
Sequence profiling tool
Encyclopedia
A sequence profiling tool in bioinformatics
is a type of software that presents information related to a gene
tic sequence, gene name, or keyword input. Such tools generally take a query such as a DNA
, RNA
, or protein
sequence or ‘keyword’ and search one or more database
s for information related to that sequence. Summaries and aggregate results are provided in standardized format describing the information that would otherwise have required visits to many smaller sites or direct literature searches to compile. Many sequence profiling tools are software portals or gateways that simplify the process of finding information about a query in the large and growing number of bioinformatics databases. The access to these kinds of tools is either web based or locally downloadable executables.
" era has given rise to a range of web-based tools and software to compile, organize, and deliver large amounts of primary sequence information, as well as protein structures
, gene annotations, sequence alignment
s, and other common bioinformatics tasks.
In general, there exist three types of databases and service providers. The first one includes the popular public-domain or open-access databases supported by funding and grants such as NCBI
, ExPASy
, Ensembl
, and PDB
. The second one includes smaller or more specific databases organized and compiled by individual research groups Examples include Yeast Genome Database, RNA database. The third and final one includes private corporate or institutional databases that require payment or institutional affiliation to access. Such examples rare given the globalization of the public databases unless the purported service is ‘in-development’ or the end point of the analysis is of commercial value.
Typical scenarios of a profiling approach become relevant, particularly, in the cases of the first two groups, where researchers commonly wish to combine information derived from several sources about a single query or target sequence. For example, users might use the sequence alignment and search tool BLAST
to identify homologs
of their gene of interest in other species, and then use these results to locate a solved protein structure for one of the homologs. Similarly, they might also want to know the likely secondary structure
of the mRNA encoding the gene of interest, or whether a company sells a DNA construct
containing the gene. Sequence profiling tools serve to automate and integrate the process of seeking such disparate information by rendering the process of searching several different external databases transparent to the user.
Many public databases are already extensively linked so that complementary information in another database is easily accessible; for example, Genbank
and the PDB
are closely intertwined. However, specialized tools organized and hosted by specific research groups can be difficult to integrate into this linkage effort because they are narrowly focused, are frequently modified, or use custom versions of common file formats. Advantages of sequence profiling tools include the ability to use multiple of these specialized tools in a single query and present the output with a common interface, the ability to direct the output of one set of tools or database searches into the input of another, and the capacity to disseminate hosting and compilation obligations to a network of research groups and institutions rather than a single centralized repository.
 ]
]
Most of the profiling tools available on the web today fall into this category. The user, upon visiting the site/tool, enters any relevant information like a keyword e.g. dystrophy, diabetes etc., or GenBank
accession numbers, PDB ID. All the relevant hits by the search are presented in a format unique to each tool’s main focus. Profiling tools based on keyword searches are essentially search engine
s that are highly specialized for bioinformatics work, thereby eliminating a clutter of irrelevant or non-scholarly hits that might occur with a traditional search engine like Google
. Most keyword-based profiling tools allow flexible types of keyword input, accession numbers from indexed databases as well as traditional keyword descriptors.
Each profiling tool has its own focus and area of interest. For example, the NCBI
search engine Entrez
segregates its hits by category, so that users looking for protein structure information can screen out sequences with no corresponding structure, while users interested in perusing the literature on a subject can view abstracts of papers published in scholarly journals without distraction from gene or sequence results. The Pubmed
biosciences literature database is a popular tool for literature searches, though this service is nearly equaled with the more general Google Scholar
.
Keyword-based data aggregation services like the Bioinformatic Harvester performs provide reports from a variety of third-party servers in an as-is format so that users need not visit the website or install the software for each individual component service. This is particularly invaluable given the rapid emergence of various sites providing different sequence analysis and manipulation tools. Another aggregative web portal, the Human Protein Reference Database (Hprd
), contains manually annotated and curated entries for human proteins. The information provided is thus both selective and comprehensive, and the query format is flexible and intuitive. The pros of developing manually curated databases include presentation of proofread material and the concept of ‘molecule authorities’ to undertake the responsibility of specific proteins. However, the cons are that they are typically slower to update and may not contain very new or disputed data.
 A typical sequence profiling tool carries this further by using an actual DNA, RNA, or protein sequence as an input and allows the user to visit different web-based analysis tools to obtain the information desired. Such tools are also commonly supplied with commercial laboratory equipment like gene sequencers or sometimes sold as software applications for molecular biology. In another public-database example, the BLAST
A typical sequence profiling tool carries this further by using an actual DNA, RNA, or protein sequence as an input and allows the user to visit different web-based analysis tools to obtain the information desired. Such tools are also commonly supplied with commercial laboratory equipment like gene sequencers or sometimes sold as software applications for molecular biology. In another public-database example, the BLAST
sequence search report from NCBI
provides a link from its alignment report to other relevant information in its own databases, if such specific information exists.
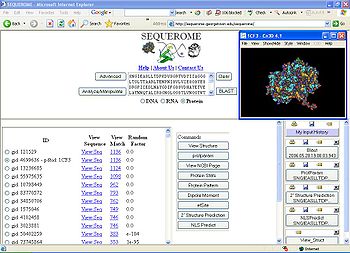
For example, a retrieved record that contains a human sequence will carry a separate link that connects to its location on a human genome map; a record that contains a sequence for which a 3-D structure has been solved would carry a link that connects it to its structure database. Sequerome
, a public service tool, links the entire BLAST report to many third party servers/sites that provide highly specific services in sequence manipulations such as restriction enzyme
maps, open reading frame
analyses for nucleotide
sequences, and secondary structure
prediction. The tool provides added advantage of maintaining a research log of the operations performed by the user, which can be then conveniently archived using 'mail', 'print' or 'save' functionality. Thus an entire operation of researching on a sequence using different research tools and thus carrying a project to its completion can be completed within one browser interface. Consequently, future generation of sequence profiling tools would include ability to collaborate online with researchers to share project logs and research tools, annotate results of sequence analysis or lab work, customize and automate the processing of sets of sequence data etc. InstaSeq is a Google powered search tool that allows the user to directly enter a sequence and search the entire World Wide Web. This unique search engine, which is the only one of its kind, is in contrast to searching specific databases e.g. GenBank
.
As a result the user can end up with a privately hosted document or a page from a lesser known database from just about anywhere in the world. Though the presence of sequence based profilers are far and few in the present scenario, their key role will become evident when huge amounts of sequence data need to be cross processed across portals and domains.
Data produced by microarray experiments, two-hybrid screening
, and other high-throughput biological experiments is voluminous and difficult to analyze by hand; the efforts of structural genomics
collaborations that are aimed at quickly solving large numbers of highly varied protein structures also increase the need for integration between sequence and structure databases and portals. This impetus toward developing more comprehensive and more user-friendly methods of sequence profiling makes this an active area of research among current genomics researchers.
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
is a type of software that presents information related to a gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
tic sequence, gene name, or keyword input. Such tools generally take a query such as a DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
, or protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
sequence or ‘keyword’ and search one or more database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
s for information related to that sequence. Summaries and aggregate results are provided in standardized format describing the information that would otherwise have required visits to many smaller sites or direct literature searches to compile. Many sequence profiling tools are software portals or gateways that simplify the process of finding information about a query in the large and growing number of bioinformatics databases. The access to these kinds of tools is either web based or locally downloadable executables.
Introduction and usage
The "post-genomicsGenomics
Genomics is a discipline in genetics concerning the study of the genomes of organisms. The field includes intensive efforts to determine the entire DNA sequence of organisms and fine-scale genetic mapping efforts. The field also includes studies of intragenomic phenomena such as heterosis,...
" era has given rise to a range of web-based tools and software to compile, organize, and deliver large amounts of primary sequence information, as well as protein structures
Tertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
, gene annotations, sequence alignment
Sequence alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are...
s, and other common bioinformatics tasks.
In general, there exist three types of databases and service providers. The first one includes the popular public-domain or open-access databases supported by funding and grants such as NCBI
National Center for Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information is part of the United States National Library of Medicine , a branch of the National Institutes of Health. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by Senator Claude Pepper...
, ExPASy
ExPASy
ExPASy is a bioinformatics resource portal operated by the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and in particular the SIB Web Team. It is an extensible and integrative portal accessing many scientific resources, databases and software tools in different areas of life sciences...
, Ensembl
Ensembl
Ensembl is a joint scientific project between the European Bioinformatics Institute and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, which was launched in 1999 in response to the imminent completion of the Human Genome Project...
, and PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
. The second one includes smaller or more specific databases organized and compiled by individual research groups Examples include Yeast Genome Database, RNA database. The third and final one includes private corporate or institutional databases that require payment or institutional affiliation to access. Such examples rare given the globalization of the public databases unless the purported service is ‘in-development’ or the end point of the analysis is of commercial value.
Typical scenarios of a profiling approach become relevant, particularly, in the cases of the first two groups, where researchers commonly wish to combine information derived from several sources about a single query or target sequence. For example, users might use the sequence alignment and search tool BLAST
BLAST
In bioinformatics, Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, or BLAST, is an algorithm for comparing primary biological sequence information, such as the amino-acid sequences of different proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequences...
to identify homologs
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
of their gene of interest in other species, and then use these results to locate a solved protein structure for one of the homologs. Similarly, they might also want to know the likely secondary structure
Secondary structure
In biochemistry and structural biology, secondary structure is the general three-dimensional form of local segments of biopolymers such as proteins and nucleic acids...
of the mRNA encoding the gene of interest, or whether a company sells a DNA construct
DNA construct
A DNA construct is an artificially constructed segment of nucleic acid that is going to be "transplanted" into a target tissue or cell...
containing the gene. Sequence profiling tools serve to automate and integrate the process of seeking such disparate information by rendering the process of searching several different external databases transparent to the user.
Many public databases are already extensively linked so that complementary information in another database is easily accessible; for example, Genbank
GenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. This database is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence...
and the PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
are closely intertwined. However, specialized tools organized and hosted by specific research groups can be difficult to integrate into this linkage effort because they are narrowly focused, are frequently modified, or use custom versions of common file formats. Advantages of sequence profiling tools include the ability to use multiple of these specialized tools in a single query and present the output with a common interface, the ability to direct the output of one set of tools or database searches into the input of another, and the capacity to disseminate hosting and compilation obligations to a network of research groups and institutions rather than a single centralized repository.
Keyword based profilers

Most of the profiling tools available on the web today fall into this category. The user, upon visiting the site/tool, enters any relevant information like a keyword e.g. dystrophy, diabetes etc., or GenBank
GenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. This database is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence...
accession numbers, PDB ID. All the relevant hits by the search are presented in a format unique to each tool’s main focus. Profiling tools based on keyword searches are essentially search engine
Search engine
A search engine is an information retrieval system designed to help find information stored on a computer system. The search results are usually presented in a list and are commonly called hits. Search engines help to minimize the time required to find information and the amount of information...
s that are highly specialized for bioinformatics work, thereby eliminating a clutter of irrelevant or non-scholarly hits that might occur with a traditional search engine like Google
Google
Google Inc. is an American multinational public corporation invested in Internet search, cloud computing, and advertising technologies. Google hosts and develops a number of Internet-based services and products, and generates profit primarily from advertising through its AdWords program...
. Most keyword-based profiling tools allow flexible types of keyword input, accession numbers from indexed databases as well as traditional keyword descriptors.
Each profiling tool has its own focus and area of interest. For example, the NCBI
National Center for Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information is part of the United States National Library of Medicine , a branch of the National Institutes of Health. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by Senator Claude Pepper...
search engine Entrez
Entrez
The Entrez Global Query Cross-Database Search System is a powerful federated search engine, or web portal that allows users to search many discrete health sciences databases at the National Center for Biotechnology Information website...
segregates its hits by category, so that users looking for protein structure information can screen out sequences with no corresponding structure, while users interested in perusing the literature on a subject can view abstracts of papers published in scholarly journals without distraction from gene or sequence results. The Pubmed
PubMed
PubMed is a free database accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine at the National Institutes of Health maintains the database as part of the Entrez information retrieval system...
biosciences literature database is a popular tool for literature searches, though this service is nearly equaled with the more general Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes most peer-reviewed online journals of Europe and America's largest...
.
Keyword-based data aggregation services like the Bioinformatic Harvester performs provide reports from a variety of third-party servers in an as-is format so that users need not visit the website or install the software for each individual component service. This is particularly invaluable given the rapid emergence of various sites providing different sequence analysis and manipulation tools. Another aggregative web portal, the Human Protein Reference Database (Hprd
HPRD
The Human Protein Reference Database is a protein database accessible through the internet.The HPRD is a result of an international collaborative effort between the in Bangalore, India and the at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, USA. HPRD contains manually curated scientific information...
), contains manually annotated and curated entries for human proteins. The information provided is thus both selective and comprehensive, and the query format is flexible and intuitive. The pros of developing manually curated databases include presentation of proofread material and the concept of ‘molecule authorities’ to undertake the responsibility of specific proteins. However, the cons are that they are typically slower to update and may not contain very new or disputed data.
Sequence data based profilers

BLAST
In bioinformatics, Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, or BLAST, is an algorithm for comparing primary biological sequence information, such as the amino-acid sequences of different proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequences...
sequence search report from NCBI
National Center for Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information is part of the United States National Library of Medicine , a branch of the National Institutes of Health. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by Senator Claude Pepper...
provides a link from its alignment report to other relevant information in its own databases, if such specific information exists.
For example, a retrieved record that contains a human sequence will carry a separate link that connects to its location on a human genome map; a record that contains a sequence for which a 3-D structure has been solved would carry a link that connects it to its structure database. Sequerome
Sequerome
Sequerome is a web-based Sequence profiling tool for integrating the results of a BLAST sequence-alignment report with external research tools and servers that perform advanced sequence manipulations, and allowing the user to record the steps of such an analysis...
, a public service tool, links the entire BLAST report to many third party servers/sites that provide highly specific services in sequence manipulations such as restriction enzyme
Restriction enzyme
A Restriction Enzyme is an enzyme that cuts double-stranded DNA at specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites. Such enzymes, found in bacteria and archaea, are thought to have evolved to provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses...
maps, open reading frame
Open reading frame
In molecular genetics, an open reading frame is a DNA sequence that does not contain a stop codon in a given reading frame.Normally, inserts which interrupt the reading frame of a subsequent region after the start codon cause frameshift mutation of the sequence and dislocate the sequences for stop...
analyses for nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
sequences, and secondary structure
Secondary structure
In biochemistry and structural biology, secondary structure is the general three-dimensional form of local segments of biopolymers such as proteins and nucleic acids...
prediction. The tool provides added advantage of maintaining a research log of the operations performed by the user, which can be then conveniently archived using 'mail', 'print' or 'save' functionality. Thus an entire operation of researching on a sequence using different research tools and thus carrying a project to its completion can be completed within one browser interface. Consequently, future generation of sequence profiling tools would include ability to collaborate online with researchers to share project logs and research tools, annotate results of sequence analysis or lab work, customize and automate the processing of sets of sequence data etc. InstaSeq is a Google powered search tool that allows the user to directly enter a sequence and search the entire World Wide Web. This unique search engine, which is the only one of its kind, is in contrast to searching specific databases e.g. GenBank
GenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. This database is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence...
.
As a result the user can end up with a privately hosted document or a page from a lesser known database from just about anywhere in the world. Though the presence of sequence based profilers are far and few in the present scenario, their key role will become evident when huge amounts of sequence data need to be cross processed across portals and domains.
Future growth and directions
The proliferation of bioinformatics tools for genetic analysis aids researchers in identifying and categorizing genes and gene sets of interest in their work; however, the large variety of tools that perform substantially similar aggregative and analytical functions can also confuse and frustrate new users. The decentralization encouraged by aggregative tools allows individual research groups to maintain specialized servers dedicated to specific types of data analysis in the expectation that their output will be collected into a larger report on a gene or protein of interest to other researchers.Data produced by microarray experiments, two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening
Two-hybrid screening is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions and protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively.The premise behind the test is the activation of...
, and other high-throughput biological experiments is voluminous and difficult to analyze by hand; the efforts of structural genomics
Structural genomics
Structural genomics seeks to describe the 3-dimensional structure of every protein encoded by a given genome. This genome-based approach allows for a high-throughput method of structure determination by a combination of experimental and modeling approaches...
collaborations that are aimed at quickly solving large numbers of highly varied protein structures also increase the need for integration between sequence and structure databases and portals. This impetus toward developing more comprehensive and more user-friendly methods of sequence profiling makes this an active area of research among current genomics researchers.
See also
- EntrezEntrezThe Entrez Global Query Cross-Database Search System is a powerful federated search engine, or web portal that allows users to search many discrete health sciences databases at the National Center for Biotechnology Information website...
- MetadataMetadataThe term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
- Sequence analysisSequence analysisIn bioinformatics, the term sequence analysis refers to the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alignment, searches against biological...
- Sequence motifSequence motifIn genetics, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and has, or is conjectured to have, a biological significance...
- SequeromeSequeromeSequerome is a web-based Sequence profiling tool for integrating the results of a BLAST sequence-alignment report with external research tools and servers that perform advanced sequence manipulations, and allowing the user to record the steps of such an analysis...

