Reflection coefficient
Encyclopedia
The reflection coefficient is used in physics
and electrical engineering
when wave
propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude
or the intensity
of a reflected
wave relative to an incident wave. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient
.
 Different specialties have different applications for the term.
Different specialties have different applications for the term.
s, the reflection coefficient is the ratio
of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the amplitude of the incident wave. In particular, at a discontinuity in a transmission line
, it is the complex
ratio of the electric field
strength of the reflected wave (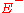 ) to that of the incident wave (
) to that of the incident wave (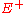 ). This is typically represented with a
). This is typically represented with a 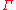 (capital gamma
(capital gamma
) and can be written as:
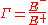
The reflection coefficient may also be established using other field or circuit
quantities.
The reflection coefficient can be given by the equations below, where is the impedance
is the impedance
toward the source,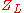 is the impedance toward the load
is the impedance toward the load
:

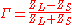
Notice that a negative reflection coefficient means that the reflected wave receives a 180°, or , phase shift.
, phase shift.
The absolute magnitude
(designated by vertical bars) of the reflection coefficient can be calculated from the standing wave ratio
, :
:
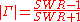
The reflection coefficient is displayed graphically using a Smith chart
.
, intensity and amplitude reflection coefficients are used. Typically, the former are represented by a capital R, while the latter are represented by a lower-case r.
.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
when wave
Wave
In physics, a wave is a disturbance that travels through space and time, accompanied by the transfer of energy.Waves travel and the wave motion transfers energy from one point to another, often with no permanent displacement of the particles of the medium—that is, with little or no associated mass...
propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
or the intensity
Intensity (physics)
In physics, intensity is a measure of the energy flux, averaged over the period of the wave. The word "intensity" here is not synonymous with "strength", "amplitude", or "level", as it sometimes is in colloquial speech...
of a reflected
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
wave relative to an incident wave. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient
Transmission coefficient
The transmission coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered...
.

Telecommunications
In telecommunicationTelecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
s, the reflection coefficient is the ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the amplitude of the incident wave. In particular, at a discontinuity in a transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
, it is the complex
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
ratio of the electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
strength of the reflected wave (
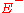 ) to that of the incident wave (
) to that of the incident wave (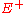 ). This is typically represented with a
). This is typically represented with a  (capital gamma
(capital gammaGamma
Gamma is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Gimel . Letters that arose from Gamma include the Roman C and G and the Cyrillic letters Ge Г and Ghe Ґ.-Greek:In Ancient Greek, gamma represented a...
) and can be written as:
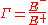
The reflection coefficient may also be established using other field or circuit
Electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
quantities.
The reflection coefficient can be given by the equations below, where
 is the impedance
is the impedanceElectrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
toward the source,
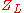 is the impedance toward the load
is the impedance toward the loadExternal electric load
If an electric circuit has a well-defined output terminal, the circuit connected to this terminal is the load....
:

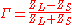
Notice that a negative reflection coefficient means that the reflected wave receives a 180°, or
 , phase shift.
, phase shift.The absolute magnitude
Absolute value
In mathematics, the absolute value |a| of a real number a is the numerical value of a without regard to its sign. So, for example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of -3 is also 3...
(designated by vertical bars) of the reflection coefficient can be calculated from the standing wave ratio
Standing wave ratio
In telecommunications, standing wave ratio is the ratio of the amplitude of a partial standing wave at an antinode to the amplitude at an adjacent node , in an electrical transmission line....
,
 :
: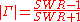
The reflection coefficient is displayed graphically using a Smith chart
Smith chart
The Smith chart, invented by Phillip H. Smith , is a graphical aid or nomogram designed for electrical and electronics engineers specializing in radio frequency engineering to assist in solving problems with transmission lines and matching circuits...
.
Seismology
Reflection coefficient is used in feeder testing for reliability of medium.Optics and microwaves
In opticsOptics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, intensity and amplitude reflection coefficients are used. Typically, the former are represented by a capital R, while the latter are represented by a lower-case r.
Semipermeable membranes
The reflection coefficient in semipermeable membranes relates to how such a membrane can reflect solute particles from passing through. A value of zero results in all particles passing through. A value of one is such that no particle can pass. It is used in the Starling equationStarling equation
The Starling equation is an equation that illustrates the role of hydrostatic and oncotic forces in the movement of fluid across capillary membranes.Capillary fluid movement may occur as a result of three processes:...
.
Power cables in high-power electrical drives
The reflection coefficient characterizes an amplitude of voltage reflections between motor and inverter.External links
- Flash tutorial for understanding reflection A flash program that shows how a reflected wave is generated , the reflection coefficient and VSWR

