
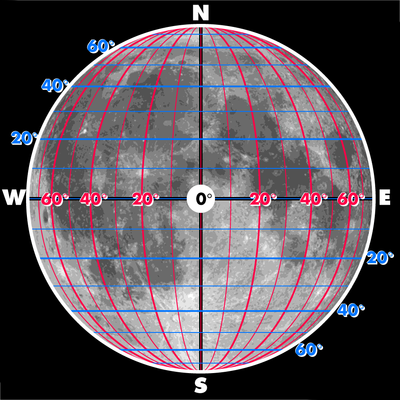
Selenographic coordinates
Encyclopedia
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
. Any position on the lunar surface can be referenced by specifying two numerical values, which are comparable to the latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
and longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
of Earth. The longitude gives the position east or west of the Moon's prime meridian, which is the line of longitude passing through the point on the lunar surface directly facing Earth. (See also Earth's prime meridian
Prime Meridian
The Prime Meridian is the meridian at which the longitude is defined to be 0°.The Prime Meridian and its opposite the 180th meridian , which the International Date Line generally follows, form a great circle that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.An international...
.) This can be thought of as the mid-point of the visible Moon as seen from the Earth. The latitude gives the position north or south of the lunar equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
. Both of these coordinates are given in terms of degrees
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
.
Astronomers defined the fundamental location in the selenographic coordinate system by the small, bowl-shaped satellite crater 'Mösting A
Mösting (crater)
Mösting is a small lunar crater that is located in the southeastern fringes of the Mare Insularum. The ruined crater Sömmering lies to the northwest. To the southeast is the large crater-bay of Flammarion. Mösting has a terraced inner wall and a small central hill at the mid-point of the floor.To...
'. The coordinates of this crater are defined as:
| Latitude: | 3° 12' 43.2" South |
| Longitude: | 5° 12' 39.6" West |
The coordinate system has become precisely defined due to the Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment
Lunar laser ranging experiment
The ongoing Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment measures the distance between the Earth and the Moon using laser ranging. Lasers on Earth are aimed at retroreflectors planted on the moon during the Apollo program, and the time for the reflected light to return is determined...
.
Anything past 90°E or 90°W would not be seen from Earth, except for libration
Libration
In astronomy, libration is an oscillating motion of orbiting bodies relative to each other, notably including the motion of the Moon relative to Earth, or of Trojan asteroids relative to planets.-Lunar libration:...
, which makes 59% of the Moon visible.
Selenographic colongitude
The selenographic colongitude is the longitude of the morning terminator on the MoonLunar terminator
The Lunar terminator is the division between the illuminated and dark parts of the Earth's Moon.. It is the lunar equivalent of the division between night and day on the Earth's sphere, although the Moon's much lower rate of rotation means it takes longer for it to pass across the surface.Due to...
, as measured in degrees westward from the prime meridian. The morning terminator forms a half-circle across the Moon where the Sun is just starting to rise. As the Moon continues in its orbit, this line advances in longitude. The value of the selenographic colongitude increases from 0° to 359° in the direction of the advancing terminator.
Sunrise occurs at the prime meridian when the Lunar phase
Lunar phase
A lunar phase or phase of the moon is the appearance of the illuminated portion of the Moon as seen by an observer, usually on Earth. The lunar phases change cyclically as the Moon orbits the Earth, according to the changing relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun...
reaches First Quarter, after one fourth of a lunar day
Lunar day
In space exploration, a lunar day is the period of time it takes for the Earth's Moon to complete one full rotation on its axis with respect to the Sun. Equivalently, it is the time it takes the Moon to make one complete orbit around the Earth and come back to the same phase...
. At this location the selenographic colongitude at sunrise is defined as 0°. Thus, by the time of the Full Moon
Full Moon
Full moon is a lunar phase.Full Moon may also refer to:- Literature :* Full Moon , a novel by P. G. Wodehouse* Full Moon o Sagashite or Full Moon, a manga* Full Moon Press, an American small-press publisher...
the colongitude increases to 90°; at Last Quarter it is 180°, and at the New Moon
New moon
In astronomical terminology, the new moon is the lunar phase that occurs when the Moon, in its monthly orbital motion around Earth, lies between Earth and the Sun, and is therefore in conjunction with the Sun as seen from Earth...
the colongitude reaches 270°. Note that the Moon is nearly invisible from the Earth at New Moon phase except during a solar eclipse
Solar eclipse
As seen from the Earth, a solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, and the Moon fully or partially blocks the Sun as viewed from a location on Earth. This can happen only during a new moon, when the Sun and the Moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth. At least...
.
The low angle of incidence
Angle of incidence
Angle of incidence is a measure of deviation of something from "straight on", for example:* in the approach of a ray to a surface, or* the angle at which the wing or horizontal tail of an airplane is installed on the fuselage, measured relative to the axis of the fuselage.-Optics:In geometric...
of arriving sunlight tends to pick out features by the sharp shadows they cast, thus the area near the terminator is usually the most favorable for viewing or photograph
Photograph
A photograph is an image created by light falling on a light-sensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic imager such as a CCD or a CMOS chip. Most photographs are created using a camera, which uses a lens to focus the scene's visible wavelengths of light into a reproduction of...
ing lunar features through a telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
. The observer will need to know the location of the terminator to plan observations of selected features. The selenographic colongitude is useful for this purpose.
The selenographic longitude of the evening terminator is equal to the colongitude plus 180°.
Longitude
Longitude on the Moon is measured both east and west from its prime meridianPrime Meridian
The Prime Meridian is the meridian at which the longitude is defined to be 0°.The Prime Meridian and its opposite the 180th meridian , which the International Date Line generally follows, form a great circle that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.An international...
. When no direction is specified, east is positive and west is negative.
Roughly speaking, the Moon's prime meridian lies near the center of the Moon's disc as seen from Earth. For precise applications, many coordinate systems have been defined for the Moon, each with a slightly different prime meridian. The IAU
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
recommends the "mean Earth/polar axis" system, in which the prime meridian is the average direction (from the Moon's center) of the Earth's center.

