
Bond order
Encyclopedia
Bond order is the number of chemical bond
s between a pair of atom
s. For example, in diatomic
nitrogen
N≡N the bond order is 3, while in acetylene
H−C≡C−H the bond order between the two carbon
atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order gives an indication to the stability of a bond. In a more advanced context, bond order need not be an integer. A good example of this is bonds between carbon in the molecule
benzene
, where the delocalized molecular orbital
s contain 3 pi electrons over six carbons essentially yielding half a pi bond
, together with the sigma bond
, the bond order is 1.5. Furthermore, bond orders of 1.0, for example, can arise under complex scenarios and essentially refer to bond strength relative to bonds with order 1.
In molecular orbital theory
, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons as per the equation below. This often but not always yields the same result. Bond order is also an index of bond strength
and is also used extensively in valence bond theory
.
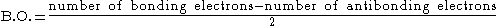
Bond orders of one-half can be stable, as shown by the stability of H2+ (bond length 106 pm, bond energy 269 kJ/mol) and He2+ (bond length 108 pm, bond energy 251 kJ/mol).
The bond order concept is used in molecular dynamics
and bond order potential
s. The magnitude of the bond order is associated with the bond length
. According to Linus Pauling
in 1947, the bond order is experimentally described by:
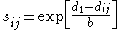
where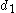 is the single bond length,
is the single bond length, 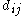 is the bond length experimentally measured, and b is a constant, depending on the atoms. Pauling suggested a value of 0.353 Å for b. The above definition of bond order is somewhat ad hoc and only easy to apply for diatomic
is the bond length experimentally measured, and b is a constant, depending on the atoms. Pauling suggested a value of 0.353 Å for b. The above definition of bond order is somewhat ad hoc and only easy to apply for diatomic
molecules. A standard quantum mechanical definition for bond order has been debated for a long time.
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
s between a pair of atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s. For example, in diatomic
Diatomic
Diatomic molecules are molecules composed only of two atoms, of either the same or different chemical elements. The prefix di- means two in Greek. Common diatomic molecules are hydrogen , nitrogen , oxygen , and carbon monoxide . Seven elements exist in the diatomic state in the liquid and solid...
nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
N≡N the bond order is 3, while in acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
H−C≡C−H the bond order between the two carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order gives an indication to the stability of a bond. In a more advanced context, bond order need not be an integer. A good example of this is bonds between carbon in the molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
, where the delocalized molecular orbital
Molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term "orbital" was first...
s contain 3 pi electrons over six carbons essentially yielding half a pi bond
Pi bond
In chemistry, pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds where two lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap two lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
, together with the sigma bond
Sigma bond
In chemistry, sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond. They are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is most clearly defined for diatomic molecules using the language and tools of symmetry groups. In this formal approach, a σ-bond is...
, the bond order is 1.5. Furthermore, bond orders of 1.0, for example, can arise under complex scenarios and essentially refer to bond strength relative to bonds with order 1.
In molecular orbital theory
Molecular orbital theory
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule...
, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons as per the equation below. This often but not always yields the same result. Bond order is also an index of bond strength
Bond strength
In chemistry, bond strength is measured between two atoms joined in a chemical bond. It is the degree to which each atom linked to another atom contributes to the valency of this other atom...
and is also used extensively in valence bond theory
Valence bond theory
In chemistry, valence bond theory is one of two basic theories, along with molecular orbital theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds...
.
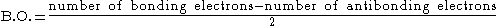
Bond orders of one-half can be stable, as shown by the stability of H2+ (bond length 106 pm, bond energy 269 kJ/mol) and He2+ (bond length 108 pm, bond energy 251 kJ/mol).
The bond order concept is used in molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics is a computer simulation of physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a period of time, giving a view of the motion of the atoms...
and bond order potential
Bond order potential
Bond order potential is a class of empirical potentials used, e.g., in molecular dynamics and molecular statics simulations. Examples include the Tersoff potential, the Brenner potential, the Finnis-Sinclair potentials...
s. The magnitude of the bond order is associated with the bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
. According to Linus Pauling
Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling was an American chemist, biochemist, peace activist, author, and educator. He was one of the most influential chemists in history and ranks among the most important scientists of the 20th century...
in 1947, the bond order is experimentally described by:
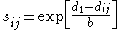
where
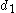 is the single bond length,
is the single bond length, 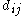 is the bond length experimentally measured, and b is a constant, depending on the atoms. Pauling suggested a value of 0.353 Å for b. The above definition of bond order is somewhat ad hoc and only easy to apply for diatomic
is the bond length experimentally measured, and b is a constant, depending on the atoms. Pauling suggested a value of 0.353 Å for b. The above definition of bond order is somewhat ad hoc and only easy to apply for diatomicDiatomic
Diatomic molecules are molecules composed only of two atoms, of either the same or different chemical elements. The prefix di- means two in Greek. Common diatomic molecules are hydrogen , nitrogen , oxygen , and carbon monoxide . Seven elements exist in the diatomic state in the liquid and solid...
molecules. A standard quantum mechanical definition for bond order has been debated for a long time.

