
Tethered particle motion
Encyclopedia
Tethered particle motion (TPM) is a biophysical method that is used for studying various polymers such as DNA
and their interaction with other entities such as proteins.
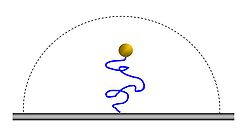 The method allows observers to measure various physical properties on the substances, as well as to measure the properties of biochemical interactions with other substances such as proteins and enzymes.
The method allows observers to measure various physical properties on the substances, as well as to measure the properties of biochemical interactions with other substances such as proteins and enzymes.
TPM is a single molecule experiment method.
to the surface, and gold beads were attached to one end of the DNA molecules. In the beginning, the RNA polymerase "captures" the DNA near the gold bead. During the transcription
, the DNA "slides" on the RNA polymerase so the distance between the RNA polymerase and the gold bead (the tether length)is increased. Using an optical microscope
the area that the bead moves in was detected. The transcription rate was extracted from data.
Since then, a lot of TPM experiments have been done, and the method was improved in many ways such as beads types, biochemstry techniques, imaging (faster cameras, different microscopy methods etc.) data analysis and combination with other single-molecule techniques (e.g. optical or magnetical tweezers).
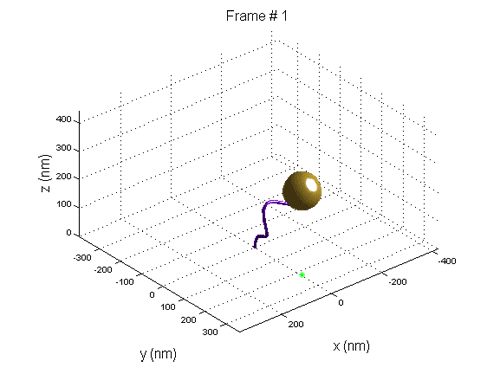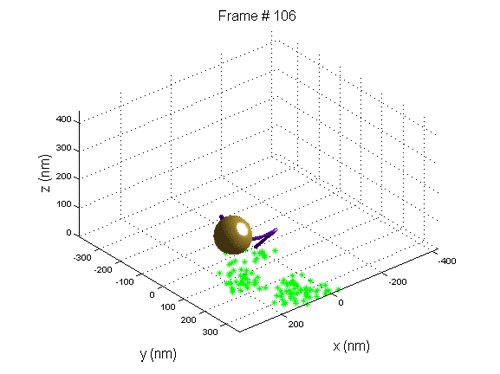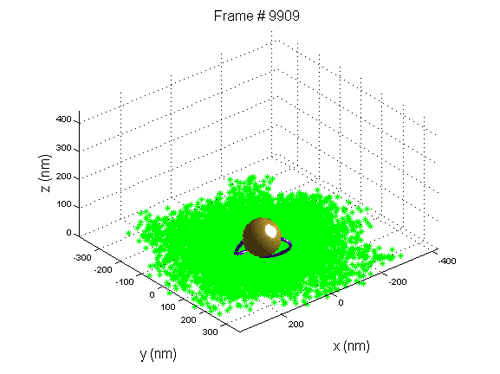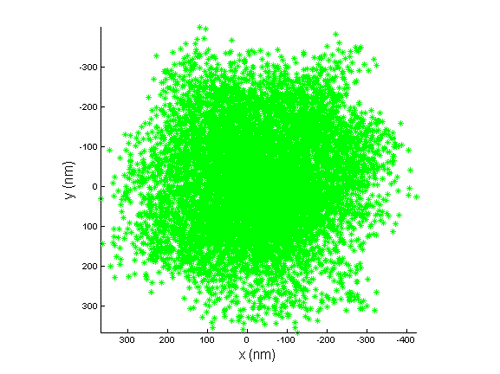
Both the polymer and the bead stay in an aqueous environment, so the bead moves in Brownian motion
. Because of the tether, the motion is restricted. Using an optical microscope
and CCD camera, one can track the bead position in a time series. Although the bead is usually smaller than the diffraction limit, so the image is a spot which is larger than the bead itself (point spread function
), the center of the spot represents the projection on the X-Y plane of the end of the polymer (end-to-end vector
). Analyzing the distribution of the bead position can tell us a lot of information about the polymer.
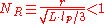
where is the bead radius,
is the bead radius,  is the contour length
is the contour length
of the polymer and is the persistence length
is the persistence length
(50 nm in physiological conditions) of the polymer. (It is possible to work also when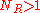 , but it should be treated carefully.)
, but it should be treated carefully.)
All of the bead types and diameters (with the biochemistry marker, look at the tether assembly section) are manufactured by commercial companies, and can purchased easily.
Next, the surface should be coated with an antibody or other reactive molecule (such as anti-digoxigenin
) that will bind to an antigen (digoxigenin
) at one end of the polymer. After an incubation of about 45min, the excess antibody has to be washed away.
After washing the excess antibody, the polymer should be injected into the chip and incubated for about the same time. The polymer had been modified before at the ends. One end has a biotin tail and the other has a digoxigenin tail. After incubation, unbound polymer has to be washed out from the cell. Then, anti-biotin
coated beads should be injected to the flowcell and incubate for about 30-45min. Excess beads should be washed out.
). In addition, the pixel
size on the camera may reduce the resolution of the measure.
In order to extract the exact bead's position (that corresponds to the end-to-end vector), the center of the spot should be found as accurate as possible. It can be done with good resolution using two different techniques, both based on spot characteristics. The light intensity in the focal plane distributed as airy disk, and has circular symmetry.
Gaussian fitting: A 2-dimensional Gaussian function is a good approximation for airy disk. By fitting this function to the spot one can find the parameters and
and 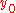 that are the coordinates of the center of the spot, and of the end-to-end vector.
that are the coordinates of the center of the spot, and of the end-to-end vector.
"Center of mass": The second technique is to find the center of intensity, using the definition of center of mass
:

where is the center of mass coordinate,
is the center of mass coordinate, 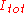 is the total intensity of the spot, and
is the total intensity of the spot, and 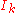 and
and  are the intensity and coordinate of the k-th pixel. Because of the circular symmetry, the coordinate of the center of intensity is the coordinate of the center of the bead.
are the intensity and coordinate of the k-th pixel. Because of the circular symmetry, the coordinate of the center of intensity is the coordinate of the center of the bead.
Both techniques give us the coordinate of the end-to-end vector in a resolution better than pixel size.
Frequency: The Brownian motion frequency is much larger than the drift frequency, so one can use high-pass filter
in order to remove the drift. Similar effect can achieve by smoothing the data, and subtraction of the smoothed from the data (see figure).
Averaging over few beads: If few beads are shown in the frame, because every bead moving randomly, averaging over the position of them for every frame should give us the drift (it should subtracted from the data for having clean data).
Immobilized bead: If an immobilized bead is shown in the frame, we can take its position as a reference, and correct the data by the immobilized bead's position. (Another advantage of looking at immobilized bead, is the fact that the motion of it can tell us about the accuracy of the measure.)
Of course one can use more than one method.
statistics to the end-to-end vector of the polymer. For 1-dimensional we'll get the Normal distribution, and for 2-dimensional the Rayleigh distribution:
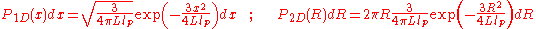
where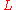 is the contour length and
is the contour length and 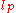 is the persistence length.
is the persistence length.
After collecting the data of time series, one should fitting the histogram
of the data to the distribution function (one or two dimensional). If the contour length of the polymer is known, the only fitting parameter is the persistence length.
, the polymer acts like Hookian spring. According to Boltzmann distribution
, the distribution is proprtional to exponent of the ratio between the elastic energy
and the thermal energy
:

where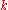 is the spring constant,
is the spring constant, 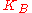 is Boltzmann constant and
is Boltzmann constant and  is the temperature. By taking the logarithm
is the temperature. By taking the logarithm
of the distribution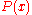 and fitting it to a parabola
and fitting it to a parabola
shape, one can get the spring constant of the polymer:
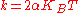
where is the coefficient of
is the coefficient of 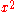 from the parabola fit.
from the parabola fit.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
and their interaction with other entities such as proteins.

TPM is a single molecule experiment method.
History
TPM was first introduced by Schafer, Gelles, Sheetz and Landick in 1991. In their research, they attached RNA polymeraseRNA polymerase
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that produces RNA. In cells, RNAP is needed for constructing RNA chains from DNA genes as templates, a process called transcription. RNA polymerase enzymes are essential to life and are found in all organisms and many viruses...
to the surface, and gold beads were attached to one end of the DNA molecules. In the beginning, the RNA polymerase "captures" the DNA near the gold bead. During the transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
, the DNA "slides" on the RNA polymerase so the distance between the RNA polymerase and the gold bead (the tether length)is increased. Using an optical microscope
Optical microscope
The optical microscope, often referred to as the "light microscope", is a type of microscope which uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small samples. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly designed in their present compound form in the...
the area that the bead moves in was detected. The transcription rate was extracted from data.
Since then, a lot of TPM experiments have been done, and the method was improved in many ways such as beads types, biochemstry techniques, imaging (faster cameras, different microscopy methods etc.) data analysis and combination with other single-molecule techniques (e.g. optical or magnetical tweezers).
Principle of the method
One end of a polymer is attached to a small bead (tens to hundreds of nanometer), while the other end is attached to a surface.Both the polymer and the bead stay in an aqueous environment, so the bead moves in Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
. Because of the tether, the motion is restricted. Using an optical microscope
Optical microscope
The optical microscope, often referred to as the "light microscope", is a type of microscope which uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small samples. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly designed in their present compound form in the...
and CCD camera, one can track the bead position in a time series. Although the bead is usually smaller than the diffraction limit, so the image is a spot which is larger than the bead itself (point spread function
Point spread function
The point spread function describes the response of an imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is a system's impulse response, the PSF being the impulse response of a focused optical system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob...
), the center of the spot represents the projection on the X-Y plane of the end of the polymer (end-to-end vector
End-to-end vector
In the physical chemistry study of polymers, the end-to-end vector is the vector that points from one end of a polymer to the other end.The norm of the end-to-end vector is called the end-to-end distance....
). Analyzing the distribution of the bead position can tell us a lot of information about the polymer.

Excursion number
In order that the motion would be polymer dominated, and not bead dominated, one should notice that the excursion number will be less than 1: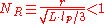
where
 is the bead radius,
is the bead radius, 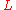 is the contour length
is the contour lengthContour length
Contour length is a term used in molecular physics. The contour length of a polymer chain is its length at maximum physically possible extension....
of the polymer and
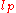 is the persistence length
is the persistence lengthPersistence length
The persistence length is a basic mechanical property quantifying the stiffness of a polymer or of a string.Informally, for pieces of the polymer that are shorter than the persistence length, the molecule behaves rather like a flexible elastic rod, while for pieces of the polymer that are much...
(50 nm in physiological conditions) of the polymer. (It is possible to work also when
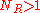 , but it should be treated carefully.)
, but it should be treated carefully.)Bead types
- Metal beads: The metallic beads (usually gold) scatter light with high intensity, so one can use very small beads (~40 nm diameter), and still have a good picture. From the other hand, metallic beads are not the appropriate tool for optical tweezersOptical tweezersOptical tweezers are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to provide an attractive or repulsive force , depending on the refractive index mismatch to physically hold and move microscopic dielectric objects...
experiments. - Polystyrene beads: The polystyrenePolystyrenePolystyrene ) also known as Thermocole, abbreviated following ISO Standard PS, is an aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon that is manufactured from petroleum by the chemical industry...
bead scatter light weaker than metallic (in order to get the same intensity as getting from 40 nm gold bead, the polystyrene bead should be ~125 nm!), but it has the advantage that it can be combined with optical tweezers experiments. - Fluorospheres: The major advantage of fluorospheres is that the excitation wavelengthWavelengthIn physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
and the emission wavelength are not the same, so dichroic filterDichroic filterA dichroic filter, thin-film filter, or interference filter is a very accurate color filter used to selectively pass light of a small range of colors while reflecting other colors. By comparison, dichroic mirrors and dichroic reflectors tend to be characterized by the color of light that they...
can be used to give a cleaner signal. The disadvantage of the fluorospheres is photobleachingPhotobleachingPhotobleaching is the photochemical destruction of a fluorophore. In microscopy, photobleaching may complicate the observation of fluorescent molecules, since they will eventually be destroyed by the light exposure necessary to stimulate them into fluorescing...
.
All of the bead types and diameters (with the biochemistry marker, look at the tether assembly section) are manufactured by commercial companies, and can purchased easily.
Chip assembly
A chip can be made of two coverslips. One of them should be drilled to make two hole, allowing the reagents to be injected into the flowcell. The slides should be cleaned to remove dirt. A bath sonicator is a good tool for that, 15 minutes in Isopropanol should do the trick. Next, the a channel should be made. One way of doing so is to cut parafilm in the center, leaving a frame of parafilm that would be used as a spacer between the slides. The slides should be assembled one on the other with the cut parafilm between them. The final step is to heat the chip so that the parafilm will melt and glue the slides together.Tether Assembly
First, the chip has to be passivated so that the polymer won't stick to the glass, there are plenty of blocking reagents available (BSA, alpha-casein, etc.) and one should find what works best for the specific situationNext, the surface should be coated with an antibody or other reactive molecule (such as anti-digoxigenin
Digoxigenin
Digoxigenin is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants Digitalis purpurea, Digitalis orientalis and Digitalis lanata , where it is attached to sugars, to form the glycosides Digoxigenin (DIG) is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants...
) that will bind to an antigen (digoxigenin
Digoxigenin
Digoxigenin is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants Digitalis purpurea, Digitalis orientalis and Digitalis lanata , where it is attached to sugars, to form the glycosides Digoxigenin (DIG) is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants...
) at one end of the polymer. After an incubation of about 45min, the excess antibody has to be washed away.
After washing the excess antibody, the polymer should be injected into the chip and incubated for about the same time. The polymer had been modified before at the ends. One end has a biotin tail and the other has a digoxigenin tail. After incubation, unbound polymer has to be washed out from the cell. Then, anti-biotin
Biotin
Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring...
coated beads should be injected to the flowcell and incubate for about 30-45min. Excess beads should be washed out.
Data Analysis
Tracking
As mentioned above, the image doesn't show the bead itself but a larger spot according to its PSF (Point spread functionPoint spread function
The point spread function describes the response of an imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is a system's impulse response, the PSF being the impulse response of a focused optical system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob...
). In addition, the pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
size on the camera may reduce the resolution of the measure.
In order to extract the exact bead's position (that corresponds to the end-to-end vector), the center of the spot should be found as accurate as possible. It can be done with good resolution using two different techniques, both based on spot characteristics. The light intensity in the focal plane distributed as airy disk, and has circular symmetry.
Gaussian fitting: A 2-dimensional Gaussian function is a good approximation for airy disk. By fitting this function to the spot one can find the parameters
 and
and 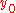 that are the coordinates of the center of the spot, and of the end-to-end vector.
that are the coordinates of the center of the spot, and of the end-to-end vector."Center of mass": The second technique is to find the center of intensity, using the definition of center of mass
Center of mass
In physics, the center of mass or barycenter of a system is the average location of all of its mass. In the case of a rigid body, the position of the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body...
:

where
 is the center of mass coordinate,
is the center of mass coordinate, 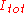 is the total intensity of the spot, and
is the total intensity of the spot, and 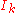 and
and  are the intensity and coordinate of the k-th pixel. Because of the circular symmetry, the coordinate of the center of intensity is the coordinate of the center of the bead.
are the intensity and coordinate of the k-th pixel. Because of the circular symmetry, the coordinate of the center of intensity is the coordinate of the center of the bead.Both techniques give us the coordinate of the end-to-end vector in a resolution better than pixel size.
Drift correction
Usually, the whole system drifts during the measuring. There are several methods to correct the drift, generally these can divided into 3 groups:Frequency: The Brownian motion frequency is much larger than the drift frequency, so one can use high-pass filter
High-pass filter
A high-pass filter is a device that passes high frequencies and attenuates frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system...
in order to remove the drift. Similar effect can achieve by smoothing the data, and subtraction of the smoothed from the data (see figure).
Averaging over few beads: If few beads are shown in the frame, because every bead moving randomly, averaging over the position of them for every frame should give us the drift (it should subtracted from the data for having clean data).
Immobilized bead: If an immobilized bead is shown in the frame, we can take its position as a reference, and correct the data by the immobilized bead's position. (Another advantage of looking at immobilized bead, is the fact that the motion of it can tell us about the accuracy of the measure.)
Of course one can use more than one method.
Polymer characterization
It is common to fit random walkRandom walk
A random walk, sometimes denoted RW, is a mathematical formalisation of a trajectory that consists of taking successive random steps. For example, the path traced by a molecule as it travels in a liquid or a gas, the search path of a foraging animal, the price of a fluctuating stock and the...
statistics to the end-to-end vector of the polymer. For 1-dimensional we'll get the Normal distribution, and for 2-dimensional the Rayleigh distribution:
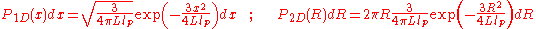
where
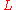 is the contour length and
is the contour length and 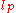 is the persistence length.
is the persistence length.After collecting the data of time series, one should fitting the histogram
Histogram
In statistics, a histogram is a graphical representation showing a visual impression of the distribution of data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable and was first introduced by Karl Pearson...
of the data to the distribution function (one or two dimensional). If the contour length of the polymer is known, the only fitting parameter is the persistence length.
Spring constant
Due to entropic forceEntropic force
In physics, an entropic force acting in a system is a phenomenological force resulting from the entire system's statistical tendency to increase its entropy, rather than from a particular underlying microscopic force.-Polymers:...
, the polymer acts like Hookian spring. According to Boltzmann distribution
Boltzmann distribution
In chemistry, physics, and mathematics, the Boltzmann distribution is a certain distribution function or probability measure for the distribution of the states of a system. It underpins the concept of the canonical ensemble, providing its underlying distribution...
, the distribution is proprtional to exponent of the ratio between the elastic energy
Elastic energy
Elastic energy is the potential mechanical energy stored in the configuration of a material or physical system as work is performed to distort its volume or shape....
and the thermal energy
Thermal energy
Thermal energy is the part of the total internal energy of a thermodynamic system or sample of matter that results in the system's temperature....
:

where
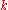 is the spring constant,
is the spring constant, 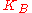 is Boltzmann constant and
is Boltzmann constant and  is the temperature. By taking the logarithm
is the temperature. By taking the logarithmLogarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of the distribution
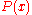 and fitting it to a parabola
and fitting it to a parabolaParabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
shape, one can get the spring constant of the polymer:
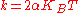
where
 is the coefficient of
is the coefficient of 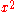 from the parabola fit.
from the parabola fit.Advantage
- Simple setup system.
- Not expensive.
- Observations are made in the polymer's natural environment (no external forces are being used).
- Suitable to various microscopy method (e.g. TIRFM, Dark field, Differential interference contrast microscopyDifferential interference contrast microscopyDifferential interference contrast microscopy , also known as Nomarski Interference Contrast or Nomarski microscopy, is an optical microscopy illumination technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained, transparent samples...
, etc.). - Can be combined and manipulated using other methods.
- High variety of applications.

