Special wind turbines
Encyclopedia
As of 2010, the most common type of wind turbine is the three-bladed horizontal-axis wind turbine (HAWT).
This article deals with various types of wind turbine
that differ from the standard type. Some types have had limited commercial use, while others have only been demonstrated or are only theoretical concepts with no practical applications.
uses only 2-blade turbines. Turbines with two blades are manufactured by Nordic Windpower
(Model N 1000) and by GC China.
is an example of a DAWT.
Counter-rotating turbines can be used to increase the rotation speed of the electrical generator. As of 2005, no large practical counter-rotating HAWTs are commercially sold. When the counter-rotating turbines are on the same side of the tower, the blades in front are angled forwards slightly so as to avoid hitting the rear ones. If the turbine blades are on opposite sides of the tower, it is best that the blades at the back be smaller than the blades at the front and set to stall at a higher wind speed. This allows the generator to function at a wider wind speed range than a single-turbine generator for a given tower. To reduce sympathetic vibrations, the two turbines should turn at speeds with few common multiples, for example 7:3 speed ratio. Overall, this is a more complicated design than the single-turbine wind generator, but it taps more of the wind's energy at a wider range of wind speeds.
Appa designed and demonstrated a contra-rotor wind turbine in FY 2000–2002 funded by California Energy Commission. This study showed 30 to 40% more power extraction than a comparable single-rotor system. Further, it was observed that the slower the rotor speed, the better the performance. Consequently, Megawatt machines benefit most.
This also cancels the gyroscopic forces. There will be an improvement in overall efficiency.
More information here http://www.worldofrenewables.com/page.php?pageid=65
Two files in the Linked In profile of Ferrand Stobart should be examined. contrawind02.pdf and trimblenotes.pdf both down loadable from the Box files
Imagine a stack of CDs on a central shaft with a small air gap in between, the surface tension of moving air as it passes through the small gaps creates friction and using this energy causes the CDs to rotate around the shaft. The Fuller has addition vanes to help direct the air for improved performance, hence it isn't totally bladeless, as has been suggested.
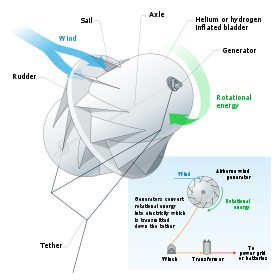
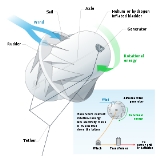
It has been suggested that wind turbines could be flown in high-speed winds using high altitude wind power
tactics, taking advantage of the steadier winds at high altitudes. A system of automatically controlled tethered kites could also be used to capture energy from high-altitude winds.
.
to extract the energy due to air heated by the Sun and rising through a large vertical Solar updraft tower
.
Wind turbines are part of experimental wave powered generators where air displaced by waves drives turbines.
 The great majority of wind turbines around the world belong to individuals or corporations who use them to generate electric power or to perform mechanical work. As such, wind turbines are primarily designed to be working devices. However, the large size and height above surroundings of modern industrial wind turbines, combined with their moving rotors, often makes them among the most conspicuous objects in their areas. A few localities have exploited the attention-getting nature of wind turbines by placing them on public display, either with visitor centers around their bases, or with viewing areas farther away. The wind turbines themselves are generally of conventional horizontal-axis, three-bladed design, and generate power to feed electrical grids, but they also serve the unconventional roles of technology demonstration, public relations, and education.
The great majority of wind turbines around the world belong to individuals or corporations who use them to generate electric power or to perform mechanical work. As such, wind turbines are primarily designed to be working devices. However, the large size and height above surroundings of modern industrial wind turbines, combined with their moving rotors, often makes them among the most conspicuous objects in their areas. A few localities have exploited the attention-getting nature of wind turbines by placing them on public display, either with visitor centers around their bases, or with viewing areas farther away. The wind turbines themselves are generally of conventional horizontal-axis, three-bladed design, and generate power to feed electrical grids, but they also serve the unconventional roles of technology demonstration, public relations, and education.
in Switzerland, Council House 2 in Melbourne
, Australia
. Ridgeblade in the UK is like a vertical wind turbine on its side mounted on the apex of a pitched roof. Discovery Tower
is an office building in Houston, Texas
, that incorporates 10 wind turbines in its architecture.
The Museum of Science
in Boston, Massachusetts began constructing a rooftop Wind Turbine Lab in 2009. The Lab will test nine wind turbines from five different manufacturers on the roof of the Museum. Rooftop wind turbines may suffer from turbulence, especially in cities, which reduces power output and accelerates turbine wear. The lab seeks to address the general lack of performance data for urban wind turbines.
Due to the structural limitations of buildings, the limited space in urban areas, and safety considerations, wind turbines mounted on buildings are usually small (with nameplate capacities in the low kilowatts), rather than the megawatt-class wind turbines which are most economical for wind farm
s. A partial exception is the Bahrain World Trade Centre with three 225 kW wind turbines mounted between twin skyscrapers.
This article deals with various types of wind turbine
Wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or...
that differ from the standard type. Some types have had limited commercial use, while others have only been demonstrated or are only theoretical concepts with no practical applications.
Two blades
Nearly all modern wind turbines uses rotors with three blades, but some use only two blades. This was the type used at GROWIAN, some other prototypes and several wind turbine types manufactured by NedWind. Eemmeerdijk Wind ParkEemmeerdijk Wind Park
Eemmeerdijk Wind Park is a wind park consisting of 19 turbines situated at Zeewolde, Netherlands.It is one of the few windparks using just wind turbines with two blades. It was built in 1998 and uses...
uses only 2-blade turbines. Turbines with two blades are manufactured by Nordic Windpower
Nordic Windpower
Nordic Windpower is a privately owned manufacturer of wind turbines that was founded as a government run business in Sweden and is now based in Kansas City, Missouri in the United States....
(Model N 1000) and by GC China.
Ducted rotor
Still something of a research project, the ducted rotor consists of a turbine inside a duct which flares outwards at the back. They are also referred as Diffuser-Augmented Wind Turbines (i.e. DAWT). The main advantage of the ducted rotor is that it can operate in a wide range of winds and generate a higher power per unit of rotor area. Another advantage is that the generator operates at a high rotation rate, so it doesn't require a bulky gearbox, so the mechanical portion can be smaller and lighter. A disadvantage is that (apart from the gearbox) it is more complicated than the unducted rotor and the duct is usually quite heavy, which puts an added load on the tower. The Éolienne BolléeÉolienne Bollée
The Éolienne Bollée is an unusual wind turbine, unique for having a stator and a rotor, as a water turbine has. The eponymous invention was first patented in 1868 by Ernest Sylvain Bollée in France...
is an example of a DAWT.
Co-axial, multi-rotor
Two or more rotors may be mounted to the same driveshaft, with their combined co-rotation together turning the same generator — fresh wind is brought to each rotor by sufficient spacing between rotors combined with an offset angle (alpha) from the wind direction. Wake vorticity is recovered as the top of a wake hits the bottom of the next rotor. Power has been multiplied several times using co-axial, multiple rotors in testing conducted by inventor and researcher Douglas Selsam, for the California Energy Commission in 2004. The first commercially available co-axial multi-rotor turbine is the patented dual-rotor American Twin Superturbine from Selsam Innovations in California, with 2 propellers separated by 12 feet. It is the most powerful 7 feet (2.1 m) turbine available, due to this extra rotor.Counter-rotating horizontal-axis
When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a proportional but opposite force on that system. A single rotor wind turbine causes a significant amount of tangential or rotational air flow to be created by the spinning blades. The energy of this tangential air flow is wasted in a single-rotor propeller design. To use this wasted effort, the placement of a second rotor behind the first takes advantage of the disturbed airflow. Contra-rotation wind energy collection with two rotors, one behind the other, can gain up to 40% more energy from a given swept area as compared with a single rotor. Much work has been done recently on this in the USA. A patent application dated 1992 exists based on work done with the Trimblemill. Other advantages of contra-rotation include no gear boxes, auto centering on the wind - no yaw motors/mechanism required. Ability to be point suspended, thus reducing support structure overturning moments theoretical ability to be “grid linked” without electronics, thus giving the possibility of "arrays".Counter-rotating turbines can be used to increase the rotation speed of the electrical generator. As of 2005, no large practical counter-rotating HAWTs are commercially sold. When the counter-rotating turbines are on the same side of the tower, the blades in front are angled forwards slightly so as to avoid hitting the rear ones. If the turbine blades are on opposite sides of the tower, it is best that the blades at the back be smaller than the blades at the front and set to stall at a higher wind speed. This allows the generator to function at a wider wind speed range than a single-turbine generator for a given tower. To reduce sympathetic vibrations, the two turbines should turn at speeds with few common multiples, for example 7:3 speed ratio. Overall, this is a more complicated design than the single-turbine wind generator, but it taps more of the wind's energy at a wider range of wind speeds.
Appa designed and demonstrated a contra-rotor wind turbine in FY 2000–2002 funded by California Energy Commission. This study showed 30 to 40% more power extraction than a comparable single-rotor system. Further, it was observed that the slower the rotor speed, the better the performance. Consequently, Megawatt machines benefit most.
This also cancels the gyroscopic forces. There will be an improvement in overall efficiency.
More information here http://www.worldofrenewables.com/page.php?pageid=65
Two files in the Linked In profile of Ferrand Stobart should be examined. contrawind02.pdf and trimblenotes.pdf both down loadable from the Box files
Furling tail and twisting blades
In addition to variable pitch blades, furling tails and twisting blades are other improvements on wind turbines. Similar to the variable pitch blades, they may also greatly increase the efficiency of the turbine and be used in "do-it-yourself" constructionTelescopic blades
A next step in making improvements to wind turbines may be in the use of telescopic blades. Telescopic blades can change the blade's length, thus increasing or decreasing the turbine's swept area. Telescopic blades make a turbine more productive by increasing the turbine's rotor diameter during low-wind conditions. In high-wind conditions, when the turbine is in need of reducing loads, the blades can be retracted to make the rotor smaller.Aerogenerator
The Aerogenerator is a special design of vertical axis wind turbine which could allow greater energy outputs.Augmented
The "G" Model VAWT Turbine is equipped with three self-positioning Augmentation And Directioning Wings (AADW) placed as the outer sections of classical Darrieus blades. The GMWT can increase almost fivefold the efficiency of classical Darrieus Blades: AADWs adjust themselves to the wind direction without any external power. The resulting combination ("G" Model Wind Turbine) works with very low cut-in wind speed, has self starting ability, together with a high capacity factor. Detailed information is available at: http://windturbine-performance.com/www/turkcegiris.htmFuller
The "Fuller" wind turbine is a fully enclosed wind turbine which uses boundary layers instead of blades.Imagine a stack of CDs on a central shaft with a small air gap in between, the surface tension of moving air as it passes through the small gaps creates friction and using this energy causes the CDs to rotate around the shaft. The Fuller has addition vanes to help direct the air for improved performance, hence it isn't totally bladeless, as has been suggested.
Aerial

It has been suggested that wind turbines could be flown in high-speed winds using high altitude wind power
High altitude wind power
High-altitude wind power has been imagined as a source of useful energy since 1833 with John Etzler's vision of capturing the power of winds high in the sky by use of tether and cable technology...
tactics, taking advantage of the steadier winds at high altitudes. A system of automatically controlled tethered kites could also be used to capture energy from high-altitude winds.
H-rotor
This is a vertical axis turbine, but it isn't favored because of its poor efficiency. One blade is pushed by the wind while the other is being pushed in the opposite direction. Consequently only one blade is working at a timeWind belt
Invented by Shawn Frayne. A belt vibrates by the passing flow of air. A magnet is mounted at one end of the belt.Vaneless ion wind generator
For an unusual way to induce a voltage using an aerosol of ionised water, see vaneless ion wind generatorVaneless ion wind generator
A vaneless ion wind generator or power fence is a proposed wind power device that produces electrical energy directly by using the wind to pump electric charge from one electrode to another, with no moving parts....
.
Piezoelectric
Another special type of wind turbines are the piezoelectric wind turbines. Turbines with diameters on the scale of 10 centimeters work by flexing piezoelectric crystals as they rotate, sufficient to power small electronic devices.Traffic-driven
A few proposals call for generating power from the otherwise wasted energy in the draft created by traffic.Blade Tip Power System (BTPS)
Designed by Imad Mahawili with Honeywell/WindTronics. This design uses many nylon blades and turns a permanent magnet generator inside out. The magnets are on the tips of the blades, and the stator is on the outside of the generator.Solar chimney
Wind turbines may also be used in conjunction with a solar collectorSolar thermal collector
A solar thermal collector is a solar collector designed to collect heat by absorbing sunlight. The term is applied to solar hot water panels, but may also be used to denote more complex installations such as solar parabolic, solar trough and solar towers or simpler installations such as solar air...
to extract the energy due to air heated by the Sun and rising through a large vertical Solar updraft tower
Solar updraft tower
The solar updraft tower is a renewable-energy power plant. It combines the chimney effect, the greenhouse effect and the wind turbine. Air is heated by sunshine and contained in a very large greenhouse-like structure around the base of a tall chimney, and the resulting convection causes air to...
.
Wind turbines are part of experimental wave powered generators where air displaced by waves drives turbines.
Wind turbines on public display

Rooftop wind-turbines
Wind-turbines can be installed on the top of a roof of a building. This is not as common as may first be assumed. Some examples include Marthalen Landi-SiloMarthalen Landi-Silo
Marthalen Landi-Silo is a 35 metres high silo east of Marthalen in Switzerland. Marthalen Landi-Silo is one of the few buildings with a wind turbine on the roof....
in Switzerland, Council House 2 in Melbourne
Melbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
. Ridgeblade in the UK is like a vertical wind turbine on its side mounted on the apex of a pitched roof. Discovery Tower
Discovery Tower
Hess Tower is a 29-story building located adjacent to Discovery Green park in downtown Houston, Texas. It was formerly called Discovery Tower until Hess Corporation leased the entire tower in January 2009....
is an office building in Houston, Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
, that incorporates 10 wind turbines in its architecture.
The Museum of Science
Museum of Science, Boston
The Museum of Science is a Boston, Massachusetts landmark, located in Science Park, a plot of land spanning the Charles River. Along with over 500 interactive exhibits, the Museum features a number of live presentations throughout the building every day, along with shows at the Charles Hayden...
in Boston, Massachusetts began constructing a rooftop Wind Turbine Lab in 2009. The Lab will test nine wind turbines from five different manufacturers on the roof of the Museum. Rooftop wind turbines may suffer from turbulence, especially in cities, which reduces power output and accelerates turbine wear. The lab seeks to address the general lack of performance data for urban wind turbines.
Due to the structural limitations of buildings, the limited space in urban areas, and safety considerations, wind turbines mounted on buildings are usually small (with nameplate capacities in the low kilowatts), rather than the megawatt-class wind turbines which are most economical for wind farm
Wind farm
A wind farm is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electric power. A large wind farm may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines, and cover an extended area of hundreds of square miles, but the land between the turbines may be used for agricultural or other...
s. A partial exception is the Bahrain World Trade Centre with three 225 kW wind turbines mounted between twin skyscrapers.
See also
- Vertical-axis wind turbine
- Savonius wind turbineSavonius wind turbineSavonius wind turbines are a type of vertical-axis wind turbine , used for converting the force of the wind into torque on a rotating shaft...
- Compact wind acceleration turbineCompact wind acceleration turbineCompact Wind Acceleration Turbines are a class of wind turbine that uses structures to accelerate wind before it enters the wind-generating element....

