Steviol glycoside
Encyclopedia
The steviol glycosides are responsible for the sweet taste of the leaves of the stevia
plant (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni).
These compounds range in sweetness
from 40 to 300 times sweeter than sucrose
.
They are heat-stable, pH-stable, and do not ferment. They also do not induce a glycemic response
when ingested, making them attractive as natural sweeteners
to diabetics and others on carbohydrate
-controlled diets.
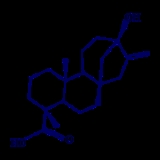
known as steviol
is the aglycone
of stevia's sweet glycoside
s, which are constructed by replacing steviol's carboxyl hydrogen
atom
(at the bottom left of the figure) with glucose
to form an ester
, and replacing the hydroxyl hydrogen (at the top of the figure) with combinations of glucose and rhamnose
to form an ether
. The two primary compounds, stevioside and rebaudioside A, use only glucose: Stevioside has two linked glucose molecules at the hydroxyl site, whereas rebaudioside A has three, with the middle glucose of the triplet connected to the central steviol structure.
In terms of weight fraction, the four major steviol glycosides found in the stevia plant tissue are:
Rebaudioside B, D, and E may also be present in minute quantities; however, it is suspected that rebaudioside B is a byproduct of the isolation technique.
The two majority compounds stevioside and rebaudioside, primarily responsible for the sweet taste of stevia leaves, were first isolated by two French
chemists in 1931.
Rebiana is the trade name for a zero-calorie sweetener containing mainly rebaudioside A (also called Reb A). Truvia is the consumer brand for Rebiana marketed by Cargill
and developed jointly with The Coca-Cola Company
. PureVia is PepsiCo
's brand
of Reb A sweetener. Enliten is Corn Products International
's brand
of Reb A sweetener.
has been criticized on procedural grounds that the data were mishandled in such a way that even distilled water
would appear mutagenic.
More recent studies appear to establish the safety of steviol and its glycosides. In 2006, the World Health Organization
(WHO) performed a thorough evaluation of recent experimental studies of stevia extracts conducted on animals and humans, and concluded that “stevioside and rebaudioside A are not genotoxic in vitro
or in vivo
and that the genotoxicity of steviol and some of its oxidative derivatives in vitro is not expressed in vivo.”
The report also found no evidence of carcinogenic activity. The report also suggested the possibility of health benefits, in that “stevioside has shown some evidence of pharmacological effects in patients with hypertension or with type-2 diabetes”, but concluded that further study was required to determine proper dosage.
The European Food Safety Authority
evaluated the safety of steviol glycosides, extracted from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni plant, as sweetener and expressed its opinion on 10 March 2010. The authority concluded an Acceptable Daily Intake
(ADI) for steviol glycosides, expressed as steviol equivalents, of 4 mg/kg bodyweight/day.
Stevia
Stevia is a genus of about 240 species of herbs and shrubs in the sunflower family , native to subtropical and tropical regions from western North America to South America. The species Stevia rebaudiana, commonly known as sweetleaf, sweet leaf, sugarleaf, or simply stevia, is widely grown for its...
plant (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni).
These compounds range in sweetness
Sweetness
Sweetness is one of the five basic tastes and is almost universally regarded as a pleasurable experience. Foods rich in simple carbohydrates such as sugar are those most commonly associated with sweetness, although there are other natural and artificial compounds that are sweet at much lower...
from 40 to 300 times sweeter than sucrose
Sucrose
Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. A white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste, it is best known for its role in human nutrition. The molecule is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose with the molecular formula...
.
They are heat-stable, pH-stable, and do not ferment. They also do not induce a glycemic response
Blood sugar
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or animal. Normally in mammals, the body maintains the blood glucose level at a reference range between about 3.6 and 5.8 mM , or 64.8 and 104.4 mg/dL...
when ingested, making them attractive as natural sweeteners
Sugar substitute
A sugar substitute is a food additive that duplicates the effect of sugar in taste, usually with less food energy. Some sugar substitutes are natural and some are synthetic. Those that are not natural are, in general, called artificial sweeteners....
to diabetics and others on carbohydrate
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
-controlled diets.
Structure
The diterpeneDiterpene
Diterpenes are a type of terpenes composed of four isoprene units. They derive from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol...
known as steviol
Steviol
Steviol is a diterpene first isolated from Stevia rebaudiana in 1931. Its chemical structure was not fully elucidated until 1960.Steviol is found in the form of glycosides including the sweet chemical compound stevioside....
is the aglycone
Aglycone
An aglycone is the non-sugar compound remaining after replacement of the glycosyl group from a glycoside by a hydrogen atom. The spelling aglycon is sometimes encountered .Classes of phytochemicals found in the aglycone and glycosides forms :...
of stevia's sweet glycoside
Glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to a non-carbohydrate moiety, usually a small organic molecule. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme...
s, which are constructed by replacing steviol's carboxyl hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
(at the bottom left of the figure) with glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
to form an ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
, and replacing the hydroxyl hydrogen (at the top of the figure) with combinations of glucose and rhamnose
Rhamnose
Rhamnose is a naturally occurring deoxy sugar. It can be classified as either a methyl-pentose or a 6-deoxy-hexose. Rhamnose occurs in nature in its L-form as L-rhamnose . This is unusual, since most of the naturally occurring sugars are in D-form...
to form an ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
. The two primary compounds, stevioside and rebaudioside A, use only glucose: Stevioside has two linked glucose molecules at the hydroxyl site, whereas rebaudioside A has three, with the middle glucose of the triplet connected to the central steviol structure.
In terms of weight fraction, the four major steviol glycosides found in the stevia plant tissue are:
- 5–10% stevioside (250–300X of sugar)
- 2–4% rebaudioside A — most sweet (350–450X of sugar) and least bitter
- 1–2% rebaudioside C
- ½–1% dulcoside A.
Rebaudioside B, D, and E may also be present in minute quantities; however, it is suspected that rebaudioside B is a byproduct of the isolation technique.
The two majority compounds stevioside and rebaudioside, primarily responsible for the sweet taste of stevia leaves, were first isolated by two French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
chemists in 1931.
Availability
Steviol glycosides were first commercialized as a sweetener in 1971 by the Japanese firm Morita Kagaku Kogyo Co., Ltd., a leading stevia extract producer in Japan.Rebiana is the trade name for a zero-calorie sweetener containing mainly rebaudioside A (also called Reb A). Truvia is the consumer brand for Rebiana marketed by Cargill
Cargill
Cargill, Incorporated is a privately held, multinational corporation based in Minnetonka, Minnesota. Founded in 1865, it is now the largest privately held corporation in the United States in terms of revenue. If it were a public company, it would rank, as of 2011, number 13 on the Fortune 500,...
and developed jointly with The Coca-Cola Company
The Coca-Cola Company
The Coca-Cola Company is an American multinational beverage corporation and manufacturer, retailer and marketer of non-alcoholic beverage concentrates and syrups. The company is best known for its flagship product Coca-Cola, invented in 1886 by pharmacist John Stith Pemberton in Columbus, Georgia...
. PureVia is PepsiCo
PepsiCo
PepsiCo Inc. is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Purchase, New York, United States, with interests in the manufacturing, marketing and distribution of grain-based snack foods, beverages, and other products. PepsiCo was formed in 1965 with the merger of the Pepsi-Cola Company...
's brand
Brand
The American Marketing Association defines a brand as a "Name, term, design, symbol, or any other feature that identifies one seller's good or service as distinct from those of other sellers."...
of Reb A sweetener. Enliten is Corn Products International
Corn Products International
Corn Products International, Inc. is an Illinois-based refiner and processor of corn-based food additives and sweeteners. It operates factories in 15 countries.- Company :...
's brand
Brand
The American Marketing Association defines a brand as a "Name, term, design, symbol, or any other feature that identifies one seller's good or service as distinct from those of other sellers."...
of Reb A sweetener.
Health effects
A 1985 study reporting that steviol may be a mutagenMutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens...
has been criticized on procedural grounds that the data were mishandled in such a way that even distilled water
Distilled water
Distilled water is water that has many of its impurities removed through distillation. Distillation involves boiling the water and then condensing the steam into a clean container.-History:...
would appear mutagenic.
More recent studies appear to establish the safety of steviol and its glycosides. In 2006, the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) performed a thorough evaluation of recent experimental studies of stevia extracts conducted on animals and humans, and concluded that “stevioside and rebaudioside A are not genotoxic in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
or in vivo
In vivo
In vivo is experimentation using a whole, living organism as opposed to a partial or dead organism, or an in vitro controlled environment. Animal testing and clinical trials are two forms of in vivo research...
and that the genotoxicity of steviol and some of its oxidative derivatives in vitro is not expressed in vivo.”
The report also found no evidence of carcinogenic activity. The report also suggested the possibility of health benefits, in that “stevioside has shown some evidence of pharmacological effects in patients with hypertension or with type-2 diabetes”, but concluded that further study was required to determine proper dosage.
The European Food Safety Authority
European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority is an agency of the European Union that provides independent scientific advice and communication on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain, created by European Regulation 178/2002....
evaluated the safety of steviol glycosides, extracted from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni plant, as sweetener and expressed its opinion on 10 March 2010. The authority concluded an Acceptable Daily Intake
Acceptable daily intake
Acceptable daily intake or ADI is a measure of the amount of a specific substance in food or drinking water that can be ingested on a daily basis over a lifetime without an appreciable health risk...
(ADI) for steviol glycosides, expressed as steviol equivalents, of 4 mg/kg bodyweight/day.

