
Switched fabric
Encyclopedia
Switched fabric, switching fabric, or just fabric, is a network
topology
where network nodes connect with each other via one or more network switch
es (particularly via crossbar switch
es, hence the name). The term is popular in telecommunication
, Fibre Channel
storage area network
s and other high-speed networks, including InfiniBand
. The term is in contrast to a broadcast medium, such as early forms of Ethernet
.
Switched fabrics can offer better total throughput than broadcast networks, because traffic is spread across multiple physical links.
Similarly, some modern computers use a switched fabric, such as PCI Express
, HyperTransport
, or QuickPath, instead of a bus. Again, the advantage of the switched fabric is performance.
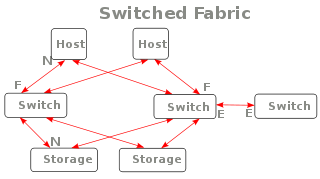 In the Fibre Channel switched fabric topology (called FC-SW), devices are connected to each other through one or more Fibre Channel switch
In the Fibre Channel switched fabric topology (called FC-SW), devices are connected to each other through one or more Fibre Channel switch
es. This topology allows the connection of up to the theoretical maximum of 16 million devices, limited only by the available address space (224).
Multiple switches in a fabric usually form a mesh network, with devices being on the "edges" ("leaves") of the mesh. While this topology has the best scalability
properties of the three FC topologies, it is also the most expensive, the only one requiring a costly fibre channel switch
.
Visibility among nodes in a fabric is typically controlled with zoning
.
Most Fibre Channel network designs employ two separate fabrics for redundancy
. The two fabrics share the edge nodes (devices), but are otherwise unconnected. One of the advantages of this topology is capability of failover
, meaning that in case one link breaks or a switch is out of order, datagram
s can use the second fabric.
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
topology
Network topology
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements of a computer or biological network....
where network nodes connect with each other via one or more network switch
Network switch
A network switch or switching hub is a computer networking device that connects network segments.The term commonly refers to a multi-port network bridge that processes and routes data at the data link layer of the OSI model...
es (particularly via crossbar switch
Crossbar switch
In electronics, a crossbar switch is a switch connecting multiple inputs to multiple outputs in a matrix manner....
es, hence the name). The term is popular in telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
, Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel, or FC, is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards , an American National Standards Institute –accredited standards...
storage area network
Storage area network
A storage area network is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated, block level data storage. SANs are primarily used to make storage devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes, accessible to servers so that the devices appear like locally attached devices...
s and other high-speed networks, including InfiniBand
InfiniBand
InfiniBand is a switched fabric communications link used in high-performance computing and enterprise data centers. Its features include high throughput, low latency, quality of service and failover, and it is designed to be scalable...
. The term is in contrast to a broadcast medium, such as early forms of Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
.
Switched fabrics can offer better total throughput than broadcast networks, because traffic is spread across multiple physical links.
Similarly, some modern computers use a switched fabric, such as PCI Express
PCI Express
PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
, HyperTransport
HyperTransport
HyperTransport , formerly known as Lightning Data Transport , is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001...
, or QuickPath, instead of a bus. Again, the advantage of the switched fabric is performance.
Switched fabric in Fibre Channel

Fibre Channel switch
In the computer storage field, a Fibre Channel switch is a network switch compatible with the Fibre Channel protocol. It allows the creation of a Fibre Channel fabric, that is currently the core component of most storage area networks . The fabric is a network of Fibre Channel devices which...
es. This topology allows the connection of up to the theoretical maximum of 16 million devices, limited only by the available address space (224).
Multiple switches in a fabric usually form a mesh network, with devices being on the "edges" ("leaves") of the mesh. While this topology has the best scalability
Scalability
In electronics scalability is the ability of a system, network, or process, to handle growing amount of work in a graceful manner or its ability to be enlarged to accommodate that growth...
properties of the three FC topologies, it is also the most expensive, the only one requiring a costly fibre channel switch
Fibre Channel switch
In the computer storage field, a Fibre Channel switch is a network switch compatible with the Fibre Channel protocol. It allows the creation of a Fibre Channel fabric, that is currently the core component of most storage area networks . The fabric is a network of Fibre Channel devices which...
.
Visibility among nodes in a fabric is typically controlled with zoning
Fibre Channel zoning
In storage networking, Fibre Channel zoning is the partitioning of a Fibre Channel fabric into smaller subsets to restrict interference, add security, and to simplify management. While a SAN makes available several virtual disks , each system connected to the SAN should only be allowed access to a...
.
Most Fibre Channel network designs employ two separate fabrics for redundancy
Redundancy (engineering)
In engineering, redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system, usually in the case of a backup or fail-safe....
. The two fabrics share the edge nodes (devices), but are otherwise unconnected. One of the advantages of this topology is capability of failover
Failover
In computing, failover is automatic switching to a redundant or standby computer server, system, or network upon the failure or abnormal termination of the previously active application, server, system, or network...
, meaning that in case one link breaks or a switch is out of order, datagram
Datagram
A datagram is a basic transfer unit associated with a packet-switched network in which the delivery, arrival time, and order are not guaranteed....
s can use the second fabric.
See also
- Clos networkClos networkIn the field of telecommunications, a Clos network is a kind of multistage circuit switching network, first formalized by Charles Clos in 1953, which represents a theoretical idealization of practical multi-stage telephone switching systems. Clos networks are required when the physical circuit...
- Fabric Application Interface StandardFabric Application Interface StandardThe Fabric Application Interface Standard or FAIS is a common application programming interface framework for implementing storage applications in a storage networking environment...
- Fibre ChannelFibre ChannelFibre Channel, or FC, is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards , an American National Standards Institute –accredited standards...
- Arbitrated loopArbitrated loopArbitrated loop, also known as FC-AL, is a Fibre Channel topology in which devices are connected in a one-way loop fashion in a ring topology. Historically it was a lower-cost alternative to a fabric topology. It allowed connection of many servers and computer storage devices without using then...
, for second alternate FC topology - Fibre Channel point-to-point, for alternate FC topology
- Arbitrated loop
- Network topologyNetwork topologyNetwork topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements of a computer or biological network....
- Storage area networkStorage area networkA storage area network is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated, block level data storage. SANs are primarily used to make storage devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes, accessible to servers so that the devices appear like locally attached devices...

