
Sunrise equation
Encyclopedia
The sunrise equation as follows can be used to derive the time of sunrise
and sunset
for any solar declination and latitude
in terms of local solar time when sunrise
and sunset
actually occur:

where:
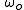 is the hour angle
is the hour angle
in degrees at either sunrise
(when negative value is taken) or sunset
(when positive value is taken); is the latitude
is the latitude
of the observer on the Earth
; is the sun declination
is the sun declination
.
rotates at the angular speed of 15°/hour and, therefore, gives the time of sunrise
gives the time of sunrise
as the number of hour
s before the local noon, or the time of sunset
as the number of hour
s after the local noon. Here the term local noon indicates the local time when the sun
is exactly to the south
or north
or exactly overhead.
The convention is usually that the value of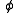 is 0 at the Equator
is 0 at the Equator
, positive in Northern Hemisphere
and negative in Southern Hemisphere
. And the value of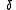 is 0 at the vernal and autumnal equinoxes when the sun is exactly above the Equator, positive during the Northern Hemisphere
is 0 at the vernal and autumnal equinoxes when the sun is exactly above the Equator, positive during the Northern Hemisphere
summer
and negative during the Northern Hemisphere
winter
.
Please note that the above equation is applicable only when indeed there is a sunrise
or sunset
when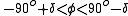 during the Northern Hemisphere
during the Northern Hemisphere
summer
, and when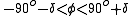 during the Northern Hemisphere
during the Northern Hemisphere
winter
. Out of these latitudinal ranges, it is either 24-hour day
time or 24-hour nighttime.
(which lifts the solar disc by approximately 0.6° when it is on the horizon) and the non-zero angle subtended by the solar disc (about 0.5°). The times of the rising and the setting of the upper solar limb as given in astronomical almanacs correct for this by using the more general equation

with the altitude
(a) of the center of the solar disc set to about -0.83° (or -50 arcminutes).
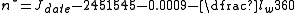

where:
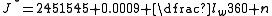
where:
 is an approximation of solar noon at lw.
is an approximation of solar noon at lw.

where:
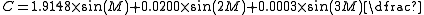
where:

where:
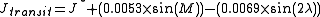
where:
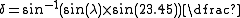
where:
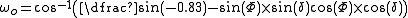
where:
This is the main equation from above with the solar disc correction.
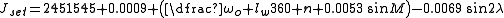
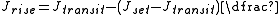
where:
and latitude
of the place and standard time
of the place. Finding the sun-rise (and sun-set) time we need three parameters; viz. latitude
, longitude
, date on which sun-rise is to be computed. Let take an example of Kathmandu (27° 42′ 0″ N, 85° 20′ 0″ E) for September 5.
Step 1. Find date difference since March 21 (September 4- March 21=167); then assume A=167*0.985626=164.60°.
Step 2. Find B, where B= Sin-1(0.398749 * Sin 164.60)= 6.07846 (this is in degree, where the sun is over in north, 6.07846° north from equator).
Step 3. Find C in minutes, where C=4*Sin-1(TanB*TanL) =4*Sin-1(Tan 6.07846o*Tan 27° 42′ 0″) =4*3.20496 = 12.81=13 minutes
Sunrise in all places of earth having 27° 42′ 0″ N is 13 minute earlier (because of +ve 13) than 6:00 i.e. 5:47 at local time.
Sunset for that time shall be 12- sunrise time (outcome shall be in time)
Day-length for that time shall be 2* sunset time (outcome shall be in hours)
Step 4. Find the time difference with standard time (or Greenwich Time
) to the local time. That shall be the sun-rise (watch) time.
For September 5, Kathmandu(85° 20′ 0″ E, 27° 42′ 0″ N) Sun-rise at 5 hour 41 minutes (23:54 Monday).
Time difference of Greenwich
and Nepal
standard time is 5 hours 45 minutes. Standard time Nepal and local time of Kathmandu is 4 minutes slow (west).
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
and sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
for any solar declination and latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
in terms of local solar time when sunrise
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
and sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
actually occur:

where:
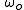 is the hour angle
is the hour angleHour angle
In astronomy and celestial navigation, the hour angle is one of the coordinates used in the equatorial coordinate system to give the position of a point on the celestial sphere....
in degrees at either sunrise
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
(when negative value is taken) or sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
(when positive value is taken);
 is the latitude
is the latitudeLatitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
of the observer on the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
;
 is the sun declination
is the sun declinationDeclination
In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and...
.
Theory of the Equation
The EarthEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
rotates at the angular speed of 15°/hour and, therefore,
 gives the time of sunrise
gives the time of sunriseSunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
as the number of hour
Hour
The hour is a unit of measurement of time. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minutes, or 3,600 seconds...
s before the local noon, or the time of sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
as the number of hour
Hour
The hour is a unit of measurement of time. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minutes, or 3,600 seconds...
s after the local noon. Here the term local noon indicates the local time when the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
is exactly to the south
South
South is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.South is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to east and west.By convention, the bottom side of a map is south....
or north
North
North is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.North is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west.By convention, the top side of a map is north....
or exactly overhead.
The convention is usually that the value of
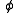 is 0 at the Equator
is 0 at the EquatorEquator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
, positive in Northern Hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and negative in Southern Hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
. And the value of
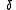 is 0 at the vernal and autumnal equinoxes when the sun is exactly above the Equator, positive during the Northern Hemisphere
is 0 at the vernal and autumnal equinoxes when the sun is exactly above the Equator, positive during the Northern HemisphereNorthern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
and negative during the Northern Hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
winter
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in temperate climates, between autumn and spring. At the winter solstice, the days are shortest and the nights are longest, with days lengthening as the season progresses after the solstice.-Meteorology:...
.
Please note that the above equation is applicable only when indeed there is a sunrise
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
or sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
when
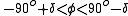 during the Northern Hemisphere
during the Northern HemisphereNorthern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
, and when
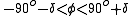 during the Northern Hemisphere
during the Northern HemisphereNorthern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
winter
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in temperate climates, between autumn and spring. At the winter solstice, the days are shortest and the nights are longest, with days lengthening as the season progresses after the solstice.-Meteorology:...
. Out of these latitudinal ranges, it is either 24-hour day
Day
A day is a unit of time, commonly defined as an interval equal to 24 hours. It also can mean that portion of the full day during which a location is illuminated by the light of the sun...
time or 24-hour nighttime.
Generalized Equation
Also note that the above equation neglects the influence of atmospheric refractionAtmospheric refraction
Atmospheric refraction is the deviation of light or other things like humanelectromagnetic wave from a straight line as it passes through the atmosphere due to the variation in air density as a function of altitude...
(which lifts the solar disc by approximately 0.6° when it is on the horizon) and the non-zero angle subtended by the solar disc (about 0.5°). The times of the rising and the setting of the upper solar limb as given in astronomical almanacs correct for this by using the more general equation

with the altitude
Altitude
Altitude or height is defined based on the context in which it is used . As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context...
(a) of the center of the solar disc set to about -0.83° (or -50 arcminutes).
Complete calculation on Earth
The generalized equation relies on a number of other variables which need to be calculated before it can itself be calculated. These equations already have all of the solar-earth constants put into them with angular constants in degrees.Calculate current Julian Cycle
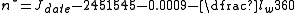

where:
- Jdate is the Julian DayJulian dayJulian day is used in the Julian date system of time measurement for scientific use by the astronomy community, presenting the interval of time in days and fractions of a day since January 1, 4713 BC Greenwich noon...
; - lw is the longitude west (west is positive, east is negative) of the observer on the Earth;
- n is the Julian cycle since Jan 1st, 2000.
Approximate Solar Noon
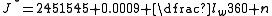
where:
 is an approximation of solar noon at lw.
is an approximation of solar noon at lw.Solar Mean Anomaly

where:
- M is the solar Mean AnomalyMean anomalyIn celestial mechanics, the mean anomaly is a parameter relating position and time for a body moving in a Kepler orbit. It is based on the fact that equal areas are swept at the focus in equal intervals of time....
.
Equation of Center
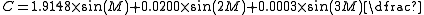
where:
- C is the Equation of the centerEquation of the centerFor further closely related mathematical developments see also Two-body problem, also Gravitational two-body problem, also Kepler orbit, and Kepler problem...
.
Ecliptic Longitude

where:
- λ is the ecliptic longitude.
Solar Transit
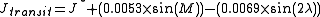
where:
- Jtransit is the hour angle for solar transit (or solar noon).
Declination of the Sun
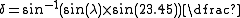
where:
- δ is the declination of the sun.
Hour Angle
This is the equation from above with the solar disc correction.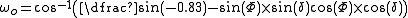
where:
- ωo is the hour angle;
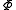 is the north latitude of the observer (north is positive, south is negative) on the Earth.
is the north latitude of the observer (north is positive, south is negative) on the Earth.
This is the main equation from above with the solar disc correction.
Calculate Sunrise and Sunset
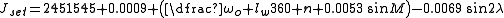
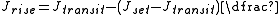
where:
- Jset is the actual Julian Date of sunset;
- Jrise is the actual Julian Date of sunrise.
Sun Rise Time : Nepali Method
Sun rise at the morning is based on longitudeLongitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
and latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
of the place and standard time
Standard time
Standard time is the result of synchronizing clocks in different geographical locations within a time zone to the same time rather than using the local meridian as in local mean time or solar time. Historically, this helped in the process of weather forecasting and train travel. The concept...
of the place. Finding the sun-rise (and sun-set) time we need three parameters; viz. latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
, longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
, date on which sun-rise is to be computed. Let take an example of Kathmandu (27° 42′ 0″ N, 85° 20′ 0″ E) for September 5.
Step 1. Find date difference since March 21 (September 4- March 21=167); then assume A=167*0.985626=164.60°.
Step 2. Find B, where B= Sin-1(0.398749 * Sin 164.60)= 6.07846 (this is in degree, where the sun is over in north, 6.07846° north from equator).
Step 3. Find C in minutes, where C=4*Sin-1(TanB*TanL) =4*Sin-1(Tan 6.07846o*Tan 27° 42′ 0″) =4*3.20496 = 12.81=13 minutes
Sunrise in all places of earth having 27° 42′ 0″ N is 13 minute earlier (because of +ve 13) than 6:00 i.e. 5:47 at local time.
Sunset for that time shall be 12- sunrise time (outcome shall be in time)
Day-length for that time shall be 2* sunset time (outcome shall be in hours)
Step 4. Find the time difference with standard time (or Greenwich Time
Greenwich Mean Time
Greenwich Mean Time is a term originally referring to mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London. It is arguably the same as Coordinated Universal Time and when this is viewed as a time zone the name Greenwich Mean Time is especially used by bodies connected with the United...
) to the local time. That shall be the sun-rise (watch) time.
For September 5, Kathmandu(85° 20′ 0″ E, 27° 42′ 0″ N) Sun-rise at 5 hour 41 minutes (23:54 Monday).
Time difference of Greenwich
Greenwich
Greenwich is a district of south London, England, located in the London Borough of Greenwich.Greenwich is best known for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich Meridian and Greenwich Mean Time...
and Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
standard time is 5 hours 45 minutes. Standard time Nepal and local time of Kathmandu is 4 minutes slow (west).

