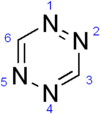
Tetrazine
Encyclopedia

Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
that consists of a six-membered aromatic ring containing four nitrogen atoms with the molecular formula C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
2H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
2N
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
4. The name tetrazine is used in the nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ....
of derivatives of this compound. Three core-ring isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
s exist: 1,2,3,4-tetrazines, 1,2,3,5-tetrazines and 1,2,4,5-tetrazines.
1,2,3,4-tetrazines
1,2,3,4-Tetrazines are often isolated fused to an aromatic ring system and are stabilized as the dioxide derivatives.1,2,4,5-tetrazine
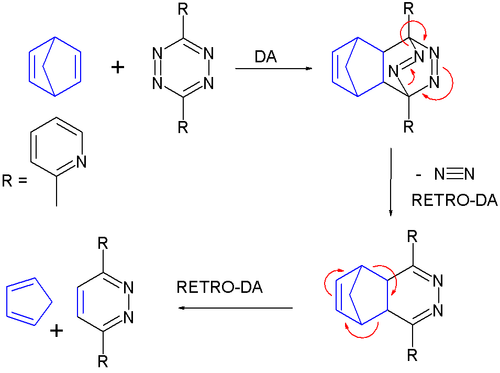
1,2,4,5-Tetrazines are very well known and myriad 3,6-disubstituted 1,2,4,5-tetrazines are known. These materials are of use in the area of energetic chemistry.The compound 3,6-di-2-pyridyl-1,2,4,5-tetrazine has two pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
substituents and is of importance as a reagent in Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon...
s. It reacts with norbornadiene
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound. This bicyclic hydrocarbon is the most stable diolefin derived from the norbornane and norbornene. Norbornadiene is primarily of interest as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis, but it has been heavily studied due to its high reactivity and distinctive...
in a sequence of one DA reactions and two retro-DA reactions to cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. This colorless liquid has a strong and unpleasant odor. At room temperature, this cyclic diene dimerizes over the course of hours to give dicyclopentadiene via a Diels–Alder reaction...
and a pyridazine
Pyridazine
Pyridazine is a heteroaromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C4H4N2, sometimes called 1,2-diazine. It contains a six-membered ring with two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C....
with exchange of an acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
unit:
With norbornadiene fused to an arene the reaction stops at an intermediary stage
See also
- 6-membered rings with one nitrogen atom:pyridinePyridinePyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
s - 6-membered rings with two nitrogen atoms: diazineDiazineDiazine refers to a group of organic compounds having the molecular formula C4H4N2. Each contains a benzene ring in which two of the C-H fragments have been replaced by isolobal nitrogen...
s - 6-membered rings with three nitrogen atoms: triazineTriazineA triazine is one of three organic chemicals, isomeric with each other, whose molecular formula is 333 and whose empirical formula is CHN.- Structure :...
s - 6-membered rings with six nitrogen atoms: hexazineHexazineHexazine is a hypothetical allotrope of nitrogen composed of 6 nitrogen atoms arranged in a ring-like structure analogous to that of benzene. It would be the final member of the azabenzene series, having all of the methylidyne groups of the benzene molecule replaced with nitrogen atoms...