Spin echo
Encyclopedia
In magnetic resonance
, a spin echo is the refocusing of precessing
spin
magnetisation by a pulse of resonant radiation
. Modern nuclear magnetic resonance
and magnetic resonance imaging
rely heavily on this effect.
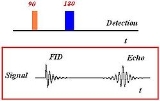
The NMR signal
observed following an initial excitation pulse decays with time due to both spin-spin relaxation
and any inhomogeneous effects which cause different spins to precess at different rates e.g. a distribution of chemical shift
s or magnetic field gradients
. Relaxation leads to an irreversible loss of magnetisation (decoherence), but the inhomogeneous dephasing can be reversed by applying a 180° or inversion pulse that inverts the magnetisation vectors. If the inversion pulse is applied after a period of dephasing, the inhomogeneous evolution will rephase to form an echo at time
of dephasing, the inhomogeneous evolution will rephase to form an echo at time 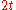 . The intensity of the echo relative to the initial signal is given by
. The intensity of the echo relative to the initial signal is given by 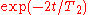 where
where 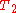 is the time constant for spin-spin relaxation.
is the time constant for spin-spin relaxation.
Echo phenomena are important features of coherent spectroscopy
which have been used in fields other than magnetic resonance including laser spectroscopy and neutron scattering
. Echoes were first detected in nuclear magnetic resonance by Erwin Hahn
in 1950
, and spin echoes are sometimes referred to as Hahn echoes. In nuclear magnetic resonance
and magnetic resonance imaging
, radiofrequency radiation is most commonly used.
who pointed out the advantages of a 180 degree refocusing pulse.
The pulse sequence may be better understood by breaking it down into the following steps:
The spin echo sequence. A) - The vertical red arrow is the average magnetic moment of a group of spins, such as protons. All are vertical in the vertical magnetic field and spinning on their long axis, but this illustration is in a rotating reference frame
where the spins are stationary on average. B) A 90 degree pulse has been applied that flips the arrow into the horizontal (x-y) plane. C) Due to local magnetic field inhomogeneities (variations in the magnetic field at different parts of the sample that are constant in time), as the net moment precesses, some spins slow down due to lower local field strength (and so begin to progressively trail behind) while some speed up due to higher field strength and start getting ahead of the others. This makes the signal decay. D) A 180 degree pulse is now applied so that the slower spins lead ahead of the main moment and the fast ones trail behind. E) Progressively, the fast moments catch up with the main moment and the slow moments drift back toward the main moment. F) Complete refocusing has occurred and at this time, an accurate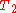 echo can be measured with all
echo can be measured with all 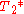 effects removed. Quite separately, return of the red arrow towards the vertical (not shown) would reflect the
effects removed. Quite separately, return of the red arrow towards the vertical (not shown) would reflect the 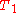 relaxation.
relaxation.
Several simplifications are used in this animation: no decoherence is included and each spin experiences perfect pulses during which the environment provides no spreading.
180 degrees is radians so 180° pulses are often called
radians so 180° pulses are often called  pulses.
pulses.
 pulse. In simple cases, an exponential decay is measured which is described by the
pulse. In simple cases, an exponential decay is measured which is described by the 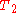 time.
time.
 , and then a second 90° pulse is applied such that the “pancake” is now in the x-z plane. After a further time
, and then a second 90° pulse is applied such that the “pancake” is now in the x-z plane. After a further time 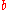 a third pulse is applied and a stimulated echo is observed after waiting a time
a third pulse is applied and a stimulated echo is observed after waiting a time  after the last pulse.
after the last pulse.
Magnetic resonance
Magnetic resonance can mean:*Nuclear magnetic resonance*Electron spin resonance*Magnetic resonance imaging *Functional magnetic resonance imaging *Muon spin spectroscopy...
, a spin echo is the refocusing of precessing
Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotation axis of a rotating body. It can be defined as a change in direction of the rotation axis in which the second Euler angle is constant...
spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
magnetisation by a pulse of resonant radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
. Modern nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a physical phenomenon in which magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation...
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
rely heavily on this effect.
The NMR signal
Free induction decay
In Fourier Transform NMR, free induction decay is the observable NMR signal generated by non-equilibrium nuclear spin magnetisation precessing about the magnetic field ....
observed following an initial excitation pulse decays with time due to both spin-spin relaxation
Relaxation (NMR)
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging the term relaxation describes several processes by which nuclear magnetization prepared in a non-equilibrium state return to the equilibrium distribution. In other words, relaxation describes how fast spins "forget" the...
and any inhomogeneous effects which cause different spins to precess at different rates e.g. a distribution of chemical shift
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
s or magnetic field gradients
Pulsed field gradient
A pulsed field gradient is a short, timed pulse with spatial-dependent field intensity. Any gradient is identified by four characteristics: axis, strength, shape and duration....
. Relaxation leads to an irreversible loss of magnetisation (decoherence), but the inhomogeneous dephasing can be reversed by applying a 180° or inversion pulse that inverts the magnetisation vectors. If the inversion pulse is applied after a period
 of dephasing, the inhomogeneous evolution will rephase to form an echo at time
of dephasing, the inhomogeneous evolution will rephase to form an echo at time 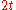 . The intensity of the echo relative to the initial signal is given by
. The intensity of the echo relative to the initial signal is given by 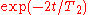 where
where 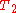 is the time constant for spin-spin relaxation.
is the time constant for spin-spin relaxation.Echo phenomena are important features of coherent spectroscopy
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
which have been used in fields other than magnetic resonance including laser spectroscopy and neutron scattering
Neutron spin echo
Neutron spin echo spectroscopy is an inelastic neutron scattering technique invented by Ferenc Mezei in the 1970's, and developed in collaboration with John Hayter.In recognition of his work and in other areas, Mezei was awarded the first in 1999....
. Echoes were first detected in nuclear magnetic resonance by Erwin Hahn
Erwin Hahn
Erwin L. Hahn is a U.S. physicist, best known for his work on nuclear magnetic resonance . In 1950 he discovered the spin echo....
in 1950
, and spin echoes are sometimes referred to as Hahn echoes. In nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a physical phenomenon in which magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation...
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
, radiofrequency radiation is most commonly used.
Principle
The spin echo concept of Erwin Hahn was explained in his 1950 paper, and was further developed by Carr and PurcellEdward Mills Purcell
Edward Mills Purcell was an American physicist who shared the 1952 Nobel Prize for Physics for his independent discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance in liquids and in solids. Nuclear magnetic resonance has become widely used to study the molecular structure of pure materials and the...
who pointed out the advantages of a 180 degree refocusing pulse.
The pulse sequence may be better understood by breaking it down into the following steps:
The spin echo sequence. A) - The vertical red arrow is the average magnetic moment of a group of spins, such as protons. All are vertical in the vertical magnetic field and spinning on their long axis, but this illustration is in a rotating reference frame
Rotating reference frame
A rotating frame of reference is a special case of a non-inertial reference frame that is rotating relative to an inertial reference frame. An everyday example of a rotating reference frame is the surface of the Earth. A rotating frame of reference is a special case of a non-inertial reference...
where the spins are stationary on average. B) A 90 degree pulse has been applied that flips the arrow into the horizontal (x-y) plane. C) Due to local magnetic field inhomogeneities (variations in the magnetic field at different parts of the sample that are constant in time), as the net moment precesses, some spins slow down due to lower local field strength (and so begin to progressively trail behind) while some speed up due to higher field strength and start getting ahead of the others. This makes the signal decay. D) A 180 degree pulse is now applied so that the slower spins lead ahead of the main moment and the fast ones trail behind. E) Progressively, the fast moments catch up with the main moment and the slow moments drift back toward the main moment. F) Complete refocusing has occurred and at this time, an accurate
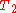 echo can be measured with all
echo can be measured with all  effects removed. Quite separately, return of the red arrow towards the vertical (not shown) would reflect the
effects removed. Quite separately, return of the red arrow towards the vertical (not shown) would reflect the 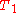 relaxation.
relaxation.Several simplifications are used in this animation: no decoherence is included and each spin experiences perfect pulses during which the environment provides no spreading.
180 degrees is
 radians so 180° pulses are often called
radians so 180° pulses are often called  pulses.
pulses.Hahn echo decay
A Hahn echo decay experiment can be used to measure the dephasing time, as shown in the animation below. The size of the echo is recorded for different spacings of the two pulses. This reveals the decoherence which is not refocused by the pulse. In simple cases, an exponential decay is measured which is described by the
pulse. In simple cases, an exponential decay is measured which is described by the 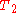 time.
time.Stimulated echo
Hahn's 1950 paper showed that another method for generating spin echoes is to apply three successive 90° pulses. After the first 90° pulse, the magnetization vector spreads out as described above, forming what can be thought of as a “pancake” in the x-y plane. The spreading continues for a time , and then a second 90° pulse is applied such that the “pancake” is now in the x-z plane. After a further time
, and then a second 90° pulse is applied such that the “pancake” is now in the x-z plane. After a further time  a third pulse is applied and a stimulated echo is observed after waiting a time
a third pulse is applied and a stimulated echo is observed after waiting a time  after the last pulse.
after the last pulse.Photon echo
Hahn echos have also been observed at optical frequencies . For this, resonant light is applied to a material with an inhomogeneously broadened absorption resonance. Instead of using two spin states in a magnetic field, photon echoes use two energy levels that are present in the material even in zero magnetic field .See also
- Nuclear magnetic resonanceNuclear magnetic resonanceNuclear magnetic resonance is a physical phenomenon in which magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation...
- Magnetic resonance imagingMagnetic resonance imagingMagnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
- Neutron spin echoNeutron spin echoNeutron spin echo spectroscopy is an inelastic neutron scattering technique invented by Ferenc Mezei in the 1970's, and developed in collaboration with John Hayter.In recognition of his work and in other areas, Mezei was awarded the first in 1999....
- Electron paramagnetic resonanceElectron paramagnetic resonanceElectron paramagnetic resonance or electron spin resonance spectroscopyis a technique for studying chemical species that have one or more unpaired electrons, such as organic and inorganic free radicals or inorganic complexes possessing a transition metal ion...
Animations and Simulations
- http://scratch.mit.edu/projects/nevit/872879 Spin Echo Simulation
- The animation show pulse sequences like spin echo sequence

