SCIAMACHY
Encyclopedia
Envisat
Envisat is an Earth-observing satellite. It was launched on 1 March 2002 aboard an Ariane 5 from the Guyana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guyana into a Sun synchronous polar orbit at an altitude of...
.
It is a satellite spectrometer
Spectrometer
A spectrometer is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the light's intensity but could also, for instance, be the polarization...
designed to measure sunlight
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
, transmitted
Transmittance
In optics and spectroscopy, transmittance is the fraction of incident light at a specified wavelength that passes through a sample. A related term is absorptance, or absorption factor, which is the fraction of radiation absorbed by a sample at a specified wavelength...
, reflected
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
and scattered
Scattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
by the earth's atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
or surface
Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost shell of a rocky planet. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.- Earth's lithosphere :...
in the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
, visible
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
and near infrared wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
region (240 nm
Nanometre
A nanometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a metre. The name combines the SI prefix nano- with the parent unit name metre .The nanometre is often used to express dimensions on the atomic scale: the diameter...
- 2380 nm) at moderate spectral resolution (0.2 nm - 1.5 nm).
Launch
SCIAMACHY, aboard the ENVISAT satellite, was launched by ESA (European Space AgencyEuropean Space Agency
The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...
) from Kourou
Kourou
Kourou is a commune in French Guiana, an overseas region and department of France located in South America.Kourou is the location of the Guiana Space Centre, France and ESA's main spaceport.-Geography:...
, French Guiana
French Guiana
French Guiana is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department located on the northern Atlantic coast of South America. It has borders with two nations, Brazil to the east and south, and Suriname to the west...
, in March 2002.
Operation
The absorptionAbsorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
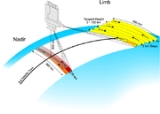
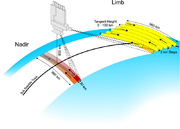
, reflection and scattering characteristics of the atmosphere are determined by measuring the extraterrestrial solar irradiance and the upwelling radiance observed in different viewing geometries. The ratio of extraterrestrial irradiance and the upwelling radiance can be inverted to provide information about the amounts and distribution of important atmospheric constituents, which absorb or scatter light, and the spectral reflectance (or albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
) of the Earth's surface.
Purpose
SCIAMACHY was conceived to improve global knowledge and understanding of a variety of issues of importance for the chemistryChemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
and physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
of the Earth's atmosphere (troposphere
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 80% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols....
, stratosphere
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second major layer of Earth's atmosphere, just above the troposphere, and below the mesosphere. It is stratified in temperature, with warmer layers higher up and cooler layers farther down. This is in contrast to the troposphere near the Earth's surface, which is cooler...
and mesosphere
Mesosphere
The mesosphere is the layer of the Earth's atmosphere that is directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere temperature decreases with increasing height. The upper boundary of the mesosphere is the mesopause, which can be the coldest naturally occurring...
) and potential changes resulting from either anthropogenic
Anthropogenic
Human impact on the environment or anthropogenic impact on the environment includes impacts on biophysical environments, biodiversity and other resources. The term anthropogenic designates an effect or object resulting from human activity. The term was first used in the technical sense by Russian...
behavior or natural phenomena.
External links
- ESAEuropean Space AgencyThe European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...
: SCIAMACHY - SCIAMACHY-News of DLR
- SCIAMACHY-Homepage of the institute IUP-IFE Bremen
- SCIAMACHY Portal

