screen is parted into plates (overlapping and connected by capacitors) with bias voltage on each plate and a bias current on coil behind plate whose flux is closed by an outer core. In this way the tube can be configured to act as a weak achromatic quadrupole lens with an aperture with a grid and a delay line detector in the diffraction plane to do angle resolved measurements. Changing the field the angle of the field of view can be changed and a deflecting bias can be superimposed to scan through all angles.
When no delay line detector is used focusing the ions onto a detector can be accomplished through the use of two or three einzel lens
es placed in the vacuum tube located between the ion source and the detector.
The sample should be immersed into the tube with holes and apertures for and against stray light to do magnetic experiments and to control the electrons from their start.
- In electronicsElectronicsElectronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, the TOF method is used to estimate the electron mobilityElectron mobilityIn solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterizes how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor, when pulled by an electric field. In semiconductors, there is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility...
. Originally, it was designed for measurement of low-conductive thin films, later adjusted for common semiconductors. This experimental technique is used for metal-dielectric-metal structures as well as organic field-effect transitors. The excess charges are generated by application of the laser or voltage pulse.
- In time-of-flight mass spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometry is a method of mass spectrometry in which an ion's mass-to-charge ratio is determined via a time measurement. Ions are accelerated by an electric field of known strength. This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy as any other ion that has...
, ions are accelerated by an electrical field to the same kinetic energyKinetic energyThe kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
with the velocity of the ion depending on the mass-to-charge ratioMass-to-charge ratioThe mass-to-charge ratio ratio is a physical quantity that is widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics. It appears in the scientific fields of lithography, electron microscopy, cathode ray tubes, accelerator physics, nuclear physics, Auger...
. Thus the time-of-flight is used to measure velocity, from which the mass-to-charge ratio can be determined. The time-of-flight of electronElectronThe electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s is used to measure their kinetic energy.
- In near infrared spectroscopyNear infrared spectroscopyNear-infrared spectroscopy is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum...
, the TOF method is used to measure the media-dependent optical pathlength over a range of optical wavelengths, from which composition and properties of the media can be analyzed.
- In ultrasonic flow meterUltrasonic flow meterAn ultrasonic flow meter is a type of flow meter that measures the velocity of a liquid or gas by using the principle of ultrasound. Using ultrasonic transducers, the flow meter can measure the average velocity along the path of an emitted beam of ultrasound, by averaging the difference in...
measurement, TOF is used to measure speed of signal propagation upstream and downstream of flow of a media, in order to estimate total flow velocity. This measurement is made in a collinear direction with the flow.
- In planar Doppler velocimetryPlanar Doppler VelocimetryPlanar Doppler Velocimetry , also referred to as Doppler Global Velocimetry , determines flow velocity across a plane by measuring the Doppler shift in frequency of light scattered by particles contained in the flow...
(optical flow meter measurement), TOF measurements are made perpendicular to the flow by timing when individual particles cross two or more locations along the flow (collinear measurements would require generally high flow velocities and extremely narrow-band optical filters).
- In optical interferometry, the pathlength difference between sample and reference arms can be measured by TOF methods, such as frequency modulation followed by phase shift measurement or cross correlation of signals. Such methods are used in laser radar and laser tracker systems for medium-long range distance measurement.
- In kinematicsKinematicsKinematics is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies and systems without consideration of the forces that cause the motion....
, TOF is the duration in which a projectile is traveling through the air. Given the initial velocity of a particle launched from the ground, the downward (i.e. gravitational) acceleration
of a particle launched from the ground, the downward (i.e. gravitational) acceleration  , and the projectile's angle of projection θ (measured relative to the horizontal), then a simple rearrangement of the SUVAT equation
, and the projectile's angle of projection θ (measured relative to the horizontal), then a simple rearrangement of the SUVAT equation
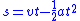
results in this equation

for the time of flight of a projectile.
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry is a method of mass spectrometry in which an ion's mass-to-charge ratio is determined via a time measurement. Ions are accelerated by an electric field of known strength. This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy as any other ion that has...
(TOFMS) is a method of mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
in which ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s are accelerated by an electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
of known strength. This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
as any other ion that has the same charge. The velocity of the ion depends on the mass-to-charge ratio
Mass-to-charge ratio
The mass-to-charge ratio ratio is a physical quantity that is widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics. It appears in the scientific fields of lithography, electron microscopy, cathode ray tubes, accelerator physics, nuclear physics, Auger...
. The time that it subsequently takes for the particle to reach a detector at a known distance is measured. This time will depend on the mass-to-charge ratio
Mass-to-charge ratio
The mass-to-charge ratio ratio is a physical quantity that is widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics. It appears in the scientific fields of lithography, electron microscopy, cathode ray tubes, accelerator physics, nuclear physics, Auger...
of the particle (heavier particles reach lower speeds). From this time and the known experimental parameters one can find the mass-to-charge ratio
Mass-to-charge ratio
The mass-to-charge ratio ratio is a physical quantity that is widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics. It appears in the scientific fields of lithography, electron microscopy, cathode ray tubes, accelerator physics, nuclear physics, Auger...
of the ion. The elapsed time from the instant a particle leaves a source to the instant it reaches a detector.
Ultrasonic and optical time-of-flight flow meters
An ultrasonic flow meterUltrasonic flow meter
An ultrasonic flow meter is a type of flow meter that measures the velocity of a liquid or gas by using the principle of ultrasound. Using ultrasonic transducers, the flow meter can measure the average velocity along the path of an emitted beam of ultrasound, by averaging the difference in...
measures the velocity of a liquid or gas through a pipe using acoustic sensors. This has some advantages over other measurement techniques. The results are slightly affected by temperature, density or conductivity. Maintenance is inexpensive because there are no moving parts
Moving parts
The moving parts of a machine are those parts of it that move. Machines comprise both moving and fixed parts. The moving parts have controlled and constrained motions....
.
Ultrasonic flow meters come in three different types: transmission (contrapropagating transit time) flowmeters, reflection (Doppler) flowmeters, and open-channel flowmeters. Transit time flowmeters work by measuring the time difference between an ultrasonic pulse sent in the flow direction and an ultrasound pulse sent opposite the flow direction. Doppler flowmeters measure the doppler shift resulting in reflecting an ultrasonic beam off either small particles in the fluid, air bubbles in the fluid, or the flowing fluid's turbulence. Open channel flow meters measure upstream levels in front of flume
Flume
A flume is an open artificial water channel, in the form of a gravity chute, that leads water from a diversion dam or weir completely aside a natural flow. Often, the flume is an elevated box structure that follows the natural contours of the land. These have been extensively used in hydraulic...
s or weir
Weir
A weir is a small overflow dam used to alter the flow characteristics of a river or stream. In most cases weirs take the form of a barrier across the river that causes water to pool behind the structure , but allows water to flow over the top...
s.
Optical time-of-flight sensors consist of two light beams projected into the fluid whose detection is either interrupted or instigated by the passage of small particles (which are assumed to be following the flow). This is not dissimilar from the optical beams used as safety devices in motorized garage doors or as triggers in alarm systems. The speed of the particles is calculated by knowing the spacing between the two beams. If there is only one detector, then the time difference can be measured via autocorrelation
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
. If there are two detectors, one for each beam, then direction can also be known. Since the location of the beams is relatively easy to determine, the precision of the measurement depends primarily on how small the setup can be made. If the beams are too far apart, the flow could change substantially between them, thus the measurement becomes an average over that space. Moreover, multiple particles could reside between them at any given time, and this would corrupt the signal since the particles are indistinguishable. For such a sensor to provide valid data, it must be small relative to the scale of the flow and the seeding density. MOEMS approaches yield extremely small packages, making such sensors applicable in a variety of situations.
High-precision measurements in physics
Usually the tube is praised for simplicity, but for precision measurements of charged low energy particles the electric and the magnetic field in the flight tube has to be controlled within 10 mV and 1 nT respectively.The work function homogeneity of the tube can be controlled by a Kelvin probe
Kelvin probe force microscope
Kelvin probe force microscopy , also known as surface potential microscopy, is a noncontact variant of atomic force microscopy that was invented in 1991. With KPFM, the work function of surfaces can be observed at atomic or molecular scales...
. The magnetic field can be measured by a fluxgate compass
Fluxgate compass
The basic fluxgate compass is a simple electromagnetic device that employs two or more small coils of wire around a core of highly permeable magnetic material, to directly sense the direction of the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field...
. High frequencies are passively shielded and damped by radar absorbent material
Radar absorbent material
Radar-absorbent material, or RAM, is a class of materials used in stealth technology to disguise a vehicle or structure from radar detection. A material's absorbency at a given frequency of radar wave depends upon its composition...
. To generate arbitrary low frequencies field the screen is parted into plates (overlapping and connected by capacitors) with bias voltage on each plate and a bias current on coil behind plate whose flux is closed by an outer core. In this way the tube can be configured to act as a weak achromatic quadrupole lens with an aperture with a grid and a delay line detector in the diffraction plane to do angle resolved measurements. Changing the field the angle of the field of view can be changed and a deflecting bias can be superimposed to scan through all angles.
When no delay line detector is used focusing the ions onto a detector can be accomplished through the use of two or three einzel lens
Einzel lens
An einzel lens is a charged particle lens that focuses without changing the energy of the beam. It consists of three or more sets of cylindrical or rectangular tubes in series along an axis...
es placed in the vacuum tube located between the ion source and the detector.
The sample should be immersed into the tube with holes and apertures for and against stray light to do magnetic experiments and to control the electrons from their start.

