
Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
The 3 substrates
of this enzyme are succinate semialdehyde, NAD+
, and H2O
, whereas its 3 products
are succinate, NADH
, and H+
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
s, specifically those acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is succinate-semialdehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase, succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase, succinyl semialdehyde dehydrogenase, and succinate semialdehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in glutamate and butanoate metabolism.
Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase is found in organisms ranging across the tree of life from bacteria to humans. It is important in the degradation of γ-aminobutyric acid in humans, and deficiency of the enzyme causes serious health effects (succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency
).
In bacteria, the enzyme is also involved in GABA
degradation, but can be recruited to facilitate other functions, such as converting succinate-semialdehyde formed during fission of the pyridine
ring to succinic acid for entry into the Krebs Cycle.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- succinate semialdehyde + NAD+ + H2O
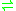 succinate + NADH + 2 H+
succinate + NADH + 2 H+
The 3 substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are succinate semialdehyde, NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
, and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its 3 products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are succinate, NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
, and H+
Hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes.Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions....
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another...
s, specifically those acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is succinate-semialdehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase, succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase, succinyl semialdehyde dehydrogenase, and succinate semialdehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in glutamate and butanoate metabolism.
Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase is found in organisms ranging across the tree of life from bacteria to humans. It is important in the degradation of γ-aminobutyric acid in humans, and deficiency of the enzyme causes serious health effects (succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency
Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency
Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency , also known as 4-hydroxybutyric aciduria or gamma-hydroxybutyric aciduria, is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of the degradation pathway of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid, or GABA...
).
In bacteria, the enzyme is also involved in GABA
Gabâ
Gabâ or gabaa, for the people in many parts of the Philippines), is the concept of a non-human and non-divine, imminent retribution. A sort of negative karma, it is generally seen as an evil effect on a person because of their wrongdoings or transgressions...
degradation, but can be recruited to facilitate other functions, such as converting succinate-semialdehyde formed during fission of the pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
ring to succinic acid for entry into the Krebs Cycle.

