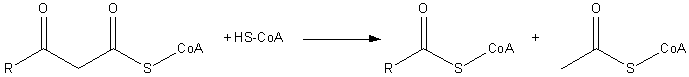
Thiolysis
Encyclopedia
Thiolysis is a reaction with a thiol
(R-SH) that cleaves one compound into two. This reaction is similar to hydrolysis
, which involves water
instead of a thiol
. This reaction is seen in β-oxidation of fatty acid
s. The depolymerisation of condensed tannins with the use of benzyl mercaptan as nucleophile is also called thiolysis.
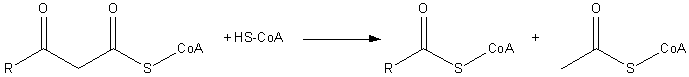
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group...
(R-SH) that cleaves one compound into two. This reaction is similar to hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
, which involves water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
instead of a thiol
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group...
. This reaction is seen in β-oxidation of fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
s. The depolymerisation of condensed tannins with the use of benzyl mercaptan as nucleophile is also called thiolysis.