
Sulfonium
Encyclopedia
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
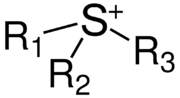
(a "cation") featuring three organic substituents attached to sulfur. They have the formula [SR3]+. Together with their negatively charged counterpart, the anion, the compounds are called sulfonium salts.
Synthesis
Sulfonium compounds are usually be synthesizedChemical synthesis
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is purposeful execution of chemical reactions to get a product, or several products. This happens by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions...
from the reaction of thioether
Thioether
A thioether is a functional group in organosulfur chemistry with the connectivity C-S-C as shown on right. Like many other sulfur-containing compounds, volatile thioethers have foul odors. A thioether is similar to an ether except that it contains a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen...
s with alkyl halides. For example, the reaction of dimethyl sulfide
Dimethyl sulfide
Dimethyl sulfide or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula 2S. Dimethyl sulfide is a water-insoluble flammable liquid that boils at and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a component of the smell produced from cooking of certain vegetables, notably maize,...
with iodomethane
Iodomethane
Methyl iodide, also called iodomethane, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally...
yields trimethylsulfonium iodide:
- + → +
Before the above reaction, the sulfur atom has two lone electron pairs. One of these lone pairs links to the methyl group. At the same time, as part of a concerted nucleophilic substitution mechanism (SN2), the iodide leaving group departs. this leaves a positively charged trimethylsulfonium ion, whose charge is balanced by the iodide. The rate of reaction is even faster with stronger methylating agents, such as methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate.
Structure
The compounds are pyramidal at sulfur. Thus Me3S+ is structurally similar to the isoelectronic compound trimethylphosphineTrimethylphosphine
Trimethylphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P3, commonly abbreviated PMe3. This colorless liquid has a strongly unpleasant odour, which is characteristic of alkylphosphines. It is a pyramidal molecule with C3v symmetry, similar to ammonia and phosphine . As a ligand, its...
. Sulfonium compounds wherein the three substituents differ are chiral and optically stable.
Biochemistry
The sulfonium (more specifically methioninium) species S-adenosylmethionine occurs widely in nature, where it is used as a source of the adensoyl radical. This radical participates in the biosynthesisBiosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
of various compounds.
Another, sulfonium (methioninium) species found in nature is S-methylmethionine
S-Methylmethionine
S-Methylmethionine is a derivative of methionine with chemical formula [3S2CHNH3CO2]+. This cation is an intermediate in many biosynthetic pathways owing to the sulfonium functional group. The natural derivative S-methylmethionine is biosynthesized from L-methionine which is first converted...
.
Organic synthesis
Sulfonium centers stabilize the formation of ylideYlide
An ylide or ylid is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom directly attached to a hetero atom with a formal positive charge , and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds...
s, which are useful in C-C forming reactions.
Industry
Some azo dyes are modified with sulfonium groups to give them a positive charge. The compound triphenylsulfonium triflateTriphenylsulfonium triflate
Triphenylsulfonium triflate is the chemical compound with the formula [3S][CF3SO3]. This colourless salt consists of a sulfonium cation and the triflate anion...
is a photoacid, a compound that under light converts to an acid.
See also
- SulfideSulfideA sulfide is an anion of sulfur in its lowest oxidation state of 2-. Sulfide is also a slightly archaic term for thioethers, a common type of organosulfur compound that are well known for their bad odors.- Properties :...
R-S-R - SulfateSulfateIn inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
R-SO4-R - SulfiteSulfiteSulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:...
R-SO3-R - SulfonateSulfonic acidSulfonic acid usually refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula RS2–OH, where R is an alkyl or aryl. The formal part of acid, HS2–OH, are formally derivatives of the "parent" inorganic compound with the formula HSO2.-Preparation:Sulfonic acid is...
R-SO3− - Onium compoundsOnium compoundsOnium compounds are cations derived by the protonation of mononuclear parent hydrides of elements of the nitrogen group , chalcogens , or halogens , and similar cations derived by the substitution of hydrogen atoms in the former by other groups, such as organic radicals, or halogens, for example...

