
T-70
Encyclopedia
The T-70 was a light tank
used by the Red Army
during World War II
, replacing both the T-60
scout tank
for reconnaissance
and the T-50
light infantry tank for infantry
support. The T-80 light tank was a more advanced version of the T-70 with a two-man turret—it was only produced in very small numbers when light tank production was abandoned. The T-90 self-propelled anti-aircraft gun was a prototype vehicle with twin machine guns, based on the T-70 chassis.
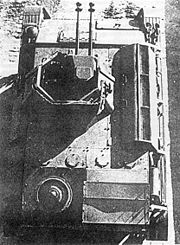
The T-70 was armed with a 45-mm L/46 gun Model 38 with forty-five rounds carried, and a coaxial 7.62-mm DT machine gun. The tank was operated by a driver and a commander who loaded and fired the gun. Armour thickness on the turret front was 60 mm, hull front and sides: 45 mm, rear and turret sides: 35 mm, roof and bottom: 10 mm.
s were considered inadequate by the Red Army, unable to keep up with the T-34
medium tank and unable to penetrate the armour of most German tanks, but they could be produced by small factories which were unable to handle the large components of medium and heavy tanks. The T-70 was an attempt to remedy some of the shortcomings of the T-60 scout tank, which had very poor cross-country mobility, thin armour, and an inadequate 20-mm gun. It also replaced the very short production run of the T-50
light infantry tank, which was more sophisticated, but also much too complicated and expensive to produce.
The T-70 was designed by Nicholas Astrov's design team at Factory No. 38 in Kirov
.
The first batch of T-70s were built with a GAZ-202 automotive engine on each side of the hull, one driving each track
. This arrangement was seen to be a serious problem, even before the first tanks were issued. It was quickly redesigned as the T-70M (although it continued to be referred to as just T-70), with the engines in-line on the right side of the tank and a normal transmission and differential. The conical turret was replaced by one more easily welded out of plate armour, and moved to the left side of the hull.
Curiously, even after the T-70's production line was redesigned, SU-76
self-propelled guns started to be built with the same unsatisfactory unsynchronized two-engine layout, and all of them were later recalled for factory rebuilding as SU-76Ms.
T-70s were put into production in March 1942 at Zavod No. 37, and along with T-60 production at GAZ
and Zavod No. 38. They completely replaced T-60 production in September 1942, although that tank remained in use until the end of the war. Production ended in October 1943, with 8,226 vehicles completed.
In April 1942, the conical turrets on early-production machines were replaced with new welded turrets. The end of the T-70's production run was built with two 85-hp GAZ-203 engines, a Mark 4
commander's periscope
replacing a vision slit, and other improvements.
The T-70 remained in service until 1948.

 The one-man turret of the Soviet light tanks made co-ordinating a tank platoon nearly impossible, because the commanders were kept busy acquiring targets, loading and firing the main gun and machine gun, and commanding their drivers.
The one-man turret of the Soviet light tanks made co-ordinating a tank platoon nearly impossible, because the commanders were kept busy acquiring targets, loading and firing the main gun and machine gun, and commanding their drivers.
The infantry tank
role was already considered obsolete. The SU-76 self-propelled gun was better suited for infantry support, its 76.2-mm gun capable of firing a larger high explosive shell
. Industrial resources could be redirected from light tanks to building SU-76s.
In an attempt to compensate, the T-80 light tank was designed, a more robust version of the T-70 with a two-man turret
. But there was enough lend-lease
equipment available to fulfill the reconnaissance role of the light tanks, and armoured cars were better suited for light scouting and liaison. All light tank production was cancelled in October 1943, after only about 120 T-80s were built. No further light tanks would be built during the war.
In November 1943 Red Army tank units were reorganized: light tanks were replaced by the T-34 and new T-34-85, which started production the following month. Light tanks continued to be used in self-propelled artillery and some other units.
The Soviets did start development work on an amphibious
light tank in 1945, resulting in the post-war PT-76
, introduced in 1954.
 The Soviet Union lacked self-propelled anti-aircraft guns
The Soviet Union lacked self-propelled anti-aircraft guns
at the beginning of World War II. The first serious design of a real air-defence vehicle was in 1942, when a twin 12.7 mm DShK machine gun turret with optical sights was built for mounting on the T-60 scout tank. The T-70 became available in the meantime, and was adopted as the basis for the T-90 self-propelled anti-aircraft gun. The program was cancelled in 1943, in favour of the ZSU-37
37 mm self-propelled anti-aircraft gun, built on an SU-76 chassis (Zaloga & Grandsen 1984:119). The ZSU-37 used the cannon developed for the M1939
towed carriage.
Light tank
A light tank is a tank variant initially designed for rapid movement, and now primarily employed in low-intensity conflict. Early light tanks were generally armed and armored similar to an armored car, but used tracks in order to provide better cross-country mobility.The light tank was a major...
used by the Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, replacing both the T-60
T-60
The T-60 scout tank was a light tank produced by the Soviet Union from 1941 to 1942. In this time over 6,292 were built. The tank was designed to replace the obsolete T-38 amphibious scout tank.-Design:...
scout tank
Tank
A tank is a tracked, armoured fighting vehicle designed for front-line combat which combines operational mobility, tactical offensive, and defensive capabilities...
for reconnaissance
Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance is the military term for exploring beyond the area occupied by friendly forces to gain information about enemy forces or features of the environment....
and the T-50
T-50 tank
The T-50 light infantry tank was built by the Soviet Union at the beginning of World War II. The design for this vehicle had some advanced features, but was complicated and expensive, and only a short production run of 69 tanks was completed...
light infantry tank for infantry
Infantry
Infantrymen are soldiers who are specifically trained for the role of fighting on foot to engage the enemy face to face and have historically borne the brunt of the casualties of combat in wars. As the oldest branch of combat arms, they are the backbone of armies...
support. The T-80 light tank was a more advanced version of the T-70 with a two-man turret—it was only produced in very small numbers when light tank production was abandoned. The T-90 self-propelled anti-aircraft gun was a prototype vehicle with twin machine guns, based on the T-70 chassis.
The T-70 was armed with a 45-mm L/46 gun Model 38 with forty-five rounds carried, and a coaxial 7.62-mm DT machine gun. The tank was operated by a driver and a commander who loaded and fired the gun. Armour thickness on the turret front was 60 mm, hull front and sides: 45 mm, rear and turret sides: 35 mm, roof and bottom: 10 mm.
Production history
By 1942, light tankLight tank
A light tank is a tank variant initially designed for rapid movement, and now primarily employed in low-intensity conflict. Early light tanks were generally armed and armored similar to an armored car, but used tracks in order to provide better cross-country mobility.The light tank was a major...
s were considered inadequate by the Red Army, unable to keep up with the T-34
T-34
The T-34 was a Soviet medium tank produced from 1940 to 1958. Although its armour and armament were surpassed by later tanks of the era, it has been often credited as the most effective, efficient and influential design of World War II...
medium tank and unable to penetrate the armour of most German tanks, but they could be produced by small factories which were unable to handle the large components of medium and heavy tanks. The T-70 was an attempt to remedy some of the shortcomings of the T-60 scout tank, which had very poor cross-country mobility, thin armour, and an inadequate 20-mm gun. It also replaced the very short production run of the T-50
T-50 tank
The T-50 light infantry tank was built by the Soviet Union at the beginning of World War II. The design for this vehicle had some advanced features, but was complicated and expensive, and only a short production run of 69 tanks was completed...
light infantry tank, which was more sophisticated, but also much too complicated and expensive to produce.
The T-70 was designed by Nicholas Astrov's design team at Factory No. 38 in Kirov
Kirov, Kirov Oblast
Kirov , formerly known as Vyatka and Khlynov, is a city in northeastern European Russia, on the Vyatka River, and the administrative center of Kirov Oblast. Population: -History:...
.
The first batch of T-70s were built with a GAZ-202 automotive engine on each side of the hull, one driving each track
Caterpillar track
Continuous tracks or caterpillar tracks are a system of vehicle propulsion in which modular metal plates linked into a continuous band are driven by two or more wheels...
. This arrangement was seen to be a serious problem, even before the first tanks were issued. It was quickly redesigned as the T-70M (although it continued to be referred to as just T-70), with the engines in-line on the right side of the tank and a normal transmission and differential. The conical turret was replaced by one more easily welded out of plate armour, and moved to the left side of the hull.
Curiously, even after the T-70's production line was redesigned, SU-76
SU-76
The SU-76 was a Soviet self-propelled gun used during and after World War II.- History :The SU-76 was based on a lengthened and widened version of the T-70 tank chassis...
self-propelled guns started to be built with the same unsatisfactory unsynchronized two-engine layout, and all of them were later recalled for factory rebuilding as SU-76Ms.
T-70s were put into production in March 1942 at Zavod No. 37, and along with T-60 production at GAZ
GAZ
GAZ or Gorkovsky Avtomobilny Zavod , translated as Gorky Automobile Plant , started in 1932 as NAZ, a cooperation between Ford and the Soviet Union. It is one of the largest companies in the Russian automotive industry....
and Zavod No. 38. They completely replaced T-60 production in September 1942, although that tank remained in use until the end of the war. Production ended in October 1943, with 8,226 vehicles completed.
In April 1942, the conical turrets on early-production machines were replaced with new welded turrets. The end of the T-70's production run was built with two 85-hp GAZ-203 engines, a Mark 4
Vickers Tank Periscope MK.IV
The Vickers Tank Periscope MK.IV, invented by Polish engineer Rudolf Gundlach, was first patented in 1936 as Gundlach Peryskop obrotowy. It was the first device to allow the tank commander to have a 360-degree view from his turret, with a single periscope...
commander's periscope
Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation from a concealed position. In its simplest form it consists of a tube with mirrors at each end set parallel to each other at a 45-degree angle....
replacing a vision slit, and other improvements.
The T-70 remained in service until 1948.
Decline of light tanks


The infantry tank
Infantry tank
The infantry tank was a concept developed by the British and French in the years leading up to World War II. Infantry tanks were tanks designed to support the infantry in the attack. To achieve this they were generally heavily armoured compared to the cruiser tanks, to allow them to operate in...
role was already considered obsolete. The SU-76 self-propelled gun was better suited for infantry support, its 76.2-mm gun capable of firing a larger high explosive shell
Shell (projectile)
A shell is a payload-carrying projectile, which, as opposed to shot, contains an explosive or other filling, though modern usage sometimes includes large solid projectiles properly termed shot . Solid shot may contain a pyrotechnic compound if a tracer or spotting charge is used...
. Industrial resources could be redirected from light tanks to building SU-76s.
In an attempt to compensate, the T-80 light tank was designed, a more robust version of the T-70 with a two-man turret
Turret
In architecture, a turret is a small tower that projects vertically from the wall of a building such as a medieval castle. Turrets were used to provide a projecting defensive position allowing covering fire to the adjacent wall in the days of military fortification...
. But there was enough lend-lease
Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease was the program under which the United States of America supplied the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, China, Free France, and other Allied nations with materiel between 1941 and 1945. It was signed into law on March 11, 1941, a year and a half after the outbreak of war in Europe in...
equipment available to fulfill the reconnaissance role of the light tanks, and armoured cars were better suited for light scouting and liaison. All light tank production was cancelled in October 1943, after only about 120 T-80s were built. No further light tanks would be built during the war.
In November 1943 Red Army tank units were reorganized: light tanks were replaced by the T-34 and new T-34-85, which started production the following month. Light tanks continued to be used in self-propelled artillery and some other units.
The Soviets did start development work on an amphibious
Amphibious vehicle
An amphibious vehicle , is a vehicle or craft, that is a means of transport, viable on land as well as on water – just like an amphibian....
light tank in 1945, resulting in the post-war PT-76
PT-76
The PT-76 is a Soviet amphibious light tank which was introduced in the early 1950s and soon became the standard reconnaissance tank of the Soviet Army and the other Warsaw Pact armed forces. It was widely exported to other friendly states, like India, Iraq, North Korea and North Vietnam. Overall,...
, introduced in 1954.
T-90 self-propelled anti-aircraft gun

Self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon
An anti-aircraft vehicle, also known as a self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon or self-propelled air defense system , is a mobile vehicle with a dedicated anti-aircraft capability...
at the beginning of World War II. The first serious design of a real air-defence vehicle was in 1942, when a twin 12.7 mm DShK machine gun turret with optical sights was built for mounting on the T-60 scout tank. The T-70 became available in the meantime, and was adopted as the basis for the T-90 self-propelled anti-aircraft gun. The program was cancelled in 1943, in favour of the ZSU-37
ZSU-37
ZSU-37 was a Soviet-made, light, self-propelled anti-aircraft gun , developed by the end of 1943 and produced at Works No. 40 in Mytishchi. It was the first Soviet series-produced tracked SPAAG...
37 mm self-propelled anti-aircraft gun, built on an SU-76 chassis (Zaloga & Grandsen 1984:119). The ZSU-37 used the cannon developed for the M1939
M1939 37 mm anti-aircraft gun
37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 was a Soviet 37 mm caliber anti-aircraft gun developed during the late 1930s and used during World War II. The land based version was replaced in Soviet service by the ZSU-57-2 during the 1950s. Guns of this type were successfully used throughout...
towed carriage.
External links
- T-70 Light Tanks at WWIIVehicles.com
- Specifications at WWIITanks.co.uk
- Photo gallery at svsm.org
- T-70 tanks, T-70 tanks in museum and monuments

