
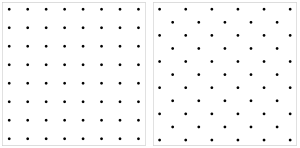
Square lattice
Encyclopedia
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the square lattice is a type of lattice
Lattice (group)
In mathematics, especially in geometry and group theory, a lattice in Rn is a discrete subgroup of Rn which spans the real vector space Rn. Every lattice in Rn can be generated from a basis for the vector space by forming all linear combinations with integer coefficients...
in a two-dimensional Euclidean space
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
. It is the two-dimensional version of the integer lattice
Integer lattice
In mathematics, the n-dimensional integer lattice , denoted Zn, is the lattice in the Euclidean space Rn whose lattice points are n-tuples of integers. The two-dimensional integer lattice is also called the square lattice, or grid lattice. Zn is the simplest example of a root lattice...
. It is one of the five types of two-dimensional lattices as classified by their symmetry group
Symmetry group
The symmetry group of an object is the group of all isometries under which it is invariant with composition as the operation...
s; its symmetry group is known symbolically as p4m.
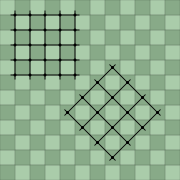
Two orientations of an image of the lattice are by far the most common. They can conveniently be referred to as "upright square lattice" and "diagonal square lattice". They differ by an angle of 45°. This is related to the fact that a square lattice can be partitioned into two square sub-lattices, as is evident in the colouring of a checkerboard
Checkerboard
A checkerboard or chequerboard is a board of chequered pattern on which English draughts is played. It is an 8×8 board and the 64 squares are of alternating dark and light color, often red and black....
.
Symmetry
The square lattice's symmetrySymmetry
Symmetry generally conveys two primary meanings. The first is an imprecise sense of harmonious or aesthetically pleasing proportionality and balance; such that it reflects beauty or perfection...
category is wallpaper group
Wallpaper group
A wallpaper group is a mathematical classification of a two-dimensional repetitive pattern, based on the symmetries in the pattern. Such patterns occur frequently in architecture and decorative art...
p4m. A pattern with this lattice of translational symmetry
Translational symmetry
In geometry, a translation "slides" an object by a a: Ta = p + a.In physics and mathematics, continuous translational symmetry is the invariance of a system of equations under any translation...
cannot have more, but may have less symmetry than the lattice itself.
An upright square lattice can be viewed as a diagonal square lattice with a mesh size that is √2 times as large, with the centers of the squares added. Correspondingly, after adding the centers of the squares of an upright square lattice we have a diagonal square lattice with a mesh size that is √2 times as small as that of the original lattice.
A pattern with 4-fold rotational symmetry
Rotational symmetry
Generally speaking, an object with rotational symmetry is an object that looks the same after a certain amount of rotation. An object may have more than one rotational symmetry; for instance, if reflections or turning it over are not counted, the triskelion appearing on the Isle of Man's flag has...
has a square lattice of 4-fold rotocenters that is a factor √2 finer and diagonally oriented relative to the lattice of translational symmetry
Translational symmetry
In geometry, a translation "slides" an object by a a: Ta = p + a.In physics and mathematics, continuous translational symmetry is the invariance of a system of equations under any translation...
.
With respect to reflection axes there are three possibilities:
- None. This is wallpaper group p4.
- In four directions. This is wallpaper group p4m.
- In two perpendicular directions. This is wallpaper group p4g. The points of intersection of the reflexion axes form a square grid which is as fine as, and oriented the same as, the square lattice of 4-fold rotocenters, with these rotocenters at the centers of the squares formed by the reflection axes.
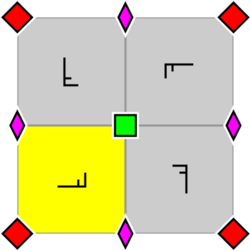 |
 |
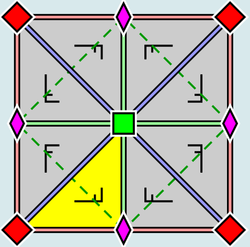 |
| Wallpaper group Wallpaper group A wallpaper group is a mathematical classification of a two-dimensional repetitive pattern, based on the symmetries in the pattern. Such patterns occur frequently in architecture and decorative art... p4, with the arrangement within a primitive cell of the 2- and 4-fold rotocenters (also applicable for p4g and p4m). A fundamental domain is indicated in yellow. |
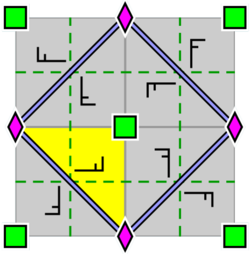
Wallpaper group p4g. There are reflection axes in two directions, not through the 4-fold rotocenters. | Wallpaper group p4m. There are reflection axes in four directions, through the 4-fold rotocenters. In two directions the reflection axes are oriented the same as, and as dense as, those for p4g, but shifted. In the other two directions they are linearly a factor √2 denser. |
See also
- square tiling
- hexagonal latticeHexagonal latticeThe hexagonal lattice or equilateral triangular lattice is one of the five 2D lattice types.Three nearby points form an equilateral triangle. In images four orientations of such a triangle are by far the most common...
- symmetry combinations
- centered square numberCentered square numberIn elementary number theory, a centered square number is a centered figurate number that gives the number of dots in a square with a dot in the center and all other dots surrounding the center dot in successive square layers. That is, each centered square number equals the number of dots within a...
- Gaussian integerGaussian integerIn number theory, a Gaussian integer is a complex number whose real and imaginary part are both integers. The Gaussian integers, with ordinary addition and multiplication of complex numbers, form an integral domain, usually written as Z[i]. The Gaussian integers are a special case of the quadratic...

