
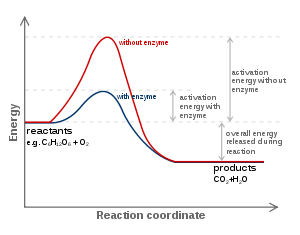
Reaction coordinate
Encyclopedia
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, a reaction coordinate is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway. It is usually a geometric parameter that changes during the conversion of one or more molecular entities
Molecular entity
According to the IUPAC Gold Book a molecular entity is "any constitutionally or isotopically distinct atom, molecule, ion, ion pair, radical, radical ion, complex, conformer, etc., identifiable as a separately distinguishable entity"....
.
These coordinates can sometimes represent a real coordinate system (such as bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
, bond angle...), although, for more complex reactions especially, this can be difficult (and non geometric parameters are used, e.g., bond order
Bond order
Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. For example, in diatomic nitrogen N≡N the bond order is 3, while in acetylene H−C≡C−H the bond order between the two carbon atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order gives an indication to the stability of a bond....
).
Reaction coordinates are often plotted against free energy
Thermodynamic free energy
The thermodynamic free energy is the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. The concept is useful in the thermodynamics of chemical or thermal processes in engineering and science. The free energy is the internal energy of a system less the amount of energy that cannot be used to...
to demonstrate in some schematic form the potential energy profile (an intersection of a potential energy surface
Potential energy surface
A potential energy surface is generally used within the adiabatic or Born–Oppenheimer approximation in quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics to model chemical reactions and interactions in simple chemical and physical systems...
) associated to the reaction.
In the formalism of transition-state theory the reaction coordinate is that coordinate in set of curvilinear coordinates obtained from the conventional ones for the reactants which, for each reaction step, leads smoothly from the configuration of the reactants through that of the transition state
Transition state
The transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest energy along this reaction coordinate. At this point, assuming a perfectly irreversible reaction, colliding reactant molecules will always...
to the configuration of the products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
. The reaction coordinate is typically chosen to follow the path along the gradient (path of shallowest ascent/deepest descent) of potential energy from reactants to products.
For example, in the homolytic dissociation of molecular hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, an apt coordinate system to choose would be the coordinate corresponding to the bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
.

