
Return loss
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications, return loss or reflection loss is the loss of signal power
resulting from the reflection caused at a discontinuity in a transmission line
or optical fiber
. This discontinuity can be a mismatch with the terminating load or with a device inserted in the line. It is usually expressed as a ratio in decibel
s (dB);
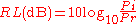
Two lines or devices are well matched if the return loss is high. A high return loss is therefore desirable as it results in a lower insertion loss
. Return loss may be given a minus sign, see below.
Taking the ratio of reflected to incident power results in a negative sign for return loss;
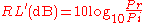
Caution is required when discussing increasing or decreasing return loss since these terms strictly have the opposite meaning when return loss is defined as a negative quantity.
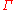
mismatch. The ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave Vr to the amplitude of the incident wave Vi is known as the reflection coefficient
 .
.
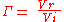
When the source and load impedances are known values, the reflection coefficient is given by
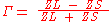
where ZS is the impedance toward the source
and ZL is the impedance toward the load.
Return loss is the negative of the magnitude of the reflection coefficient in dB. Since power is proportional to the square of the voltage, return loss is given by,
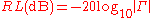
where the vertical
bars indicate magnitude
. Thus, a large positive return loss indicates the reflected power is small relative to the incident power, which indicates good impedance match from source to load.
When the actual transmitted (incident) power and the reflected power are known (i.e. through measurements and/or calculations), then the return loss in dB can be calculated as the difference between the incident power Pi (in dBm
) and the reflected power Pr (in dBm),

Return loss is identified with the S-parameter S11 from two-port network
theory.
, the loss that takes place at any discontinuity of refractive index
, especially at an air-glass
interface such as a fiber endface, at which a fraction of the optical signal is reflected back toward the source. This reflection phenomenon is also called "Fresnel reflection loss," or simply "Fresnel loss."
Fiber optic transmission systems use laser
s to transmit signals over optical fiber, and a high optical return loss (ORL) can cause the laser to stop transmitting correctly. The measurement of ORL is becoming more important in the characterization of optical networks as the use of wavelength-division multiplexing
increases. These systems use lasers that have a lower tolerance for ORL, and introduce elements into the network that are located in close proximity to the laser.
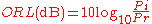
where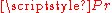 is the reflected power and
is the reflected power and 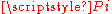 is the incident, or input, power.
is the incident, or input, power.
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
resulting from the reflection caused at a discontinuity in a transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
or optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
. This discontinuity can be a mismatch with the terminating load or with a device inserted in the line. It is usually expressed as a ratio in decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
s (dB);
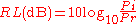
- where RL(dB) is the return loss in dB, Pi is the incident power and Pr is the reflected power.
Two lines or devices are well matched if the return loss is high. A high return loss is therefore desirable as it results in a lower insertion loss
Insertion loss
In telecommunications, insertion loss is the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line or optical fiber and is usually expressed in decibels ....
. Return loss may be given a minus sign, see below.
Sign
Properly, loss quantities, when expressed in decibels, should be positive numbers.Except for cases where an active device succeeds in reflecting back more power than was sent into it. This is the case, for instance, with the tunnel diode amplifier. However, return loss has historically been expressed as a negative number, and this convention is still widely found in the literature.Taking the ratio of reflected to incident power results in a negative sign for return loss;
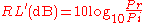
- where RL(dB) is the negative of RL(dB).
Caution is required when discussing increasing or decreasing return loss since these terms strictly have the opposite meaning when return loss is defined as a negative quantity.
Electrical
In metallic conductor systems, reflections of a signal traveling down a conductor can occur at a discontinuity or impedanceElectrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
mismatch. The ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave Vr to the amplitude of the incident wave Vi is known as the reflection coefficient
Reflection coefficient
The reflection coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude or the intensity of a reflected wave relative to an incident wave...
 .
.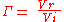
When the source and load impedances are known values, the reflection coefficient is given by
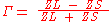
where ZS is the impedance toward the source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
and ZL is the impedance toward the load.
Return loss is the negative of the magnitude of the reflection coefficient in dB. Since power is proportional to the square of the voltage, return loss is given by,
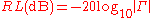
where the vertical
Vertical direction
In astronomy, geography, geometry and related sciences and contexts, a direction passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it is locally aligned with the gradient of the gravity field, i.e., with the direction of the gravitational force at that point...
bars indicate magnitude
Magnitude (mathematics)
The magnitude of an object in mathematics is its size: a property by which it can be compared as larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind; in technical terms, an ordering of the class of objects to which it belongs....
. Thus, a large positive return loss indicates the reflected power is small relative to the incident power, which indicates good impedance match from source to load.
When the actual transmitted (incident) power and the reflected power are known (i.e. through measurements and/or calculations), then the return loss in dB can be calculated as the difference between the incident power Pi (in dBm
DBm
dBm is an abbreviation for the power ratio in decibels of the measured power referenced to one milliwatt . It is used in radio, microwave and fiber optic networks as a convenient measure of absolute power because of its capability to express both very large and very small values in a short form...
) and the reflected power Pr (in dBm),

Return loss is identified with the S-parameter S11 from two-port network
Two-port network
A two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
theory.
Optical
In an optical fiberOptical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
, the loss that takes place at any discontinuity of refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
, especially at an air-glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
interface such as a fiber endface, at which a fraction of the optical signal is reflected back toward the source. This reflection phenomenon is also called "Fresnel reflection loss," or simply "Fresnel loss."
Fiber optic transmission systems use laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s to transmit signals over optical fiber, and a high optical return loss (ORL) can cause the laser to stop transmitting correctly. The measurement of ORL is becoming more important in the characterization of optical networks as the use of wavelength-division multiplexing
Wavelength-division multiplexing
In fiber-optic communications, wavelength-division multiplexing is a technology which multiplexes a number of optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths of laser light...
increases. These systems use lasers that have a lower tolerance for ORL, and introduce elements into the network that are located in close proximity to the laser.
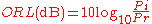
where
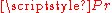 is the reflected power and
is the reflected power and  is the incident, or input, power.
is the incident, or input, power.See also
- Hybrid balanceHybrid balanceIn telecommunications, a hybrid balance is an expression of the degree of electrical symmetry between two impedances connected to two conjugate sides of a hybrid coil or resistance hybrid.Note 1: Hybrid balance is usually expressed in dB....
- Insertion lossInsertion lossIn telecommunications, insertion loss is the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line or optical fiber and is usually expressed in decibels ....
- Signal reflectionSignal reflectionSignal reflection occurs when a signal is transmitted along a transmission medium, such as a copper cable or an optical fiber, some of the signal power may be reflected back to its origin rather than being carried all the way along the cable to the far end. This happens because imperfections in the...
- Standing wave ratioStanding wave ratioIn telecommunications, standing wave ratio is the ratio of the amplitude of a partial standing wave at an antinode to the amplitude at an adjacent node , in an electrical transmission line....
- Time-domain reflectometerTime-domain reflectometerA time-domain reflectometer is an electronic instrument used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables . It can also be used to locate discontinuities in a connector, printed circuit board, or any other electrical path...
- Optical time domain reflectometerOptical time domain reflectometerAn optical time-domain reflectometer is an optoelectronic instrument used to characterize an optical fiber. An OTDR injects a series of optical pulses into the fiber under test. It also extracts, from the same end of the fiber, light that is scattered or reflected back from points along the fiber...
- Optical time domain reflectometer
- Mismatch lossMismatch lossMismatch loss in transmission line theory is the amount of power expressed in decibels that will not be available on the output due to impedance mismatches and reflections. A transmission line that is properly terminated, that is, terminated with the same impedance as that of the characteristic...

