
Regular grid
Encyclopedia



Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling of the plane is a pattern of plane figures that fills the plane with no overlaps and no gaps. One may also speak of tessellations of parts of the plane or of other surfaces. Generalizations to higher dimensions are also possible. Tessellations frequently appeared in the art...
of n-dimensional Euclidean space
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
by congruent parallelotopes (e.g. bricks). Grids of this type appear on graph paper
Graph paper
Graph paper, graphing paper, grid paper or millimeter paper is writing paper that is printed with fine lines making up a regular grid. The lines are often used as guides for plotting mathematical functions or experimental data and drawing diagrams. It is commonly found in mathematics and...
and may be used in finite element analysis as well as finite volume method
Finite volume method
The finite volume method is a method for representing and evaluating partial differential equations in the form of algebraic equations [LeVeque, 2002; Toro, 1999]....
s and finite difference method
Finite difference method
In mathematics, finite-difference methods are numerical methods for approximating the solutions to differential equations using finite difference equations to approximate derivatives.- Derivation from Taylor's polynomial :...
s. Since the derivatives of field variables can be conveniently expressed as finite differences, structured grids mainly appear in finite difference methods. Unstructured grid
Unstructured grid
An unstructured grid is a tessellation of a part of the Euclidean plane or Euclidean space by simple shapes, such as triangles or tetrahedra, in an irregular pattern...
s offer more flexibility than structured grids and hence are very useful in finite element and finite volume methods.
Each cell in the grid can be addressed by index (i, j) in two dimension
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
s or (i, j, k) in three dimensions, and each vertex
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:...
has coordinates
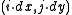 in 2D or
in 2D or 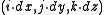 in 3D for some real numbers dx, dy, and dz representing the grid spacing.
in 3D for some real numbers dx, dy, and dz representing the grid spacing.Related grids
A Cartesian grid is a special case where the elements are unit squareUnit square
In mathematics, a unit square is a square whose sides have length 1. Often, "the" unit square refers specifically to the square in the Cartesian plane with corners at , , , and .-In the real plane:...
s or unit cube
Unit cube
A unit cube, sometimes called a cube of side 1, is a cube whose sides are 1 unit long. The volume of a 3-dimensional unit cube is 1 cubic unit, and its total surface area is 6 square units.- Unit Hypercube :...
s, and the vertices are integer points.
A rectilinear grid is a tessellation by rectangles or parallelepipeds that are not, in general, all congruent
Congruence (geometry)
In geometry, two figures are congruent if they have the same shape and size. This means that either object can be repositioned so as to coincide precisely with the other object...
to each other. The cells may still be indexed by integers as above, but the mapping from indexes to vertex coordinates is less uniform than in a regular grid. An example of a rectilinear grid that is not regular appears on logarithmic scale
Logarithmic scale
A logarithmic scale is a scale of measurement using the logarithm of a physical quantity instead of the quantity itself.A simple example is a chart whose vertical axis increments are labeled 1, 10, 100, 1000, instead of 1, 2, 3, 4...
graph paper
Graph paper
Graph paper, graphing paper, grid paper or millimeter paper is writing paper that is printed with fine lines making up a regular grid. The lines are often used as guides for plotting mathematical functions or experimental data and drawing diagrams. It is commonly found in mathematics and...
.
A curvilinear grid or structured grid is a grid with the same combinatorial structure as a regular grid, in which the cells are quadrilaterals or cuboid
Cuboid
In geometry, a cuboid is a solid figure bounded by six faces, forming a convex polyhedron. There are two competing definitions of a cuboid in mathematical literature...
s rather than rectangles or rectangular parallelepipeds.
See also
- Cartesian coordinate systemCartesian coordinate systemA Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
- Integer point
- Unstructured gridUnstructured gridAn unstructured grid is a tessellation of a part of the Euclidean plane or Euclidean space by simple shapes, such as triangles or tetrahedra, in an irregular pattern...

