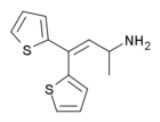
Thiambutene
Encyclopedia
The Thiambutenes are a family of opioid
analgesic
drugs developed at the British research laboratory of Burroughs-Wellcome in the late 1940s.The parent compound thiambutene has no analgesic effects, but several compounds from this group are analgesics with around the same potency as morphine
.
Notable compounds include dimethylthiambutene
, diethylthiambutene
, ethylmethylthiambutene
, pyrrolidinylthiambutene
and piperidylthiambutene
. Of these, ethylmethylthiambutene is the most potent, with 1.3x the potency of morphine, pyrrolidinylthiambutene is the least potent at 0.7x, and the rest are all around the same potency as morphine. Diethylthiambutene has been the most widely used, mainly in veterinary medicine
.
All of these compounds produced anticholinergic
and antihistamine
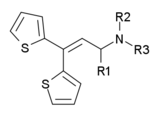
side effects, except for two of the weaker compounds diallylthiambutene and morpholinylthiambutene. They also all have a chiral centre around the alpha carbon (where the R1 group is attached) and so have two stereoisomers, with the dextro isomer being the more potent in all cases, although both isomers are active.
Three of these compounds are explicitly listed as illegal drugs under UN convention, diethylthiambutene, dimethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene, and so are illegal throughout the world, but the rest will only be illegal in countries such as the USA, Australia and New Zealand that have laws equivalent to the Federal Analog Act
.
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
analgesic
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
drugs developed at the British research laboratory of Burroughs-Wellcome in the late 1940s.The parent compound thiambutene has no analgesic effects, but several compounds from this group are analgesics with around the same potency as morphine
Morphine
Morphine is a potent opiate analgesic medication and is considered to be the prototypical opioid. It was first isolated in 1804 by Friedrich Sertürner, first distributed by same in 1817, and first commercially sold by Merck in 1827, which at the time was a single small chemists' shop. It was more...
.
Notable compounds include dimethylthiambutene
Dimethylthiambutene
Dimethylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug, most often used in veterinary medicine in Japan and to a lesser extent in other countries in the region and around the world...
, diethylthiambutene
Diethylthiambutene
Diethylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1950s which was mainly used as an anesthetic in veterinary medicine and continues, along with the other two thiambutenes dimethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene to be used for this purpose, particularly in Japan...
, ethylmethylthiambutene
Ethylmethylthiambutene
Ethylmethylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, around 1.3x the potency of morphine. It is under international control under Schedule I of the UN Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961, presumably due to high abuse potential....
, pyrrolidinylthiambutene
Pyrrolidinylthiambutene
Pyrrolidinylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family with around 3/4 of the potency of morphine. It would be considered an illegal controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the USA, Australia and New Zealand, but is legal in countries not possessing a...
and piperidylthiambutene
Piperidylthiambutene
Piperidylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, which has around the same potency as morphine. It would be considered an illegal controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the USA, Australia and New Zealand, but is legal in the rest of the world....
. Of these, ethylmethylthiambutene is the most potent, with 1.3x the potency of morphine, pyrrolidinylthiambutene is the least potent at 0.7x, and the rest are all around the same potency as morphine. Diethylthiambutene has been the most widely used, mainly in veterinary medicine
Veterinary medicine
Veterinary Medicine is the branch of science that deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease, disorder and injury in non-human animals...
.
All of these compounds produced anticholinergic
Anticholinergic
An anticholinergic agent is a substance that blocks the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central and the peripheral nervous system. An example of an anticholinergic is dicycloverine, and the classic example is atropine....
and antihistamine
Antihistamine
An H1 antagonist is a histamine antagonist of the H1 receptor that serves to reduce or eliminate effects mediated by histamine, an endogenous chemical mediator released during allergic reactions...
side effects, except for two of the weaker compounds diallylthiambutene and morpholinylthiambutene. They also all have a chiral centre around the alpha carbon (where the R1 group is attached) and so have two stereoisomers, with the dextro isomer being the more potent in all cases, although both isomers are active.
Three of these compounds are explicitly listed as illegal drugs under UN convention, diethylthiambutene, dimethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene, and so are illegal throughout the world, but the rest will only be illegal in countries such as the USA, Australia and New Zealand that have laws equivalent to the Federal Analog Act
Federal Analog Act
The Federal Analog Act, , is a controversial section of the United States Controlled Substances Act which allowed any chemical "substantially similar" to a controlled substance listed in Schedule I or II to be treated as if it were also listed in those schedules, but only if intended for human...
.

| Drug name | R1 | R2 | R3 | Analgesic Potency (Morphine = 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethylmethylthiambutene Ethylmethylthiambutene Ethylmethylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, around 1.3x the potency of morphine. It is under international control under Schedule I of the UN Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961, presumably due to high abuse potential.... |
methyl | ethyl | methyl | 1.3 |
| Dimethylthiambutene Dimethylthiambutene Dimethylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug, most often used in veterinary medicine in Japan and to a lesser extent in other countries in the region and around the world... |
methyl | methyl | methyl | 1.0 |
| Diethylthiambutene Diethylthiambutene Diethylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1950s which was mainly used as an anesthetic in veterinary medicine and continues, along with the other two thiambutenes dimethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene to be used for this purpose, particularly in Japan... |
methyl | ethyl Ethyl Ethyl may refer to:* Ethyl group, a functional group in organic chemistry* Ethyl Corporation, a fuel additive company* Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol* Cold Ethyl, a rock band founded by Nicke Andersson... |
ethyl | 1.0 |
| Piperidylthiambutene Piperidylthiambutene Piperidylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family, which has around the same potency as morphine. It would be considered an illegal controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the USA, Australia and New Zealand, but is legal in the rest of the world.... |
methyl | piperidyl Piperidine Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula 5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene units and one nitrogen atom... |
piperidyl | 1.0 |
| Pyrrolidinylthiambutene Pyrrolidinylthiambutene Pyrrolidinylthiambutene is an opioid analgesic drug from the thiambutene family with around 3/4 of the potency of morphine. It would be considered an illegal controlled substance analogue in some countries such as the USA, Australia and New Zealand, but is legal in countries not possessing a... |
methyl | pyrrolidinyl Pyrrolidine Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H9N. It is a cyclic secondary amine with a five-membered heterocycle containing four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom... |
pyrrolidinyl | 0.7 |
| Diallylthiambutene | methyl | allyl Allyl An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula H2C=CH-CH2R, where R is the connection to the rest of the molecule. It is made up of a methylene , attached to a vinyl group . The name is derived from the Latin word for garlic, Allium sativum. Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl... |
allyl | 0.5 |
| Methylisopropylthiambutene | methyl | methyl | isopropyl Isopropyl In organic chemistry, isopropyl is a propyl with a group attached to the secondary carbon. If viewed as a functional group an isopropyl is an organic compound with a propyl group attached at its secondary carbon.The bond is therefore on the middle carbon.... |
0.5 |
| Morpholinylthiambutene | methyl | morpholinyl Morpholine Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O2NH. This heterocycle, pictured at right, features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium... |
morpholinyl | 0.5 |
| Methylpropylthiambutene | methyl | methyl | propyl Propyl In organic chemistry, propyl is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula -C3H7. It is the substituent form of the alkane propane... |
0.1 |
| hydrogen Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... |
ethyl Ethyl Ethyl may refer to:* Ethyl group, a functional group in organic chemistry* Ethyl Corporation, a fuel additive company* Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol* Cold Ethyl, a rock band founded by Nicke Andersson... |
ethyl | 0.2 | |
| hydrogen | pyrrolidinyl | pyrrolidinyl | 0.1 | |
| hydrogen | piperidyl | piperidyl | 0.1 | |
| phenyl | methyl | methyl | 0.1 | |

