
Rayleigh's method of dimensional analysis
Encyclopedia
Rayleigh's method of dimensional analysis is a conceptual tool used in physics
, chemistry
, and engineering
. This form of dimensional analysis
expresses a functional relationship of some variables
in the form of an exponential equation. It was named after Lord Rayleigh
.
The method involves the following steps:
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, and engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
. This form of dimensional analysis
Dimensional analysis
In physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
expresses a functional relationship of some variables
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
in the form of an exponential equation. It was named after Lord Rayleigh
John Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh
John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, OM was an English physicist who, with William Ramsay, discovered the element argon, an achievement for which he earned the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1904...
.
The method involves the following steps:
- Gather all the independent variableIndependent variableThe terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
s that are likely to influence the dependent variable. - If X is a variable that depends upon independent variables X1, X2, X3, ..., Xn, then the functional equationFunctional equationIn mathematics, a functional equation is any equation that specifies a function in implicit form.Often, the equation relates the value of a function at some point with its values at other points. For instance, properties of functions can be determined by considering the types of functional...
can be written as X = F(X1, X2, X3, ..., Xn). - Write the above equation in the form
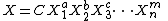 where C is a dimensionless constant and a, b, c, ..., m are arbitrary exponents.
where C is a dimensionless constant and a, b, c, ..., m are arbitrary exponents. - Express each of the quantities in the equation in some fundamental unitFundamental unitA set of fundamental units is a set of units for physical quantities from which every other unit can be generated.In the language of measurement, quantities are quantifiable aspects of the world, such as time, distance, velocity, mass, momentum, energy, and weight, and units are used to describe...
s in which the solution is required. - By using dimensional homogeneity, obtain a set of simultaneous equationsSimultaneous equationsIn mathematics, simultaneous equations are a set of equations containing multiple variables. This set is often referred to as a system of equations. A solution to a system of equations is a particular specification of the values of all variables that simultaneously satisfies all of the equations...
involving the exponents a, b, c, ..., m. - SolveEquation solvingIn mathematics, to solve an equation is to find what values fulfill a condition stated in the form of an equation . These expressions contain one or more unknowns, which are free variables for which values are sought that cause the condition to be fulfilled...
these equations to obtain the value of exponents a, b, c, ..., m. - Substitute the values of exponents in the main equation, and form the non-dimensional parameterParameterParameter from Ancient Greek παρά also “para” meaning “beside, subsidiary” and μέτρον also “metron” meaning “measure”, can be interpreted in mathematics, logic, linguistics, environmental science and other disciplines....
s by grouping the variables with like exponents.

