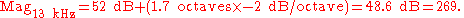Octave (electronics)
Encyclopedia
In electronics
, an octave is a doubling or halving of a frequency
. The term is derived from the musical octave
which similarly describes such frequency ratios, but the prefix octa-, denoting eight, has no significance in physics. A frequency ratio expressed in octaves is the base-2 logarithm
(binary logarithm
) of the ratio.
An amplifier or filter may be stated to have a frequency response of ±6dB per octave over a particular frequency range, which signifies that the power gain changes by ±6 decibels (a factor of four in power), when the frequency changes by a factor of 2. This slope, or more precisely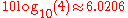 decibels per octave, corresponds to a gain proportional to frequency, which is equivalent to ±20dB per decade
decibels per octave, corresponds to a gain proportional to frequency, which is equivalent to ±20dB per decade
(factor of 10 gain change for a factor of 10 frequency change).
2. A magnitude of 400 (52 dB) at 4 kHz decreases as frequency increases at −2 dB/octave. What is the magnitude at 13 kHz?
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, an octave is a doubling or halving of a frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
. The term is derived from the musical octave
Octave
In music, an octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems"...
which similarly describes such frequency ratios, but the prefix octa-, denoting eight, has no significance in physics. A frequency ratio expressed in octaves is the base-2 logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
(binary logarithm
Binary logarithm
In mathematics, the binary logarithm is the logarithm to the base 2. It is the inverse function of n ↦ 2n. The binary logarithm of n is the power to which the number 2 must be raised to obtain the value n. This makes the binary logarithm useful for anything involving powers of 2,...
) of the ratio.
An amplifier or filter may be stated to have a frequency response of ±6dB per octave over a particular frequency range, which signifies that the power gain changes by ±6 decibels (a factor of four in power), when the frequency changes by a factor of 2. This slope, or more precisely
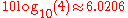 decibels per octave, corresponds to a gain proportional to frequency, which is equivalent to ±20dB per decade
decibels per octave, corresponds to a gain proportional to frequency, which is equivalent to ±20dB per decadeDecade (log scale)
One decade is a factor of 10 difference between two numbers measured on a logarithmic scale. It is especially useful when referring to frequencies and when describing frequency response of electronic systems, such as audio amplifiers and filters.-Calculations:The factor-of-ten in a decade can be...
(factor of 10 gain change for a factor of 10 frequency change).
Example
1. The distance between the frequencies 20 Hz and 40 Hz is 1 octave.2. A magnitude of 400 (52 dB) at 4 kHz decreases as frequency increases at −2 dB/octave. What is the magnitude at 13 kHz?