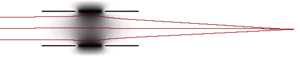
Einzel lens
Encyclopedia
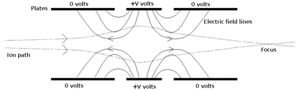
Ion optics
Ion optics involves the focusing of plasmas and ion streams, usually in mass spectrometry.-Electric field manipulation:* Electrostatic lens** Einzel lens* Electrostatic analyzer...
to focus ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s in flight which is accomplished through manipulation of the electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
in the path of the ions.
The lens elements are symmetric so the ions will regain their initial energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
on exiting the lens although the velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
of the outer particles will be altered such that they converge on to the axis. This causes the outer particles to arrive at the focus
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
intersection slightly later than the ones that travel along a straight path as they have to travel an extra distance.
Theory
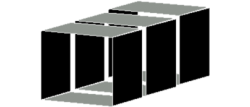
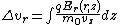
z is the axis passing through the middle of the lens. r is the direction normal to z. If the lens is constructed with cylindrical plates, the field is symmetrical around z.
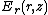 is the magnitude of the electric field in the radial direction for a particle at a particular radial distance and distance across the gap,
is the magnitude of the electric field in the radial direction for a particle at a particular radial distance and distance across the gap, 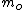 the rest mass of the particle passing through the field,
the rest mass of the particle passing through the field, 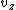 is the velocity of the particle and q is the charge of the particle. The integral occurs over the gap between the plates. This is also the interval where the lensing occurs.
is the velocity of the particle and q is the charge of the particle. The integral occurs over the gap between the plates. This is also the interval where the lensing occurs.The pair of plates is also called an electrostatic immersion lens, thus an einzel lens can be described as two or more electrostatic immersion lenses. Solving the equation above twice to find the change in radial velocity for each pair of plates can be used to calculate the focal length of the lens.
Application to television tubes