.gif)
Separatrix (dynamical systems)
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a separatrix refers to the boundary separating two modes of behaviour in a differential equation
.
:

where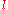 denotes the length of the pendulum,
denotes the length of the pendulum, 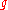 the gravitational acceleration
the gravitational acceleration
and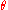 the angle between the pendulum and vertically downwards. In this system there is a conserved quantity H (the Hamiltonian
the angle between the pendulum and vertically downwards. In this system there is a conserved quantity H (the Hamiltonian
), which is given by
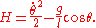
With this defined, one can plot a curve of constant H in the phase space
of system. The phase space is a graph with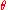 along the horizontal axis and
along the horizontal axis and 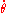 on the vertical axis - see the thumbnail to the right. The type of resulting curve depends upon the value of H.
on the vertical axis - see the thumbnail to the right. The type of resulting curve depends upon the value of H.
 If
If 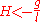 then no curve exist (
then no curve exist (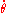 must be imaginary
must be imaginary
).
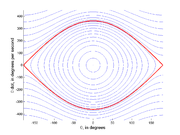
If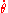 then the curve will be a simple closed curve (see curve
then the curve will be a simple closed curve (see curve
) which is nearly circular for small H and becomes "eye" shape when H approaches the upper bound. These curves correspond to the pendulum swinging periodically from side to side.
If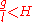 then the curve is open, and this corresponds to pendulum forever swinging through complete circles.
then the curve is open, and this corresponds to pendulum forever swinging through complete circles.
In this system the separatix is the curve that corresponds to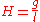 . It separates (hence the name) the phase space into two distinct areas. Within the separatrix corresponds to oscillating motion back and forth, whereas the outside of the separatrix corresponds to motion with the pendulum continuously turning through circles.
. It separates (hence the name) the phase space into two distinct areas. Within the separatrix corresponds to oscillating motion back and forth, whereas the outside of the separatrix corresponds to motion with the pendulum continuously turning through circles.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a separatrix refers to the boundary separating two modes of behaviour in a differential equation
Ordinary differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is a relation that contains functions of only one independent variable, and one or more of their derivatives with respect to that variable....
.
Example
Consider the differential equation describing the motion of a simple pendulumPendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced from its resting equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position...
:

where
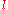 denotes the length of the pendulum,
denotes the length of the pendulum, 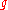 the gravitational acceleration
the gravitational accelerationGravitational acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
and
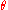 the angle between the pendulum and vertically downwards. In this system there is a conserved quantity H (the Hamiltonian
the angle between the pendulum and vertically downwards. In this system there is a conserved quantity H (the HamiltonianHamiltonian mechanics
Hamiltonian mechanics is a reformulation of classical mechanics that was introduced in 1833 by Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton.It arose from Lagrangian mechanics, a previous reformulation of classical mechanics introduced by Joseph Louis Lagrange in 1788, but can be formulated without...
), which is given by
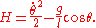
With this defined, one can plot a curve of constant H in the phase space
Phase space
In mathematics and physics, a phase space, introduced by Willard Gibbs in 1901, is a space in which all possible states of a system are represented, with each possible state of the system corresponding to one unique point in the phase space...
of system. The phase space is a graph with
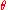 along the horizontal axis and
along the horizontal axis and  on the vertical axis - see the thumbnail to the right. The type of resulting curve depends upon the value of H.
on the vertical axis - see the thumbnail to the right. The type of resulting curve depends upon the value of H.
 then no curve exist (
then no curve exist ( must be imaginary
must be imaginaryComplex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
).
If
 then the curve will be a simple closed curve (see curve
then the curve will be a simple closed curve (see curveCurve
In mathematics, a curve is, generally speaking, an object similar to a line but which is not required to be straight...
) which is nearly circular for small H and becomes "eye" shape when H approaches the upper bound. These curves correspond to the pendulum swinging periodically from side to side.
If
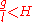 then the curve is open, and this corresponds to pendulum forever swinging through complete circles.
then the curve is open, and this corresponds to pendulum forever swinging through complete circles.In this system the separatix is the curve that corresponds to
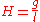 . It separates (hence the name) the phase space into two distinct areas. Within the separatrix corresponds to oscillating motion back and forth, whereas the outside of the separatrix corresponds to motion with the pendulum continuously turning through circles.
. It separates (hence the name) the phase space into two distinct areas. Within the separatrix corresponds to oscillating motion back and forth, whereas the outside of the separatrix corresponds to motion with the pendulum continuously turning through circles.External links
- Separatrix from MathWorldMathWorldMathWorld is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at...
.

