
Taxation in New Zealand
Encyclopedia
Taxation in New Zealand is collected at a national level by the Inland Revenue Department (IRD)
Inland Revenue Department (New Zealand)
Inland Revenue , previously known as the Inland Revenue Department, is the New Zealand government department responsible for the collection of over 80% of the Crown's revenue in New Zealand. It also collects and disburses social support programme payments and provides the government with policy...
on behalf of the Government of New Zealand. National taxes are levied on personal and business income, as well as on the supply of goods and services. There is no capital gains tax although certain "gains" such as profits on the sale of patent rights are deemed to be income. Local property taxes (rates
Rates (tax)
Rates are a type of property tax system in the United Kingdom, and in places with systems deriving from the British one, the proceeds of which are used to fund local government...
) are managed and collected by councils. Some goods and services carry a specific tax, referred to as an excise or a duty
Excise
Excise tax in the United States is a indirect tax on listed items. Excise taxes can be and are made by federal, state and local governments and are far from uniform throughout the United States...
such as alcohol excise or gaming duty. These are collected by a range of government agencies such as the New Zealand Customs Service
New Zealand Customs Service
The Customs Service is a state sector organisation of New Zealand whose role is to provide border control and protect the community from potential risks arising from international trade and travel, as well as collecting duties and taxes on imports to the country. New Zealand's Minister of Customs...
. There is no Social Security (Payroll) tax in New Zealand.
New Zealand went through a major program of tax reform
Tax reform
Tax reform is the process of changing the way taxes are collected or managed by the government.Tax reformers have different goals. Some seek to reduce the level of taxation of all people by the government. Some seek to make the tax system more progressive or less progressive. Some seek to simplify...
in the 1980s. The top marginal rate of income tax was reduced from 66% to 33% (increased to 39% in April 2000, 38% in April 2009 and 33% on 1 October 2010) and corporate income tax rate from 48% to 33% (reduced to 30% in 2008 and to 28% on 1 October 2010). Goods and services tax
Value added tax
A value added tax or value-added tax is a form of consumption tax. From the perspective of the buyer, it is a tax on the purchase price. From that of the seller, it is a tax only on the "value added" to a product, material or service, from an accounting point of view, by this stage of its...
was introduced, initially at a rate of 10% (then 12.5% and now 15% as [of 1 October 2010]). An OECD report in 2001 described the New Zealand tax system as one of the most neutral and efficient within its membership.
Tax reform continues in New Zealand. Here are some issues:
- business taxes and the effect on productivity and competitiveness of NZ companies
- differences in the treatment of various types of investment income
- international tax rules
Individual income tax
New Zealand residents are liable for tax on their worldwide taxable incomeTaxable income
Taxable income refers to the base upon which an income tax system imposes tax. Generally, it includes some or all items of income and is reduced by expenses and other deductions. The amounts included as income, expenses, and other deductions vary by country or system. Many systems provide that...
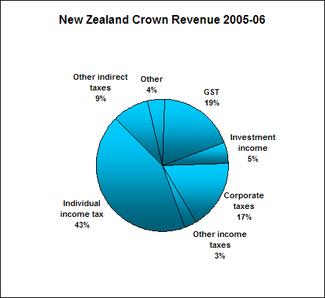
. In 2005–06, 43% of the New Zealand Government's core revenue ($22.9bn) came from individuals' income taxes.
Types of taxable income
- salary and wages
- business and self-employedSelf-employmentSelf-employment is working for one's self.Self-employed people can also be referred to as a person who works for himself/herself instead of an employer, but drawing income from a trade or business that they operate personally....
income - income from investments (interestInterestInterest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money, or money earned by deposited funds....
, dividends etc.) - rental income
- overseas income (including income from an overseas pension)
Tax rates
Income tax varies dependent on income levels in any specific tax year (personal tax years run from 1 April to 31 March).2009–2010
| Income | Tax rate |
|---|---|
| $0 – $14,000 | 12.5% |
| $14,001 – $48,000 | 21% |
| $48,001 – $70,000 | 33% |
| Over $70,000 | 38% |
| No-notification rate | 45% |
Rates are for the tax year 1 April 2009 to 31 March 2010, and are based on tax code M (primary income without student loan).
In New Zealand, the income is taxed by the amount that falls within each tax bracket. For example, if persons who earn $70,000 will pay only 33% on the amount that falls between $48,001 and $70,000 rather than paying on the full $70,000. Consequently, the corresponding income tax for that specific income will accumulate to $16,150—about 23% of the entire amount.
New Rates from October 2010
On 20 May 2010 the Government announced new income tax rates that came into effect on 1 October 2010. The new lower tax rates aimed to stimulate productivity in the economy and meant that people earning the average wage in New Zealand pay lower effective tax rates than people in Australia and the United Kingdom, an attempt to ease concerns about economic emigration.| Income | Tax rate | Composite Rate |
|---|---|---|
| $0 – $14,000 | 10.5% | |
| $14,001 – $48,000 | 17.5% | |
| $48,001 – $70,000 | 30% | |
| Over $70,000 | 33% | |
| No-notification rate | 45% |
As employee deductions are filed by employers to the IRD monthly, income earned in April to September are taxed at the old tax rate, and income earned in October to March is taxed at the new rate.
Tax credits
The amount of tax actually payable can be reduced by claiming tax credits, e.g. for donations, childcare and housekeeper, independent earners, payroll donations, income under $9,880, and children.Tax deducted at source
In most cases employers deduct the relevant amount of income tax from salary and wages prior to these being paid to the individual. This system, known as pay-as-you-earn, or PAYEPAYE
Pay as you earn or PAYE refers to a system of withholding of income tax from payments to employees. Amounts withheld are treated as advance payments of income tax due. They are refundable to the extent they exceed tax as determined on tax returns. PAYE may also refer to withholding of the...
, was introduced in 1958, prior to which employees paid tax annually.
In addition, banks and other financial institutions deduct the relevant amount of income tax on interest
Interest
Interest is a fee paid by a borrower of assets to the owner as a form of compensation for the use of the assets. It is most commonly the price paid for the use of borrowed money, or money earned by deposited funds....
and dividends as these are earned. This is known as Residents Withholding Tax.
At the end of each tax year, individuals who may not have paid the correct amount of income tax are required to submit a personal tax summary, to allow the IRD to calculate any under or overpayment of tax made during the year.
Double taxation agreements
Individuals who are tax residentTax residence
Definitions of residence for tax purposes vary considerably from state to state. For individuals, physical presence in a state is an important factor. Some states also determine residency of an individual by reference to a variety of other factors, such as the ownership of a home or availability...
in more than one country may be liable to pay tax more than once on the same income. New Zealand has double taxation
Double taxation
Double taxation is the systematic imposition of two or more taxes on the same income , asset , or financial transaction . It refers to taxation by two or more countries of the same income, asset or transaction, for example income paid by an entity of one country to a resident of a different country...
agreements with various countries that set out which country will tax specific types of income.
| Australia | Indonesia | Sweden |
| Belgium | Ireland | Switzerland |
| Canada | Italy | Taiwan |
| China | Japan | Thailand |
| Denmark | Malaysia | The Netherlands |
| Fiji | Norway | The Philippines |
| Finland | Republic of Korea | United Arab Emirates |
| France | Russian Federation | United Kingdom |
| Germany | Singapore | United States |
| India | South Africa | Mexico |
| Austria | Poland | Spain |
| Chile |
Some agreements protect pension payments as well. The agreement with the United States, for example, prohibits New Zealand from taxing American social security or government pension payments, and the reverse is also true.
ACC earner's levy
All employees pay an earner's levy to cover the cost of non-work related injuries. It is collected by Inland Revenue on behalf of the Accident Compensation CorporationAccident Compensation Corporation
The Accident Compensation Corporation is a New Zealand Crown entity responsible for administering the Accident Compensation Act 2001. The Act provides support to citizens, residents, and temporary visitors who have suffered personal injuries....
(ACC).
The earner's levy is payable on salary and wages plus any other income that is subject to PAYE
PAYE
Pay as you earn or PAYE refers to a system of withholding of income tax from payments to employees. Amounts withheld are treated as advance payments of income tax due. They are refundable to the extent they exceed tax as determined on tax returns. PAYE may also refer to withholding of the...
, for example overtime, bonuses or holiday pay. The levy is 2.04% for the year from 1 April 2010 to 31 March 2011. It is payable on income up to $110,018.
Business income tax
Businesses in New Zealand pay income tax on their net profit earned in any specific tax year. For most businesses the tax year runs from 1 April to 31 March but businesses can apply to the IRD for this to be changed.A provisional tax payer is a person or a company that had a residual income tax of more than $2500 in the previous financial year. There are three options for paying provisional tax; standard method, estimated method and GST Ratio option.
- Under the standard method provisional tax payers make three provisional tax instalments through the year based on the previous years tax liability.
- The standard method is the most common method. However a provisional tax payer can choose to estimate their provisional tax payments. Estimation allows the business owner pay to less or more tax depending on how they think their business is performing. Any under or overpayment is subject to interest so it is important that they can estimate their profit accurately.
- A provisional tax payer can also pay provisional tax using the GST ratio option. This is based on what your previous year’s residual tax liability was and what your GST Taxable supplies were for that year. You then apply this percentage to your current period GST return. Under this option you pay provisional tax at the same time as you pay GST.
At the end of the year the business files a tax return (due on the following 7 July for businesses with a tax year ending 31 March) and any under or overpayment is then calculated.
Companies pay income tax at 28% on profits. Tax rates for individuals operating as a business (that is, individuals who are self-employed
Self-employment
Self-employment is working for one's self.Self-employed people can also be referred to as a person who works for himself/herself instead of an employer, but drawing income from a trade or business that they operate personally....
) are the same as for employees. (See individual tax rates, above.)
Goods and Services Tax
Goods and services tax (GST) is an indirect taxIndirect tax
The term indirect tax has more than one meaning.In the colloquial sense, an indirect tax is a tax collected by an intermediary from the person who bears the ultimate economic burden of the tax...
introduced in New Zealand in 1986. This represented a major change in New Zealand taxation policy as until this point almost all revenue had been raised via direct taxes. GST now makes up 19% of the New Zealand Government's core revenue.
Most products
Product (business)
In general, the product is defined as a "thing produced by labor or effort" or the "result of an act or a process", and stems from the verb produce, from the Latin prōdūce ' lead or bring forth'. Since 1575, the word "product" has referred to anything produced...
or services sold in New Zealand incur GST at a rate of 15%. The main exceptions are financial services
Financial services
Financial services refer to services provided by the finance industry. The finance industry encompasses a broad range of organizations that deal with the management of money. Among these organizations are credit unions, banks, credit card companies, insurance companies, consumer finance companies,...
(e.g. banking and life insurance) and the export of goods and services overseas.
All businesses are required to register for GST once their turnover
Revenue
In business, revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. In many countries, such as the United Kingdom, revenue is referred to as turnover....
exceeds (or is likely to exceed) $60,000 per annum. Once registered, businesses charge GST on all goods and services they supply and can reclaim any GST they have been charged on goods and services they have purchased.
Fringe Benefit Tax
Employers are liable to pay Fringe benefitEmployee benefit
Employee benefits and benefits in kind are various non-wage compensations provided to employees in addition to their normal wages or salaries...
tax (FBT) on benefits given to employees in addition to their salary or wages (e.g. motor vehicles or low interest loans)
There are several methods available for calculating FBT liability, including an option of paying a flat rate of 64% on all benefits provided.
Excise Duties
In New Zealand, excise or dutyExcise
Excise tax in the United States is a indirect tax on listed items. Excise taxes can be and are made by federal, state and local governments and are far from uniform throughout the United States...
is charged on a number of products, including alcohol products, tobacco products, and some fuels.
The rates for alcohol products are as follows:
| Product | Alcohol content | Rate |
| Beer | More than 1.15%, but not more than 2.5% | 39.025¢ per litre |
| More than 2.5% | $26.021 per litre of alcohol | |
| Wine (of fresh grapes) | Not more than 14% | $2.6021 per litre |
| More than 14% | $47.392 per litre of alcohol | |
| Other fermented beverages (such as cider, perry, mead), spirits, spirituous beverages, liquers, cordials and ice cream | More than 1.15% but not more than 2.5% | 39.025¢ per litre |
| More than 2.5%, but not more than 6% | $26.021 per litre of alcohol | |
| More than 6%, but not more than 9% | $2.0816 per litre | |
| More than 9%, but not more than 14% | $2.6021 per litre | |
| More than 14% | $47.392 per litre of alcohol |
There are also excise duties on tobacco products, with a rate of $294.62 per thousand cigarettes, and $368.72 per kilo of tobacco, on other tobacco products.
The excise duties on fuel are 42.524¢ per litre (plus 8¢ per gram of lead) on motor fuel, 30.2¢ per litre on Methanol and 10.4¢ per litre on Liquified petroleum gas. Compressed natural gas has an excise of $3.17 per gigajoule.
See also
- Dividend taxDividend taxA dividend tax is an income tax on dividend payments to the stockholders of a company.-Collection:In many jurisdictions, the government requires the company to withhold at least the standard tax, paying this to the national revenue authorities and paying out only the balance to the...
- Fiscal neutrality
- International taxationInternational taxationInternational taxation is the study or determination of tax on a person or business subject to the tax laws of different countries or the international aspects of an individual country's tax laws. Governments usually limit the scope of their income taxation in some manner territorially or provide...
- Laffer curveLaffer curveIn economics, the Laffer curve is a theoretical representation of the relationship between government revenue raised by taxation and all possible rates of taxation. It is used to illustrate the concept of taxable income elasticity . The curve is constructed by thought experiment...
and the optimal tax rate argument - Tax incidenceTax incidenceIn economics, tax incidence is the analysis of the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Tax incidence is said to "fall" upon the group that, at the end of the day, bears the burden of the tax...
- Tax avoidance/evasion
- Tax resistanceTax resistanceTax resistance is the refusal to pay tax because of opposition to the government that is imposing the tax or to government policy.Tax resistance is a form of civil disobedience and direct action...
- Tax havenTax havenA tax haven is a state or a country or territory where certain taxes are levied at a low rate or not at all while offering due process, good governance and a low corruption rate....
- Tax lawTax lawTax law is the codified system of laws that describes government levies on economic transactions, commonly called taxes.-Major issues:Primary taxation issues facing the governments world over include;* taxes on income and wealth...

