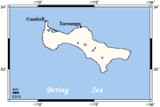
St. Lawrence Island
Encyclopedia
St. Lawrence Island is located west of mainland Alaska
in the Bering Sea
, just south of the Bering Strait
, at about 63°30' North 173°20' West. The village of Gambell
is located on the northwest cape, 58 km (36 mi) from the Chukchi Peninsula
in the Russian Far East
. The island is part of Alaska, but closer to Siberia
than to the Alaskan mainland. St. Lawrence Island is thought to be one of the last exposed portions of the land bridge
that once joined Asia with North America during the Pleistocene
period. It is the sixth largest island in the United States and the 113th largest island in the world.
defines St. Lawrence Island as Block Group 6, Census Tract
1 of Nome Census Area, Alaska
. As of the 2000 census
there were 1,292 people living on a land area of 1791.56 sq mi (4,640.1 km²). The island is about 90 miles (144.8 km) long and 8–22 miles (13–36 km) wide. The island has no trees, and the only woody plants are Arctic Willow
, standing no more than a foot (30 cm) high.
The island's abundance of seabird
s and marine mammals is due largely to the influence of the Anadyr Current, an ocean current which brings cold, nutrient-rich water from the deep waters of the Bering Sea
shelf edge.
To the south of the island is a persistent polynya
, formed when the prevailing winds from the north and east blow the migrating ice away from the coast.
and Gambell
. The two villages were given title to most of the land on St. Lawrence Island by the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act
in 1971. As a result of having title to the land, the Yupik are legally able to sell the fossilized ivory and other artifacts found on St. Lawrence Island.
The island is now inhabited mostly by Siberian Yupik engaged in hunting, fishing, and reindeer herding. The St. Lawrence Island Yupik people are also known for their skill in carving, mostly with materials from marine mammals (walrus ivory and whale bone).
The Okivik occupation is influenced by and may have been coincident with the Old Bering Sea occupation of 2000 years ago to around 700 years ago, characterized by the simpler and more homogeneous Punuk style. Stone artifacts changed from chipped stone to ground slate; carved ivory
harpoon
heads are smaller and simpler in design.
Prehistoric and early historic occupations of St. Lawrence Island were never permanent, with periods of abandonment and reoccupation depending on resource availability and changes in weather patterns. Famine was common, as evidenced by Harris lines
and enamel hypoplasia
in human skeletons. Travel to and from the mainland was common during calm weather, so the island was used as a hunting base, and occupation sites were re-used periodically rather than permanently occupied.
Major archaeology
sites at Gambell and Savoonga (Kukulik) were excavated by Otto Geist and Ivar Skarland of the University of Alaska Fairbanks
. Collections from these excavations are curated at the University of Alaska Museum on the UAF campus.
 The island was called Sivuqaq by the Yupik who lived there. It was visited by Russia
The island was called Sivuqaq by the Yupik who lived there. It was visited by Russia
n/Danish explorer Vitus Bering
on St. Lawrence's Day, August 10, 1728, and named after the day of his visit. The island was the first place in Alaska known to have been visited by European explorers.
There were about 4,000 Central Alaskan Yupik and Siberian Yupik
living in several villages on the island in the mid-19th century. They subsisted by hunting walrus
and whale
and by fishing. A famine in 1878–1880 caused many to starve and many others to leave, decimating the island's population. Nearly all the residents remaining were Siberian Yupik.
Reindeer
were introduced on the island in 1900 in an attempt to bolster the economy. The reindeer herd grew to about 10,000 animals by 1917, but has since declined. Reindeer are herded as a source of subsistence meat to this day.
, islanders served in the Alaska Territorial Guard
(ATG) following disbandment of the ATG in 1947, and with the construction of Northeast Cape Air Force Station
in 1952, many islanders joined the Alaska National Guard
to provide for the defense of the island and station.
 On June 22, 1955, during the Cold War
On June 22, 1955, during the Cold War
. a US Navy P2V Neptune with a crew of 11 was attacked by two Soviet Air Forces fighter aircraft
along the International Date Line
in international waters
over the Bering Straits, between Siberia
's Kamchatka Peninsula
and Alaska. The P2V crashed on the island's northwest cape, near the village of Gambell
. Villagers rescued the crew, which suffered 3 wounded by Soviet fire and 4 injured in crash. The Soviet Government
, in response to a US diplomatic protest, was unusually conciliatory, stating that:
The Soviet military
were under strict orders to "avoid any action beyond the limits of the Soviet state frontiers."
The Soviet Government "expressed regret in regard to the incident."
The Soviet Government, "taking into account... conditions which do not exclude the possibility of a mistake from one side or the other," was willing to compensate the US for 50% of damages sustained—the first such offer ever made by the Soviets for any Cold War shoot-down incident.
The US Government
stated that it was satisfied with the Soviet expression of regret and the offer of partial compensation, although it said that the Soviet statement also fell short of what the available information indicated.
Northeast Cape Air Force Station
, at the island's other end, was a United States Air Force
facility consisting of an Aircraft Control and Warning (AC&W) radar
site, a United States Air Force Security Service listening post; and a White Alice Communications System
(WACS) site that operated from about 1952 to about 1972. The area surrounding the Northeast Cape base site had been a traditional camp site for several Yupik families for centuries. After the base closed down in the 1970s, many of these people started to experience health problems. Even today, people who grew up at Northeast Cape have high rates of cancer and other diseases, possibly due to PCB
exposure around the site. According to the State of Alaska, those elevated cancer
rates have been shown to be comparable to the rates of other Alaskan and non-Alaskan arctic natives who were not exposed to a similar Air Force facility. In any event, the majority of the facility was removed in a $10.5 million dollar cleanup program in 2003. Monitoring of the site will continue into the future.
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
in the Bering Sea
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves....
, just south of the Bering Strait
Bering Strait
The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,...
, at about 63°30' North 173°20' West. The village of Gambell
Gambell, Alaska
Gambell is a village on St. Lawrence Island in Alaska, United States. At the 2000 census the population was 649.-Geography:Gambell is located on the northwest cape of St. Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea, southwest of Nome...
is located on the northwest cape, 58 km (36 mi) from the Chukchi Peninsula
Chukchi Peninsula
The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the...
in the Russian Far East
Russian Far East
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
. The island is part of Alaska, but closer to Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
than to the Alaskan mainland. St. Lawrence Island is thought to be one of the last exposed portions of the land bridge
Bering land bridge
The Bering land bridge was a land bridge roughly 1,000 miles wide at its greatest extent, which joined present-day Alaska and eastern Siberia at various times during the Pleistocene ice ages. Like most of Siberia and all of Manchuria, Beringia was not glaciated because snowfall was extremely light...
that once joined Asia with North America during the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
period. It is the sixth largest island in the United States and the 113th largest island in the world.
Geography
The United States Census BureauUnited States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau is the government agency that is responsible for the United States Census. It also gathers other national demographic and economic data...
defines St. Lawrence Island as Block Group 6, Census Tract
Census tract
A census tract, census area, or census district is a geographic region defined for the purpose of taking a census. Usually these coincide with the limits of cities, towns or other administrative areas and several tracts commonly exist within a county...
1 of Nome Census Area, Alaska
Nome Census Area, Alaska
Nome Census Area is a census area located in the state of Alaska, United States. As of the 2000 census, the population was 9,196. It is part of the unorganized borough and therefore has no borough seat. Its largest community by far is the city of Nome....
. As of the 2000 census
United States Census, 2000
The Twenty-second United States Census, known as Census 2000 and conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2% over the 248,709,873 persons enumerated during the 1990 Census...
there were 1,292 people living on a land area of 1791.56 sq mi (4,640.1 km²). The island is about 90 miles (144.8 km) long and 8–22 miles (13–36 km) wide. The island has no trees, and the only woody plants are Arctic Willow
Arctic Willow
Salix arctica is a tiny creeping willow . It is adapted to survive in harsh Arctic and subarctic environments, and has a circumpolar distribution round the Arctic Ocean.-Distribution:...
, standing no more than a foot (30 cm) high.
The island's abundance of seabird
Seabird
Seabirds are birds that have adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same environmental problems and feeding niches have resulted in similar adaptations...
s and marine mammals is due largely to the influence of the Anadyr Current, an ocean current which brings cold, nutrient-rich water from the deep waters of the Bering Sea
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves....
shelf edge.
To the south of the island is a persistent polynya
Polynya
A polynya or polynia is an area of open water surrounded by sea ice. It is now used as geographical term for an area of unfrozen sea within the ice pack. It is a loanword from , , which means a natural ice hole, and was adopted in the 19th century by polar explorers to describe navigable...
, formed when the prevailing winds from the north and east blow the migrating ice away from the coast.
Villages
The island contains two villages: SavoongaSavoonga, Alaska
Savoonga is a city in Nome Census Area, Alaska, one of two on St Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea. As of the 2000 census, Savoonga's population was 643.Savoonga was incorporated in 1969, and in 1971 became the joint owner with Gambell of the entire island....
and Gambell
Gambell, Alaska
Gambell is a village on St. Lawrence Island in Alaska, United States. At the 2000 census the population was 649.-Geography:Gambell is located on the northwest cape of St. Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea, southwest of Nome...
. The two villages were given title to most of the land on St. Lawrence Island by the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act
Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act
The Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act, commonly abbreviated ANCSA, was signed into law by President Richard M. Nixon on December 23, 1971, the largest land claims settlement in United States history. ANCSA was intended to resolve the long-standing issues surrounding aboriginal land claims in...
in 1971. As a result of having title to the land, the Yupik are legally able to sell the fossilized ivory and other artifacts found on St. Lawrence Island.
The island is now inhabited mostly by Siberian Yupik engaged in hunting, fishing, and reindeer herding. The St. Lawrence Island Yupik people are also known for their skill in carving, mostly with materials from marine mammals (walrus ivory and whale bone).
Prehistory
St. Lawrence Island was first occupied around 2,000 to 2,500 years ago by coastal people characterized by artifacts decorated in the Okvik (oogfik) style. Archaeological sites on the Punuk Islands, off the eastern end of St. Lawrence Island, at Kukulik, near Savoonga and on the hill slopes above Gambell have evidence of the Okivik occupation. The Okvik decorative style is zoomorphic and elaborate, executed in a sometimes crude engraving technique, with greater variation than the Old Bering Sea and Punuk styles.The Okivik occupation is influenced by and may have been coincident with the Old Bering Sea occupation of 2000 years ago to around 700 years ago, characterized by the simpler and more homogeneous Punuk style. Stone artifacts changed from chipped stone to ground slate; carved ivory
Ivory
Ivory is a term for dentine, which constitutes the bulk of the teeth and tusks of animals, when used as a material for art or manufacturing. Ivory has been important since ancient times for making a range of items, from ivory carvings to false teeth, fans, dominoes, joint tubes, piano keys and...
harpoon
Harpoon
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument used in fishing to catch fish or large marine mammals such as whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the target animal, allowing the fishermen to use a rope or chain attached to the butt of the projectile to catch the animal...
heads are smaller and simpler in design.
Prehistoric and early historic occupations of St. Lawrence Island were never permanent, with periods of abandonment and reoccupation depending on resource availability and changes in weather patterns. Famine was common, as evidenced by Harris lines
Harris lines
Harris Lines, also known as Growth arrest lines.Lines of increased bone density that represent the position of the growth plate at the time of insult to the organism and formed on long bones due to growth arrest. Can be caused by juvenile malnutrition, disease or trauma. Only visible by radiograph...
and enamel hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is the defect of the teeth in which the tooth enamel is hard but thin and deficient in amount. This is caused by defective enamel matrix formation with a deficiency in the cementing substance....
in human skeletons. Travel to and from the mainland was common during calm weather, so the island was used as a hunting base, and occupation sites were re-used periodically rather than permanently occupied.
Major archaeology
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
sites at Gambell and Savoonga (Kukulik) were excavated by Otto Geist and Ivar Skarland of the University of Alaska Fairbanks
University of Alaska Fairbanks
The University of Alaska Fairbanks, located in Fairbanks, Alaska, USA, is the flagship campus of the University of Alaska System, and is abbreviated as Alaska or UAF....
. Collections from these excavations are curated at the University of Alaska Museum on the UAF campus.
History


Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n/Danish explorer Vitus Bering
Vitus Bering
Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands...
on St. Lawrence's Day, August 10, 1728, and named after the day of his visit. The island was the first place in Alaska known to have been visited by European explorers.
There were about 4,000 Central Alaskan Yupik and Siberian Yupik
Siberian Yupik
Siberian Yupiks, or Yuits, are indigenous people who reside along the coast of the Chukchi Peninsula in the far northeast of the Russian Federation and on St. Lawrence Island in Alaska. They speak Central Siberian Yupik , a Yupik language of the Eskimo–Aleut family of languages.They were also...
living in several villages on the island in the mid-19th century. They subsisted by hunting walrus
Walrus
The walrus is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous circumpolar distribution in the Arctic Ocean and sub-Arctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the Odobenidae family and Odobenus genus. It is subdivided into three subspecies: the Atlantic...
and whale
Whale
Whale is the common name for various marine mammals of the order Cetacea. The term whale sometimes refers to all cetaceans, but more often it excludes dolphins and porpoises, which belong to suborder Odontoceti . This suborder also includes the sperm whale, killer whale, pilot whale, and beluga...
and by fishing. A famine in 1878–1880 caused many to starve and many others to leave, decimating the island's population. Nearly all the residents remaining were Siberian Yupik.
Reindeer
Reindeer
The reindeer , also known as the caribou in North America, is a deer from the Arctic and Subarctic, including both resident and migratory populations. While overall widespread and numerous, some of its subspecies are rare and one has already gone extinct.Reindeer vary considerably in color and size...
were introduced on the island in 1900 in an attempt to bolster the economy. The reindeer herd grew to about 10,000 animals by 1917, but has since declined. Reindeer are herded as a source of subsistence meat to this day.
World War II
During World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, islanders served in the Alaska Territorial Guard
Alaska Territorial Guard
The Alaska Territorial Guard or Eskimo Scouts was a military reserve force component of the US Army, organized in 1942 in response to attacks on United States soil in Hawaii and occupation of parts of Alaska by Japan during World War II. The ATG operated until 1947...
(ATG) following disbandment of the ATG in 1947, and with the construction of Northeast Cape Air Force Station
Northeast Cape Air Force Station
Northeast Cape Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It was a forward outpost, located on St...
in 1952, many islanders joined the Alaska National Guard
Alaska National Guard
The Alaska Department of Military and Veterans Affairs manages military and veterans affairs for the U.S. state of Alaska. It comprises a number of subdepartments, including the Alaska National Guard, Veterans Affairs, the Division of Homeland Security and Emergency Management, Alaska Naval...
to provide for the defense of the island and station.
Cold War

Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
. a US Navy P2V Neptune with a crew of 11 was attacked by two Soviet Air Forces fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft
A fighter aircraft is a military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat with other aircraft, as opposed to a bomber, which is designed primarily to attack ground targets...
along the International Date Line
International Date Line
The International Date Line is a generally north-south imaginary line on the surface of the Earth, passing through the middle of the Pacific Ocean, that designates the place where each calendar day begins...
in international waters
International waters
The terms international waters or trans-boundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems , and wetlands.Oceans,...
over the Bering Straits, between Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
's Kamchatka Peninsula
Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west...
and Alaska. The P2V crashed on the island's northwest cape, near the village of Gambell
Gambell, Alaska
Gambell is a village on St. Lawrence Island in Alaska, United States. At the 2000 census the population was 649.-Geography:Gambell is located on the northwest cape of St. Lawrence Island in the Bering Sea, southwest of Nome...
. Villagers rescued the crew, which suffered 3 wounded by Soviet fire and 4 injured in crash. The Soviet Government
Government of the Soviet Union
The Council of Ministers of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was the de jure government comprising the highest executive and administrative body of the Soviet Union from 1946 until 1991....
, in response to a US diplomatic protest, was unusually conciliatory, stating that:
The Soviet military
Soviet Armed Forces
The Soviet Armed Forces, also called the Armed Forces of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and Armed Forces of the Soviet Union refers to the armed forces of the Russian SFSR , and Soviet Union from their beginnings in the...
were under strict orders to "avoid any action beyond the limits of the Soviet state frontiers."
The Soviet Government "expressed regret in regard to the incident."
The Soviet Government, "taking into account... conditions which do not exclude the possibility of a mistake from one side or the other," was willing to compensate the US for 50% of damages sustained—the first such offer ever made by the Soviets for any Cold War shoot-down incident.
The US Government
Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
stated that it was satisfied with the Soviet expression of regret and the offer of partial compensation, although it said that the Soviet statement also fell short of what the available information indicated.
Northeast Cape Air Force Station
Northeast Cape Air Force Station
Northeast Cape Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It was a forward outpost, located on St...
, at the island's other end, was a United States Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
facility consisting of an Aircraft Control and Warning (AC&W) radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
site, a United States Air Force Security Service listening post; and a White Alice Communications System
White Alice Communications System
The White Alice Communications System was a United States Air Force telecommunication link system constructed in Alaska during the cold war. It featured tropospheric scatter links and line-of-sight microwave radio links...
(WACS) site that operated from about 1952 to about 1972. The area surrounding the Northeast Cape base site had been a traditional camp site for several Yupik families for centuries. After the base closed down in the 1970s, many of these people started to experience health problems. Even today, people who grew up at Northeast Cape have high rates of cancer and other diseases, possibly due to PCB
Polychlorinated biphenyl
Polychlorinated biphenyls are a class of organic compounds with 2 to 10 chlorine atoms attached to biphenyl, which is a molecule composed of two benzene rings. The chemical formula for PCBs is C12H10-xClx...
exposure around the site. According to the State of Alaska, those elevated cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
rates have been shown to be comparable to the rates of other Alaskan and non-Alaskan arctic natives who were not exposed to a similar Air Force facility. In any event, the majority of the facility was removed in a $10.5 million dollar cleanup program in 2003. Monitoring of the site will continue into the future.
External links
- Gambell and St. Lawrence Island Photos from Gambell and St. Lawrence Island, August 2001
- Video on St. Lawrence

