
Renault 4
Encyclopedia
The Renault 4, also known as the 4L , is a hatchback
economy car
produced by the French automaker Renault
between 1961 and 1992. It was the first front-wheel drive
family car produced by Renault.
The car was launched at a time when several decades of economic stagnation were giving way to growing prosperity and surging car ownership in France. The first million cars were produced by 1 February 1966, less than four and a half years after launch, a commercial success for Renault because of the timing of its introduction and the merits of its design. It was exceptionally spacious for its size, and although regarded as a small estate car when launched, it is now seen as the first hatchback
family car. Along with the Renault 16
, it pioneered the popularization to the European private motorist of the hatchback during the 1960s. The only car to pre-date its front-wheel drive and top-hinged hatchback, was the 1954 Citroën Traction Avant
Commerciale, which was marketed at commercial travelling salesmen.
. Renault was able to review the advantages and disadvantages of the 2CV design and come up with a larger, more urban vehicle. In early 1956, Renault
Chairman Pierre Dreyfus
launched this new project: designing a new model to replace the rear engined 4CV
that would become an everyman's car, capable of satisfying the needs of anybody. It would be a family car, a woman's car, a farmer's car, a city car.

while the R4 found itself in the 4CV taxation class. Actual maximum power output was claimed by Renault as 22.5 hp for the R3, and 26.5 or 32 hp for the R4, depending on price level and the type of carburettor fitted. Initially the base versions of the R3 and R4 came with a thick C-pillar behind each of the rear doors although for a 400 franc supplement over the price of the basic R4 buyers could specify a body with the C-pillar filled by a third side window which increased the weight but which soon became standard for all R4s.
The R3 and R4 were targeted unashamedly at the aging Citroen 2CV
which famously employed soft springing coupled with very long spring travel to soak up the bumps on poorly maintained country lanes. The new Renaults applied the same approach, which was a novelty for a Renault, and two of the cars appeared at the Paris Motor Show in 1961 mounted on a rolling road enhanced by vertical motion to simulate roads that oscillated at rates consistent with the cars’ suspension settings. As visitors to the exhibition queued to experience the ride they could watch the cars retaining their level pitch while the wheels furiously bounced up and down following the rhythms of the enhanced rolling road. The display had its desired effect since early in 1962 Renault repeated it at the Turin Motor Show.
The basic version of the R3 was priced just 40 francs below the lowest priced version of the Citroen 2CV
in 1961. The basic R3 was very basic, with painted bumpers and grill on the outside, the simplest possible instrument pod facing the driver along with a single sun visor, no windshield washer, and on the interior, no door panels. This basic trim was also offered in the more powerful R4. The R4L with six side windows, chrome coloured bumper and grill, and less aggressively Spartan interior trimmings cost 400 francs (roughly 8%) more than the R4 with its four side windows. Where both R3 and R4 came with the same very basic level of trim the more powerful R4 cost less than 4% above the price of the R3 which seems for most customers to have been too small a difference to justify the purchase of an R3. Similar as the Renault 4CV “Service” in 1953, customers shunned the basic model and in October 1962, the Renault R3 was discontinued.
A "super" version (branded "de luxe" in some export markets) with opening rear quarter-light windows and extra trimmings was also offered. De luxe and super versions of the R4L received a version of the engine from the Renault Dauphine
giving them a four-cylinder engine capacity of 845 cc. After the withdrawal of the 603 cc engined R3, the 747 cc R4 model continued to be listed with an entry level recommended retail price, but it was mostly the slightly larger engined L versions that found their way into customers' hands. By 1965 Renault had removed the extra "R" from their model names: the Renault R4L had become the Renault 4L.
. The original design brief called for an engine size between 600 cc and 700 cc but there was no consensus as to whether to use a four cylinder unit or to follow Citroen with a two cylinder unit. With Volkswagen now rapidly growing their market share across Europe and north America, Renault also gave serious consideration to an air-cooled boxer motor option for the forthcoming R3/R4. Using the existing water cooled unit from the 4CV
was a solution, especially in view of the extended period of teething troubles encountered by the Renault Fregate
, which had followed Renault’s last attempt to develop an ambitiously innovative powerplant. The powerplant of the 4CV was larger than that specified by management for the new model, but Renault addressed this by reducing the bore so that the overall capacity of the power plant destined for the new R3 came in at 603 cc, comfortably at the lower end of the required 600–700 cc range. However, since they already had the 747 cc version of the engine on the shelf, well proven in the 4CV, it made sense to use this as well in what would in many respects be the older car’s successor. Therefore in 1961 the R3 emerged with cylinder bore and stroke set at 49 mm × 80 mm while the R4 was launched with the 54.5 mm × 80 mm cylinder dimensions from the existing engine, giving rise to the 603 cc and 747 cc engine sizes with which the cars were launched.
Moving the engine from the back of the 4CV to the front of the new model nevertheless involved significant planning: design changes to the unit were introduced as part of the process. The inlet manifold was now a steel casting whereas on the 4CV it had been constructed of a light-weight alloy: this was driven by cost considerations now that aluminium was not so inexpensive as it had been fifteen years earlier. Renault also took the opportunity to introduce a feature which subsequently became mainstream but which at this stage was not on the agenda of competitor manufacturers (other than Peugeot
). For the new car Renault designed a “sealed-for-life” cooling system, supported by a small expansion tank on the extreme right side of the engine bay. The cooling system contained a type and quantity of anti-freeze intended to enable operation without topping up or other intervention throughout a car’s life provided ambient temperatures below minus 40 degrees were avoided.
The engines were larger than the small 425 cc (later 602 cc 29 hp), engines in the 2CV. The R4 always had a four-cylinder watercooled engine. The original Renault R4’s engine capacity of 747 cc served to differentiate the model from the more powerful Renault Dauphine
, but the Dauphine’s 845 cc engine was used in the 4 itself from 1963 onwards: for most markets at this stage the Dauphine engine now came as standard in the top of the range Renault R4 Super, and was available in some other versions only as an optional extra. Given that Renault’s 603 cc, 747 cc and 845 cc engines all shared the same cylinder stroke and were all of the same basic design, it is likely that there was very little difference between the manufacturing costs of the basic engine block between the three. From the perspective of the sales and marketing department, they did fall within different taxation classes (respectively 3CV, 4CV and 5CV) but at this end of the market tax level differences were by now less of an issue even in those European countries that still taxed cars according to engine size.
With time, the increasing trend to production of Renault 4s in a wide range of countries reduces the validity of generalised statements as to which engines were fitted when: in French built cars the old 845 cc engine soldiered on in the more lowly versions until the mid 1980s, but in 1978 the top end Renault 4 GTLs received the new 1108 cc engine: this engine was no longer new to Renault, however, being the five-bearing “Sierra” engine, first installed in the Estafette van
and R8 in the summer of 1962. A smaller version (956 cc) of this new engine replaced the by now venerable 845 cc engine in the 4 in 1986. Unlike the original "Billancourt" engine from the 4CV, Renault's “Sierra” engine rotated in a clockwise direction, so fitting it required reversing the direction of the differential in the gear box in order to avoid producing a car with one forward speed and four reverse speeds.
, described by one critic as an obsolete feature when compared to the four-speed manual of the thirteen-year old Citroën 2CV. Ironically the new Renault 4 did not inherit its transmission from the Renault 4CV nor from anyone else: the transmission was newly developed for the car. The dash-mounted gear lever was linked via a straight horizontal rod that passed over the longitudinally mounted engine and clutch directly to the gearbox right at the front. The resulting absence of any linkage at floor level permitted a flat floor across the full width of the car's cabin. Synchromesh featured only on the top two ratios, even though the low power of the engine required frequent gear changes by any driver using normal roads and wishing to make reasonable progress. On this point Renault quickly acknowledged their error and cars produced from 1962 featured synchromesh on all three ratios. In 1968 the Renault 4 finally received a four-speed transmission.
"chassisless" construction which was believed to save cost in the manufacturing process and to cut running costs by reducing vehicle weight. The Renault R3/R4 design defied this by now widely accepted mantra, employing a separate platform to which the body shell was then attached. The body's structural role in maintaining the overall rigidity of the car body was thereby reduced, placing less stress on the roof and allowing for thinner window pillars. Although the use made of a separate platform resembled, in some respects, the use that pre-war designs would have made of a chassis, the outcome was a structure described as semi-monocoque
, and it would later allow Renault to use the R4 platform, with very little modification, to build new models such as the Renault 6
and Rodeo. (Later, the successful Renault 5
used the R4 running gear but in a monocoque shell).
The R3 and R4 had four-wheel torsion-bar independent suspension
. This was an innovation which would be copied on a succession of subsequent front engined Renaults introduced during the 1960s and 70s.
The car features a shorter wheelbase on the left than on the right because the rear wheels are not mounted directly opposite one another. This concept allowed a very simple design of the rear suspension using transverse torsion bars located one behind the other without affecting handling. The front torsion bars were longitudinal. Dampening was contributed by the provision of hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers on all four wheels. Those at the rear were mounted virtually horizontally which avoided the intrusion of rear suspension componentry into the flat floored passenger cabin.
The longitudinal layout of the front wheel drive engine and transmission with engine behind the front axle, and gearbox/differential in front is identical to the Citroën Traction Avant
. The suspension is also very similar, the only difference, being the deletion of the Citroen's flexible beam between the rear wheels, to give the Renault 4 fully independent rear suspension. This is ironic as Louis Renault
, the company's founder had been the harshest critic of the Traction at the time of its launch in the 1930s.


grilles were replaced with plastic
items. There were three different dashboards, all of which were simple in design. On the right side of the car at the back the position of the fuel filler was raised by approximately 15 cm (6 inches) less than a year after the car's launch, presumably for safety reasons, but apart from this changes to the body panels amounted to nothing more than a slightly altered hood and hinge alterations.
Despite the success of the Renault 4, or perhaps as a result of it, Renault directed a lot of effort into developing its small cars. They designed the Renault 6
and the Renault 5
while the Renault 4 was still selling extremely well. Some criticised this at the time, but the Renault 5 competed in a different sector (three- and five-door supermini
). The Renault 4 is thus a bridge between the small utility vehicle (2CV) and the supermini design (R5, Peugeot 205
).
The Renault 4 remained a basic car throughout its life, nonetheless offering a comfortable ride, due to well-designed suspension, comfortable seats, powerful heater and effective ventilation. Windows used sliding mechanisms.

 There were many different 'special edition' Renault 4s. Some (including the Safari, Sixties and Jogging) were sold in special colour schemes, upholstery and other details, while others (Clan, Savane) were standard models with special decals.
There were many different 'special edition' Renault 4s. Some (including the Safari, Sixties and Jogging) were sold in special colour schemes, upholstery and other details, while others (Clan, Savane) were standard models with special decals.
There were also special models which were not solely a marketing exercise, such as the Renault 4 Sinpar 4x4, the Plein Air, a pickup truck
, LPG versions and electric versions.
In 1978, the R4 GTL arrived. It had the 1108 cc engine from the Renault 6
TL, albeit with the performance reduced for better economy, and bigger drum brakes. The GTL was identifiable by its grey front grille, grey bumpers, and grey rubber strips along the bottoms of the doors. It also had an extra air intake below the front grille (as a result, the registration plate was moved down to the bumper), and 12 inch (304.8 mm) wiper blades instead of the original 10 inch (254 mm) ones. A year later, the GTL got front disc brakes (the handbrake now working on the rear wheels) then a year later (1980) the handbrake lever was moved to the floor, there was a modified dashboard and cloth seats.
There was also a panel van
(Fourgonette) version of the R4, which with its "high cube" bodyshell and the unique 'giraffon' (giraffe hatch) at the rear became the idiosyncratic French "Boulangerie" van. For many years, this was surely the most successful vehicle of its type and for many people it represents their idea of a Renault 4 more than the passenger version. It remained on sale in Europe until 1993 and was replaced by the Renault Express (called Extra in UK and Ireland, Rapid in Germany), which was based on the second generation Renault 5
'Supercinq'.
In 1989, Colombian SOFASA produced the variants Brisa (Breeze) which was based on the French Plein Air and Jogging, which was marketed as a sportier version of the car and featured red accessories.
, the difficulties coming up with a suitable replacement (and the idea that the Renault 4's market would die with it) all meant that the Renault 4's final replacement (the Twingo) did not appear until 1992. To conclude production, a series of 1000 examples marketed as "Bye-Bye" was released, each with a numbered plaque.
To mark the end of Renault 4 production, a retrospective series of ten black and white photographs by Thierry des Ouches was published in Libération
in early December 1992. This series later won first prize from Le Club des Directeur Artistiques in the category of daily newspaper. It was also award the lion d'or at the Cannes Lions International Advertising Festival
.
In 2003, a Japanese car modification company called DAMD came up with a design called the Ancel Lapin, which could transform a Suzuki Lapin into a Renault 4 lookalike.
A Renault 4 Sinpar (the four-wheel drive version) was entered in the Paris-Dakar Rally in 1979 and 1980 by Bernard and Claude Marreau, coming fifth in 1979 and in third in 1980. Renault 4 continued to feature in many long distance rallies after production ceased, such as in 2001 in the London-Sahara-London rally (Renault 4 GTL) and the 2008 Mongol Rally
. The Renault 4 forms the basis of the 4L Trophy
, an annual rally established in 1997 for students who collect sponsorship and drive to the Sahara to deliver educational materials to children of the desert and of Morocco.
The Renault 4 GTL was homologated in Group A
. Jacky Cesbron raced one in the Monte Carlo Rally
in 1993 and the Tour de Corse
in 1991. Pinto dos Santos raced a Group N
4 GTL in visiting every round of the WRC though not all during the same season. To celebrate the car's 50th birthday, Renault entered the R4 in the Monte Carlo Rally in 2011.
Standard Renault 4s has taken part in a drag race at Santa Pod Raceway
, Northamptonshire since 2004, and covered the quarter mile in 21.438 seconds with a terminal speed of 59.14mph.
Hatchback
A Hatchback is a car body style incorporating a shared passenger and cargo volume, with rearmost accessibility via a rear third or fifth door, typically a top-hinged liftgate—and features such as fold-down rear seats to enable flexibility within the shared passenger/cargo volume. As a two-box...
economy car
Economy car
An economy car is an automobile that is designed for low cost operation. Typical economy cars are small, light weight, and inexpensive to buy. Economy car designers are forced by stringent design constraints to be inventive...
produced by the French automaker Renault
Renault
Renault S.A. is a French automaker producing cars, vans, and in the past, autorail vehicles, trucks, tractors, vans and also buses/coaches. Its alliance with Nissan makes it the world's third largest automaker...
between 1961 and 1992. It was the first front-wheel drive
Front-wheel drive
Front-wheel drive is a form of engine/transmission layout used in motor vehicles, where the engine drives the front wheels only. Most modern front-wheel drive vehicles feature a transverse engine, rather than the conventional longitudinal engine arrangement generally found in rear-wheel drive and...
family car produced by Renault.
The car was launched at a time when several decades of economic stagnation were giving way to growing prosperity and surging car ownership in France. The first million cars were produced by 1 February 1966, less than four and a half years after launch, a commercial success for Renault because of the timing of its introduction and the merits of its design. It was exceptionally spacious for its size, and although regarded as a small estate car when launched, it is now seen as the first hatchback
Hatchback
A Hatchback is a car body style incorporating a shared passenger and cargo volume, with rearmost accessibility via a rear third or fifth door, typically a top-hinged liftgate—and features such as fold-down rear seats to enable flexibility within the shared passenger/cargo volume. As a two-box...
family car. Along with the Renault 16
Renault 16
The Renault 16 is a hatchback produced by French automaker Renault between 1965 and 1980 in Le Havre, France. The reviewer in the May 1965 edition of the English "Motoring Illustrated" said: "The Renault Sixteen can thus be described as a large family car but one that is neither a four door saloon...
, it pioneered the popularization to the European private motorist of the hatchback during the 1960s. The only car to pre-date its front-wheel drive and top-hinged hatchback, was the 1954 Citroën Traction Avant
Citroën Traction Avant
The Citroën Traction Avant is an automobile which was produced by the French manufacturer Citroën from 1934 to 1957. About 760,000 units were produced.-Impact on the world:...
Commerciale, which was marketed at commercial travelling salesmen.
Origins and strategy
The Renault 4 was Renault's response to the 1948 Citroën 2CVCitroën 2CV
The Citroën 2CV |tax horsepower]]”) was an economy car produced by the French automaker Citroën between 1948 and 1990. It was technologically advanced and innovative, but with uncompromisingly utilitarian unconventional looks, and deceptively simple Bauhaus inspired bodywork, that belied the sheer...
. Renault was able to review the advantages and disadvantages of the 2CV design and come up with a larger, more urban vehicle. In early 1956, Renault
Renault
Renault S.A. is a French automaker producing cars, vans, and in the past, autorail vehicles, trucks, tractors, vans and also buses/coaches. Its alliance with Nissan makes it the world's third largest automaker...
Chairman Pierre Dreyfus
Pierre Dreyfus
Pierre Dreyfus was a high flying French civil servant who in 1955 became a top businessman....
launched this new project: designing a new model to replace the rear engined 4CV
Renault 4CV
The Renault 4CV was an economy car produced by the French manufacturer Renault from August 1947-July 1961. The first French car to sell over a million units, the 4CV was ultimately superseded by the Renault Dauphine....
that would become an everyman's car, capable of satisfying the needs of anybody. It would be a family car, a woman's car, a farmer's car, a city car.

Launch of the R3 and R4
Renault launched the Renault R3 and the Renault R4 simultaneously in July 1961. The cars shared the same body and most mechanical components, but the R3 was powered by a 603 cc version of the engine while the engine capacity of the R4 was 747 cc. This placed the R3 in the 3CV taxation classTax horsepower
The tax horsepower or taxable horsepower was an early system by which taxation rates for automobiles were reckoned in some European countries, such as Britain, Belgium, Germany, France, and Italy; some US states like Illinois charged license plate purchase and renewal fees for passenger...
while the R4 found itself in the 4CV taxation class. Actual maximum power output was claimed by Renault as 22.5 hp for the R3, and 26.5 or 32 hp for the R4, depending on price level and the type of carburettor fitted. Initially the base versions of the R3 and R4 came with a thick C-pillar behind each of the rear doors although for a 400 franc supplement over the price of the basic R4 buyers could specify a body with the C-pillar filled by a third side window which increased the weight but which soon became standard for all R4s.
The R3 and R4 were targeted unashamedly at the aging Citroen 2CV
Citroën 2CV
The Citroën 2CV |tax horsepower]]”) was an economy car produced by the French automaker Citroën between 1948 and 1990. It was technologically advanced and innovative, but with uncompromisingly utilitarian unconventional looks, and deceptively simple Bauhaus inspired bodywork, that belied the sheer...
which famously employed soft springing coupled with very long spring travel to soak up the bumps on poorly maintained country lanes. The new Renaults applied the same approach, which was a novelty for a Renault, and two of the cars appeared at the Paris Motor Show in 1961 mounted on a rolling road enhanced by vertical motion to simulate roads that oscillated at rates consistent with the cars’ suspension settings. As visitors to the exhibition queued to experience the ride they could watch the cars retaining their level pitch while the wheels furiously bounced up and down following the rhythms of the enhanced rolling road. The display had its desired effect since early in 1962 Renault repeated it at the Turin Motor Show.
The basic version of the R3 was priced just 40 francs below the lowest priced version of the Citroen 2CV
Citroën 2CV
The Citroën 2CV |tax horsepower]]”) was an economy car produced by the French automaker Citroën between 1948 and 1990. It was technologically advanced and innovative, but with uncompromisingly utilitarian unconventional looks, and deceptively simple Bauhaus inspired bodywork, that belied the sheer...
in 1961. The basic R3 was very basic, with painted bumpers and grill on the outside, the simplest possible instrument pod facing the driver along with a single sun visor, no windshield washer, and on the interior, no door panels. This basic trim was also offered in the more powerful R4. The R4L with six side windows, chrome coloured bumper and grill, and less aggressively Spartan interior trimmings cost 400 francs (roughly 8%) more than the R4 with its four side windows. Where both R3 and R4 came with the same very basic level of trim the more powerful R4 cost less than 4% above the price of the R3 which seems for most customers to have been too small a difference to justify the purchase of an R3. Similar as the Renault 4CV “Service” in 1953, customers shunned the basic model and in October 1962, the Renault R3 was discontinued.
A "super" version (branded "de luxe" in some export markets) with opening rear quarter-light windows and extra trimmings was also offered. De luxe and super versions of the R4L received a version of the engine from the Renault Dauphine
Renault Dauphine
Renault Dauphine is a rear-engined economy car manufactured by Renault in one body style — a three-box, four-door sedan — as the successor to the Renault 4CV, with over two million examples marketed worldwide during its production from 1956-1967....
giving them a four-cylinder engine capacity of 845 cc. After the withdrawal of the 603 cc engined R3, the 747 cc R4 model continued to be listed with an entry level recommended retail price, but it was mostly the slightly larger engined L versions that found their way into customers' hands. By 1965 Renault had removed the extra "R" from their model names: the Renault R4L had become the Renault 4L.
Engines
Early versions of the Renault R4 used engines and transmissions from the Renault 4CVRenault 4CV
The Renault 4CV was an economy car produced by the French manufacturer Renault from August 1947-July 1961. The first French car to sell over a million units, the 4CV was ultimately superseded by the Renault Dauphine....
. The original design brief called for an engine size between 600 cc and 700 cc but there was no consensus as to whether to use a four cylinder unit or to follow Citroen with a two cylinder unit. With Volkswagen now rapidly growing their market share across Europe and north America, Renault also gave serious consideration to an air-cooled boxer motor option for the forthcoming R3/R4. Using the existing water cooled unit from the 4CV
Renault 4CV
The Renault 4CV was an economy car produced by the French manufacturer Renault from August 1947-July 1961. The first French car to sell over a million units, the 4CV was ultimately superseded by the Renault Dauphine....
was a solution, especially in view of the extended period of teething troubles encountered by the Renault Fregate
Renault Frégate
The Renault Frégate is a full-size or executive car produced by the French automaker Renault between 1951 and 1960.-Origins:The Frégate was conceived in the years immediately following World War II...
, which had followed Renault’s last attempt to develop an ambitiously innovative powerplant. The powerplant of the 4CV was larger than that specified by management for the new model, but Renault addressed this by reducing the bore so that the overall capacity of the power plant destined for the new R3 came in at 603 cc, comfortably at the lower end of the required 600–700 cc range. However, since they already had the 747 cc version of the engine on the shelf, well proven in the 4CV, it made sense to use this as well in what would in many respects be the older car’s successor. Therefore in 1961 the R3 emerged with cylinder bore and stroke set at 49 mm × 80 mm while the R4 was launched with the 54.5 mm × 80 mm cylinder dimensions from the existing engine, giving rise to the 603 cc and 747 cc engine sizes with which the cars were launched.
Moving the engine from the back of the 4CV to the front of the new model nevertheless involved significant planning: design changes to the unit were introduced as part of the process. The inlet manifold was now a steel casting whereas on the 4CV it had been constructed of a light-weight alloy: this was driven by cost considerations now that aluminium was not so inexpensive as it had been fifteen years earlier. Renault also took the opportunity to introduce a feature which subsequently became mainstream but which at this stage was not on the agenda of competitor manufacturers (other than Peugeot
Peugeot 403
The Peugeot 403 is a car produced by French automobile manufacturer Peugeot from 1955 to 1966.-History:The 403 made its debut in saloon body style on 20 April 1955 at the Trocadéro Palace in Paris...
). For the new car Renault designed a “sealed-for-life” cooling system, supported by a small expansion tank on the extreme right side of the engine bay. The cooling system contained a type and quantity of anti-freeze intended to enable operation without topping up or other intervention throughout a car’s life provided ambient temperatures below minus 40 degrees were avoided.
The engines were larger than the small 425 cc (later 602 cc 29 hp), engines in the 2CV. The R4 always had a four-cylinder watercooled engine. The original Renault R4’s engine capacity of 747 cc served to differentiate the model from the more powerful Renault Dauphine
Renault Dauphine
Renault Dauphine is a rear-engined economy car manufactured by Renault in one body style — a three-box, four-door sedan — as the successor to the Renault 4CV, with over two million examples marketed worldwide during its production from 1956-1967....
, but the Dauphine’s 845 cc engine was used in the 4 itself from 1963 onwards: for most markets at this stage the Dauphine engine now came as standard in the top of the range Renault R4 Super, and was available in some other versions only as an optional extra. Given that Renault’s 603 cc, 747 cc and 845 cc engines all shared the same cylinder stroke and were all of the same basic design, it is likely that there was very little difference between the manufacturing costs of the basic engine block between the three. From the perspective of the sales and marketing department, they did fall within different taxation classes (respectively 3CV, 4CV and 5CV) but at this end of the market tax level differences were by now less of an issue even in those European countries that still taxed cars according to engine size.
With time, the increasing trend to production of Renault 4s in a wide range of countries reduces the validity of generalised statements as to which engines were fitted when: in French built cars the old 845 cc engine soldiered on in the more lowly versions until the mid 1980s, but in 1978 the top end Renault 4 GTLs received the new 1108 cc engine: this engine was no longer new to Renault, however, being the five-bearing “Sierra” engine, first installed in the Estafette van
Renault Estafette
The Renault Estafette is a small front-wheel drive van, first introduced in 1959 and using the water-cooled Renault Ventoux engine, ultimately in a range of body styles.-History:...
and R8 in the summer of 1962. A smaller version (956 cc) of this new engine replaced the by now venerable 845 cc engine in the 4 in 1986. Unlike the original "Billancourt" engine from the 4CV, Renault's “Sierra” engine rotated in a clockwise direction, so fitting it required reversing the direction of the differential in the gear box in order to avoid producing a car with one forward speed and four reverse speeds.
Transmission
The initial transmission was a three-speed manualManual transmission
A manual transmission, also known as a manual gearbox or standard transmission is a type of transmission used in motor vehicle applications...
, described by one critic as an obsolete feature when compared to the four-speed manual of the thirteen-year old Citroën 2CV. Ironically the new Renault 4 did not inherit its transmission from the Renault 4CV nor from anyone else: the transmission was newly developed for the car. The dash-mounted gear lever was linked via a straight horizontal rod that passed over the longitudinally mounted engine and clutch directly to the gearbox right at the front. The resulting absence of any linkage at floor level permitted a flat floor across the full width of the car's cabin. Synchromesh featured only on the top two ratios, even though the low power of the engine required frequent gear changes by any driver using normal roads and wishing to make reasonable progress. On this point Renault quickly acknowledged their error and cars produced from 1962 featured synchromesh on all three ratios. In 1968 the Renault 4 finally received a four-speed transmission.
Structure and running gear
The three principal new models introduced by Renault since the war had all featured monocoqueMonocoque
Monocoque is a construction technique that supports structural load by using an object's external skin, as opposed to using an internal frame or truss that is then covered with a non-load-bearing skin or coachwork...
"chassisless" construction which was believed to save cost in the manufacturing process and to cut running costs by reducing vehicle weight. The Renault R3/R4 design defied this by now widely accepted mantra, employing a separate platform to which the body shell was then attached. The body's structural role in maintaining the overall rigidity of the car body was thereby reduced, placing less stress on the roof and allowing for thinner window pillars. Although the use made of a separate platform resembled, in some respects, the use that pre-war designs would have made of a chassis, the outcome was a structure described as semi-monocoque
Monocoque
Monocoque is a construction technique that supports structural load by using an object's external skin, as opposed to using an internal frame or truss that is then covered with a non-load-bearing skin or coachwork...
, and it would later allow Renault to use the R4 platform, with very little modification, to build new models such as the Renault 6
Renault 6
The Renault 6 is a small family car produced by the French automaker Renault between 1968 and 1980.The Renault 6 was launched at the 1968 Paris Motor Show, and was intended to be an upmarket alternative to the Renault 4 that would compete with the Citroën Ami 6 and the recently launched Citroën Dyane...
and Rodeo. (Later, the successful Renault 5
Renault 5
The Renault 5 was first unveiled on 10 December 1971, being launched at the beginning of 1972.The Renault 5 was styled by Michel Boué, who died before the car's release, the R5 featured a steeply sloping rear hatchback and front dashboard...
used the R4 running gear but in a monocoque shell).
Suspension
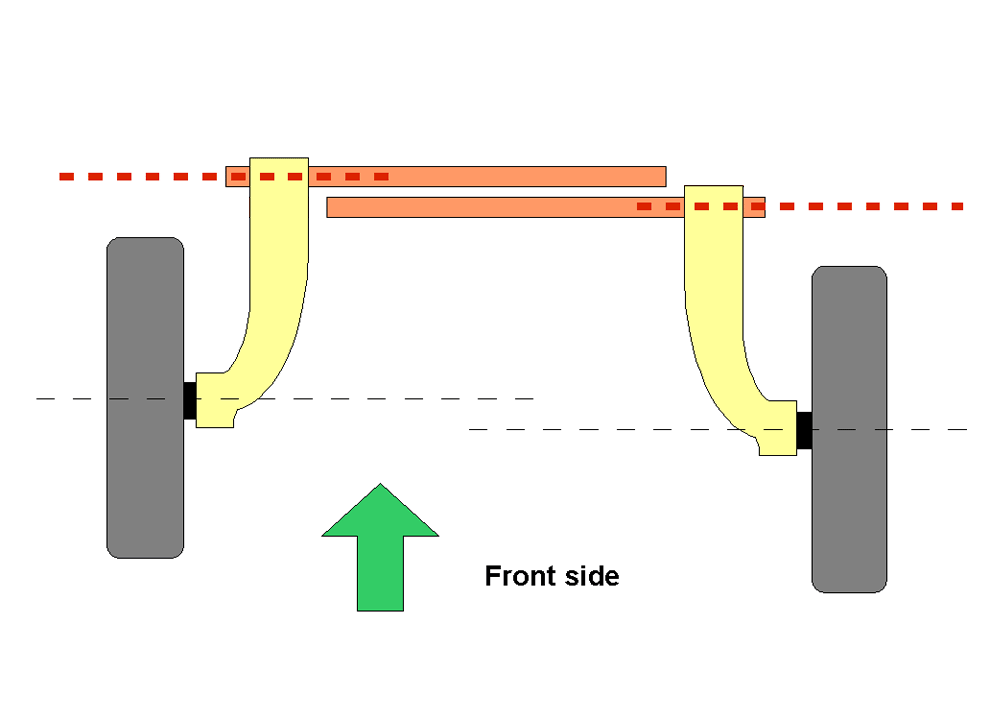 Because the rear torsion bars are located one behind the other, the wheelbase is longer on the right side than on the left. |
The R3 and R4 had four-wheel torsion-bar independent suspension
Independent suspension
Independent suspension is a broad term for any automobile suspension system that allows each wheel on the same axle to move vertically independently of each other. This is contrasted with a beam axle, live axle or deDion axle system in which the wheels are linked – movement on one side affects...
. This was an innovation which would be copied on a succession of subsequent front engined Renaults introduced during the 1960s and 70s.
The car features a shorter wheelbase on the left than on the right because the rear wheels are not mounted directly opposite one another. This concept allowed a very simple design of the rear suspension using transverse torsion bars located one behind the other without affecting handling. The front torsion bars were longitudinal. Dampening was contributed by the provision of hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers on all four wheels. Those at the rear were mounted virtually horizontally which avoided the intrusion of rear suspension componentry into the flat floored passenger cabin.
The longitudinal layout of the front wheel drive engine and transmission with engine behind the front axle, and gearbox/differential in front is identical to the Citroën Traction Avant
Citroën Traction Avant
The Citroën Traction Avant is an automobile which was produced by the French manufacturer Citroën from 1934 to 1957. About 760,000 units were produced.-Impact on the world:...
. The suspension is also very similar, the only difference, being the deletion of the Citroen's flexible beam between the rear wheels, to give the Renault 4 fully independent rear suspension. This is ironic as Louis Renault
Louis Renault (industrialist)
Louis Renault was a French industrialist, one of the founders of Renault and a pioneer of the automobile industry....
, the company's founder had been the harshest critic of the Traction at the time of its launch in the 1930s.
Around the world


- In ColombiaColombiaColombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
, the car was one of the most sold, and remained in the memory of many Colombians, it was nicknamed "" (Faithful friend) and was manufactured in the SOFASASofasaSofasa is an automobile company in Colombia that assembles imported Renault, Toyota and Delta Daihatsu vehicles. The company then exports to the Andean Community of Nations and supplies the national market of automobiles in Colombia....
plant in Envigado (a city near MedellínMedellínMedellín , officially the Municipio de Medellín or Municipality of Medellín, is the second largest city in Colombia. It is in the Aburrá Valley, one of the more northerly of the Andes in South America. It has a population of 2.3 million...
) from 1970 to 1992. Two of the most popular versions included the Master (1022 cc) and the Líder (Leader), with a more powerful 1300 cc engine. The first Renault 4 manufactured in Envigado Colombia was called Azul Pastrana, because this car was blue and President Misael Pastrana opened the plant. - In ArgentinaArgentinaArgentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
and ChileChileChile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
the 4 van (Fourgonette) is known as "Renoleta", following the nickname given to the Citroën 2CVCitroën 2CVThe Citroën 2CV |tax horsepower]]”) was an economy car produced by the French automaker Citroën between 1948 and 1990. It was technologically advanced and innovative, but with uncompromisingly utilitarian unconventional looks, and deceptively simple Bauhaus inspired bodywork, that belied the sheer...
van, "Citroneta". Due to heavy taxation on passenger vehicles in the late '50s, the first 2CV were imported unfinished, only up to the front doors and completed with an Argentine-made pickup truck bed. The Spanish word for pickup truck is "camioneta", hence "Renoleta". - In Italy the 4 was produced by Alfa RomeoAlfa RomeoAlfa Romeo Automobiles S.p.A. is an Italian manufacturer of cars. Founded as A.L.F.A. on June 24, 1910, in Milan, the company has been involved in car racing since 1911, and has a reputation for building expensive sports cars...
factory in MilanMilanMilan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
under license in 1962 until 1964, 41809 R4's were built - In Australia the car was produced between 1962–1966 in Heidelberg, VictoriaHeidelberg, VictoriaHeidelberg is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 11 km north-east from Melbourne's central business district. Its Local Government Area is the City of Banyule....
but ceased production to make way for other models - In Mexico, Renault 4 was produced in Ciudad SahagunBernardino de SahagúnBernardino de Sahagún was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain . Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he journeyed to New Spain in 1529, and spent more than 50 years conducting interviews regarding Aztec...
, a industrial city created between DINA and RenaultRenaultRenault S.A. is a French automaker producing cars, vans, and in the past, autorail vehicles, trucks, tractors, vans and also buses/coaches. Its alliance with Nissan makes it the world's third largest automaker...
in the fifties, the Renault production ceased in 1971. - In Ireland the car was produced in two plants, the first established in 1962 in NaasNaasNaas is the county town of County Kildare in Ireland. With a population of just over twenty thousand, it is also the largest town in the county. Naas is a major commuter suburb, with many people residing there and working in Dublin...
, and the other established in WexfordWexfordWexford is the county town of County Wexford, Ireland. It is situated near the southeastern corner of Ireland, close to Rosslare Europort. The town is connected to Dublin via the M11/N11 National Primary Route, and the national rail network...
in 1972, the production running until 1984. - In SloveniaSloveniaSlovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
, former YugoslaviaYugoslaviaYugoslavia refers to three political entities that existed successively on the western part of the Balkans during most of the 20th century....
, Renault 4 nicknamed "Katrca" or "cetvorka" (from French quatre, four) was produced in IMV (Industrija motornih vozilIndustrija motornih vozilIndustrija Motornih Vozil was a car manufacturer based in Novo Mesto, Slovenia.Established in 1954, IMV produced cars by license from Austin between 1967 and 1972. In 1973, it started to cooperate with Renault. Independently, IMV produced touring caravans and commercial vehicles of their own design...
) plant, from 1973 until 1992. 575,960 R4s were built there. In 1989 the plant was sold to Group Renault and renamed REVOZ d.d. - In Portugal it was known as "Quatroell", from the French "quatre elle". It was mainly used in Alentejo, by olive oil producers and farmers.
- In Spain the Renault 4L is known as "Cuatro latas".
Design
Though the Renault 4 had a long production run, development of the design was limited – it never changed size or shape. Exterior chrome trim was eventually phased out on all models and aluminiumAluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
grilles were replaced with plastic
Plastic
A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs...
items. There were three different dashboards, all of which were simple in design. On the right side of the car at the back the position of the fuel filler was raised by approximately 15 cm (6 inches) less than a year after the car's launch, presumably for safety reasons, but apart from this changes to the body panels amounted to nothing more than a slightly altered hood and hinge alterations.
Despite the success of the Renault 4, or perhaps as a result of it, Renault directed a lot of effort into developing its small cars. They designed the Renault 6
Renault 6
The Renault 6 is a small family car produced by the French automaker Renault between 1968 and 1980.The Renault 6 was launched at the 1968 Paris Motor Show, and was intended to be an upmarket alternative to the Renault 4 that would compete with the Citroën Ami 6 and the recently launched Citroën Dyane...
and the Renault 5
Renault 5
The Renault 5 was first unveiled on 10 December 1971, being launched at the beginning of 1972.The Renault 5 was styled by Michel Boué, who died before the car's release, the R5 featured a steeply sloping rear hatchback and front dashboard...
while the Renault 4 was still selling extremely well. Some criticised this at the time, but the Renault 5 competed in a different sector (three- and five-door supermini
Supermini car
A supermini is a British term that describes automobiles larger than a city car but smaller than a small family car. This car class is also known as the B-segment across Europe, and as subcompact in North America....
). The Renault 4 is thus a bridge between the small utility vehicle (2CV) and the supermini design (R5, Peugeot 205
Peugeot 205
The Peugeot 205 is a supermini produced by the French car manufacturer Peugeot between 1983 and 1998. It was declared 'Car of the Decade' by CAR magazine in 1990. The 205 won 1984 What Car? car of the year.-History:...
).
The Renault 4 remained a basic car throughout its life, nonetheless offering a comfortable ride, due to well-designed suspension, comfortable seats, powerful heater and effective ventilation. Windows used sliding mechanisms.
Variants


There were also special models which were not solely a marketing exercise, such as the Renault 4 Sinpar 4x4, the Plein Air, a pickup truck
Pickup truck
A pickup truck is a light motor vehicle with an open-top rear cargo area .-Definition:...
, LPG versions and electric versions.
In 1978, the R4 GTL arrived. It had the 1108 cc engine from the Renault 6
Renault 6
The Renault 6 is a small family car produced by the French automaker Renault between 1968 and 1980.The Renault 6 was launched at the 1968 Paris Motor Show, and was intended to be an upmarket alternative to the Renault 4 that would compete with the Citroën Ami 6 and the recently launched Citroën Dyane...
TL, albeit with the performance reduced for better economy, and bigger drum brakes. The GTL was identifiable by its grey front grille, grey bumpers, and grey rubber strips along the bottoms of the doors. It also had an extra air intake below the front grille (as a result, the registration plate was moved down to the bumper), and 12 inch (304.8 mm) wiper blades instead of the original 10 inch (254 mm) ones. A year later, the GTL got front disc brakes (the handbrake now working on the rear wheels) then a year later (1980) the handbrake lever was moved to the floor, there was a modified dashboard and cloth seats.
There was also a panel van
Panel van
A panel van is a form of solid van, smaller than a lorry or truck, without rear side windows...
(Fourgonette) version of the R4, which with its "high cube" bodyshell and the unique 'giraffon' (giraffe hatch) at the rear became the idiosyncratic French "Boulangerie" van. For many years, this was surely the most successful vehicle of its type and for many people it represents their idea of a Renault 4 more than the passenger version. It remained on sale in Europe until 1993 and was replaced by the Renault Express (called Extra in UK and Ireland, Rapid in Germany), which was based on the second generation Renault 5
Renault 5
The Renault 5 was first unveiled on 10 December 1971, being launched at the beginning of 1972.The Renault 5 was styled by Michel Boué, who died before the car's release, the R5 featured a steeply sloping rear hatchback and front dashboard...
'Supercinq'.
In 1989, Colombian SOFASA produced the variants Brisa (Breeze) which was based on the French Plein Air and Jogging, which was marketed as a sportier version of the car and featured red accessories.
End of the R4
Though reasons such as emissions and safety legislation are often given for the Renault 4's demise, its popularity would not have lasted anyway. Outmoded production methods, more advanced competition and the reasons outlined above meant that the Renault 4's days were numbered, at least as a mainstream product. There were several projects to replace the Renault 4, starting from the early seventies. However, the continuing success of the Renault 4, the need to replace the Renault 5Renault 5
The Renault 5 was first unveiled on 10 December 1971, being launched at the beginning of 1972.The Renault 5 was styled by Michel Boué, who died before the car's release, the R5 featured a steeply sloping rear hatchback and front dashboard...
, the difficulties coming up with a suitable replacement (and the idea that the Renault 4's market would die with it) all meant that the Renault 4's final replacement (the Twingo) did not appear until 1992. To conclude production, a series of 1000 examples marketed as "Bye-Bye" was released, each with a numbered plaque.
To mark the end of Renault 4 production, a retrospective series of ten black and white photographs by Thierry des Ouches was published in Libération
Libération
Libération is a French daily newspaper founded in Paris by Jean-Paul Sartre and Serge July in 1973 in the wake of the protest movements of May 1968. Originally a leftist newspaper, it has undergone a number of shifts during the 1980s and 1990s...
in early December 1992. This series later won first prize from Le Club des Directeur Artistiques in the category of daily newspaper. It was also award the lion d'or at the Cannes Lions International Advertising Festival
Cannes Lions International Advertising Festival
The Cannes Lions International Festival of Creativity is a global event for those working in advertising and related fields. The seven-day festival, incorporating the awarding of the Lions awards, is held yearly at the Palais des Festivals et des Congrès in Cannes, France...
.
In 2003, a Japanese car modification company called DAMD came up with a design called the Ancel Lapin, which could transform a Suzuki Lapin into a Renault 4 lookalike.
In motorsport
The Renault 4 was originally powered by a 20 hp engine and its suspension was never intended for sporting dynamics, so it should have been no surprise that it came last in the 1962 Monte-Carlo Rally. The Renault 4 had certain advantages in its high torque and a suspension and ground-clearance that gave it go-anywhere capabilities. This meant that Renault was able to give it a sporting image with programmes such as the "Cross Elf Cup of France" in 1974 and the "Routes du Monde" programme in 1968. The latter was a project in which Renault would lend young people cars to travel the world in, and this would help to give the Renault 4 an adventurous and durable image. The "Coupe de France Renault Cross Elf" was a series of races in France on dirt tracks with slightly tuned 782 cc R4s.A Renault 4 Sinpar (the four-wheel drive version) was entered in the Paris-Dakar Rally in 1979 and 1980 by Bernard and Claude Marreau, coming fifth in 1979 and in third in 1980. Renault 4 continued to feature in many long distance rallies after production ceased, such as in 2001 in the London-Sahara-London rally (Renault 4 GTL) and the 2008 Mongol Rally
Mongol Rally
The Mongol Rally is a car rally that begins in Europe and ends in Ulan Bator, Mongolia. The principal launch is from Goodwood Circuit, United Kingdom, with subsidiary starting points in other European countries. It is described as the "greatest adventure in the world"...
. The Renault 4 forms the basis of the 4L Trophy
4L Trophy
Established in 1997 upon the initiative of Ecole Supérieure de Commerce de Rennes, 4L Trophy is a humanitarian rally with Renault 4 cars. Its objective is to drive across the Moroccan desert to provide children with school supplies....
, an annual rally established in 1997 for students who collect sponsorship and drive to the Sahara to deliver educational materials to children of the desert and of Morocco.
The Renault 4 GTL was homologated in Group A
Group A
In relation to motorsport governed by the FIA, Group A referred to a set of regulations providing production-derived vehicles for outright competition. In contrast to the short-lived Group B and Group C, the Group A referred to production-derived vehicles limited in terms of power, weight, allowed...
. Jacky Cesbron raced one in the Monte Carlo Rally
Monte Carlo Rally
The Monte Carlo Rally or Rally Monte Carlo is a rallying event organised each year by the Automobile Club de Monaco which also organises the Formula One Monaco Grand Prix and the Rallye Monte-Carlo Historique. The rally takes place along the French Riviera in the Principality of Monaco and...
in 1993 and the Tour de Corse
Tour de Corse
The Tour de Corse - Rallye de France is a rally first held in 1956 on the island of Corsica. It was part of the World Rally Championship from the inaugural 1973 season to 2008. The name "Tour de Corse" refers to the fact that in the early days it was run around the island; nowadays it only features...
in 1991. Pinto dos Santos raced a Group N
Group N
In relation to motorsport governed by the FIA, Group N refers to a set of regulations providing 'standard' production vehicles for competition, often referred to as the "Showroom Class"....
4 GTL in visiting every round of the WRC though not all during the same season. To celebrate the car's 50th birthday, Renault entered the R4 in the Monte Carlo Rally in 2011.
Standard Renault 4s has taken part in a drag race at Santa Pod Raceway
Santa Pod Raceway
Santa Pod Raceway, in Northamptonshire, England, opened at Easter in 1966, is Europe's first permanent drag racing venue. It was built on a disused World War II American air base, RAF Podington, once used by the 92nd Bomber Group. It is now the home of European drag racing and has grown...
, Northamptonshire since 2004, and covered the quarter mile in 21.438 seconds with a terminal speed of 59.14mph.

