
Ranjana script
Encyclopedia
The Rañjanā script is an abugida
writing system which developed in the 11th century. It is primarily used for writing Nepal Bhasa
but is also used in monasteries of India
, Tibet
, coastline China
, Mongolia
, and Japan
. It is usually written from left to right but the Kutakshar form is written from top to bottom. It is considered to be the standard Nepali calligraphic script.
script of northern India
and Nepal
. The script is also used in most of the Mahayana
and Vajrayana
monasteries. Along with the Prachalit script, it is considered as one of the scripts of Nepal. It is the formal script of Nepal duly registered in the United Nation while applying for the free Nation. Therefore, it is vital script to all Nepalese as well.
The holy book Aṣṭasāhasrikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra
, lettered in gold ink, written by Bhiksu Ananda of Kapitanagar and dating back to the Nepal Sambat
year 345 (1215 A.D.), illustrates the glorious history of the script.
 The Rañjanā script is used primarily to write Nepal Bhasa, though sometimes also used to write Sanskrit
The Rañjanā script is used primarily to write Nepal Bhasa, though sometimes also used to write Sanskrit
. In Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhist traditions, it is famously used to write various mantra
s including the "Oṃ maṇipadme hūṃ
" mantra of Avalokiteśvara, the mantra of Tara
: "Om tare tuttare ture svaha", and the mantra of Manjushri: "Om ara pa cana dhi." The script is also used in Hindu scriptures.
In Chinese Buddhism and other East Asian Buddhism, the standard Sanskrit script for mantras and dharani
s was not the Rañjanā script, but rather the earlier Siddhaṃ script which was widely propagated in China during the Tang Dynasty
. However, in late imperial China
, the influence of Tibetan Buddhism
popularized the Rañjanā script as well, and so this script is also found throughout East Asia, but is not as standard as Siddhaṃ.
. ལཉྫ་), which simply derives from the Sanskrit word Rañja. This script varies slightly from the standard Rañjanā.
In Tibet, the Lanydza variant is used to write original texts of Sanskrit. Examples of such texts include the Mañjusrinama-samgiti
, the Diamond Sūtra
(Skt. Vajracchedikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra), and the Aṣṭasāhasrikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra. The Lanydza script is also found in manuscripts and printed editions of some Sanskrit-Tibetan lexicons like the Mahāvyutpatti
.
However the most frequent use for this script today is on the title pages of Tibetan texts, where the Sanskrit title is often written in Lanydza, followed by a transliteration and translation in the Tibetan script. The script is also used decoratively on temple walls, on the outside of prayer wheels, and in the drawing of mandalas.
Numerous alternative spellings of the term Lanydza exist, including the following:
A Nepalese-German project is trying to conserve the manuscripts of Rañjanā script.
A Unicode
block for the script has also been proposed by Evertype
.
Abugida
An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary...
writing system which developed in the 11th century. It is primarily used for writing Nepal Bhasa
Nepal Bhasa
Nepal Bhasa is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, particularly in Sikkim where it is one of the 11 official languages. Nepal Bhasa is the mother tongue of about 3% of the people in Nepal . It is spoken mainly by the Newars, who chiefly inhabit the towns of the...
but is also used in monasteries of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
, coastline China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Mongolia
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest...
, and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. It is usually written from left to right but the Kutakshar form is written from top to bottom. It is considered to be the standard Nepali calligraphic script.
Development
Rañjanā is a Brahmic script and shows similarities to the DevanagariDevanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
script of northern India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
. The script is also used in most of the Mahayana
Mahayana
Mahāyāna is one of the two main existing branches of Buddhism and a term for classification of Buddhist philosophies and practice...
and Vajrayana
Vajrayana
Vajrayāna Buddhism is also known as Tantric Buddhism, Tantrayāna, Mantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Esoteric Buddhism and the Diamond Vehicle...
monasteries. Along with the Prachalit script, it is considered as one of the scripts of Nepal. It is the formal script of Nepal duly registered in the United Nation while applying for the free Nation. Therefore, it is vital script to all Nepalese as well.
The holy book Aṣṭasāhasrikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra
Prajnaparamita
Prajñāpāramitā in Buddhism, means "the Perfection of Wisdom." The word Prajñāpāramitā combines the Sanskrit words prajñā with pāramitā . Prajñāpāramitā is a central concept in Mahāyāna Buddhism and its practice and understanding are taken to be indispensable elements of the Bodhisattva Path...
, lettered in gold ink, written by Bhiksu Ananda of Kapitanagar and dating back to the Nepal Sambat
Nepal Sambat
Nepal Sambat is the national lunar calendar of Nepal. It was used throughout Medieval Nepal, and into early modern Nepal, until Chandra Sumsher decided to remove it in BS 1960. It was started in 880 AD during the reign of King Raghav Dev to commemorate the payment of all the debts of Nepalese...
year 345 (1215 A.D.), illustrates the glorious history of the script.
Alphabet
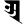 a अ a अ |
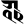 i इ i इ |
 u उ u उ |
 ṛ ऋ ṛ ऋ |
 ḷ ऌ ḷ ऌ |
 e ए e ए |
 o ओ o ओ |
 ā आ ā आ |
 ī ई ī ई |
 ū ऊ ū ऊ |
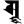 ṝ ॠ ṝ ॠ |
 ḹ ॡ ḹ ॡ |
 ai ऐ ai ऐ |
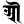 au औ au औ |
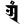 aṃ अं aṃ अं |
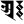 aḥ अः aḥ अः |
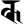 k क k क |
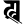 kh ख kh ख |
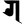 g ग g ग |
 gh घ gh घ |
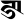 ṅ ङ ṅ ङ |
 c च c च |
 ch छ ch छ |
 j ज j ज |
 jh झ jh झ |
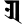 ñ ञ ñ ञ |
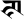 ṭ ट ṭ ट |
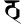 ṭh ठ ṭh ठ |
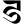 ḍ ड ḍ ड |
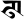 ḍh ढ ḍh ढ |
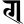 ṇ ण ṇ ण |
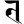 t त t त |
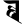 th थ th थ |
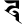 d द d द |
 dh ध dh ध |
 n न n न |
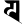 p प p प |
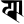 ph फ ph फ |
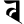 b ब b ब |
 bh भ bh भ |
 m म m म |
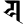 y य y य |
 r र r र |
 l ल l ल |
 v व v व |
|
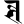 ś श ś श |
 ṣ ष ṣ ष |
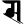 s स s स |
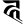 h ह h ह |
 kṣ क्ष kṣ क्ष |
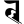 tr त्र tr त्र |
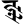 jñ ज्ञ jñ ज्ञ |
Numerals
 0 ० 0 ० |
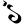 1 १ 1 १ |
 2 २ 2 २ |
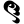 3 ३ 3 ३ |
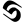 4 ४ 4 ४ |
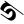 5 ५ 5 ५ |
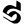 6 ६ 6 ६ |
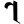 7 ७ 7 ७ |
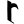 8 ८ 8 ८ |
 9 ९ 9 ९ |
Use

Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
. In Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhist traditions, it is famously used to write various mantra
Mantra
A mantra is a sound, syllable, word, or group of words that is considered capable of "creating transformation"...
s including the "Oṃ maṇipadme hūṃ
Om mani padme hum
is the six syllabled mantra particularly associated with the four-armed Shadakshari form of Avalokiteshvara , the bodhisattva of compassion...
" mantra of Avalokiteśvara, the mantra of Tara
Tara (Buddhism)
Tara or Ārya Tārā, also known as Jetsun Dolma in Tibetan Buddhism, is a female Bodhisattva in Mahayana Buddhism who appears as a female Buddha in Vajrayana Buddhism. She is known as the "mother of liberation", and represents the virtues of success in work and achievements...
: "Om tare tuttare ture svaha", and the mantra of Manjushri: "Om ara pa cana dhi." The script is also used in Hindu scriptures.
In Chinese Buddhism and other East Asian Buddhism, the standard Sanskrit script for mantras and dharani
Dharani
A ' is a type of ritual speech similar to a mantra. The terms dharani and satheesh may be seen as synonyms, although they are normally used in distinct contexts....
s was not the Rañjanā script, but rather the earlier Siddhaṃ script which was widely propagated in China during the Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
. However, in late imperial China
Late Imperial China
Late Imperial China refers to the period between the end of Mongol rule in 1368 and the establishment of the Republic of China in 1912 and includes the Ming and Qing Dynasties...
, the influence of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is the body of Buddhist religious doctrine and institutions characteristic of Tibet and certain regions of the Himalayas, including northern Nepal, Bhutan, and India . It is the state religion of Bhutan...
popularized the Rañjanā script as well, and so this script is also found throughout East Asia, but is not as standard as Siddhaṃ.
Lanydza
When Rañjanā was introduced to Tibet, it was referred to as Lanydza (TibTibetan script
The Tibetan alphabet is an abugida of Indic origin used to write the Tibetan language as well as the Dzongkha language, Denzongkha, Ladakhi language and sometimes the Balti language. The printed form of the alphabet is called uchen script while the hand-written cursive form used in everyday...
. ལཉྫ་), which simply derives from the Sanskrit word Rañja. This script varies slightly from the standard Rañjanā.
In Tibet, the Lanydza variant is used to write original texts of Sanskrit. Examples of such texts include the Mañjusrinama-samgiti
Manjushri-nama-samgiti
The Mañjuśrī-Nāma-Saṃgīti. is considered amongst the most advanced teachings given by the Shakyamuni Buddha...
, the Diamond Sūtra
Diamond Sutra
The Diamond Sūtra , is a short and well-known Mahāyāna sūtra from the Prajñāpāramitā, or "Perfection of Wisdom" genre, and emphasizes the practice of non-abiding and non-attachment...
(Skt. Vajracchedikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra), and the Aṣṭasāhasrikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra. The Lanydza script is also found in manuscripts and printed editions of some Sanskrit-Tibetan lexicons like the Mahāvyutpatti
Mahavyutpatti
The Mahāvyutpatti , The Great Volume of Precise Understanding or Essential Etymology, was compiled in Tibet during the late eighth to early ninth centuries CE, providing a dictionary composed of thousands of Sanskrit and Tibetan terms designed as means to provide standardised Buddhist texts in...
.
However the most frequent use for this script today is on the title pages of Tibetan texts, where the Sanskrit title is often written in Lanydza, followed by a transliteration and translation in the Tibetan script. The script is also used decoratively on temple walls, on the outside of prayer wheels, and in the drawing of mandalas.
Numerous alternative spellings of the term Lanydza exist, including the following:
- Lanja
- Landzha
- Lantsa
- Lantsha
- Lentsa
- Lendza
Recent developments
After falling into disuse in the mid-20th century, the script has recently seen dramatically increased use. It is used by many local governments such as those of Kathmandu Metropolitan City, Lalitpur Sub-Metropolitan City, Bhaktapur Municipality, Thimi Municipality, Kirtipur Municipality, Banepa Municipality, in signboards, letterpads, and such. Regular programs are held in the Kathmandu Valley to promote the script and training classes are held to preserve the language. The script is being endorsed by the Nepal Bhasa movement and is used for headings in newspapers and websites.A Nepalese-German project is trying to conserve the manuscripts of Rañjanā script.
A Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
block for the script has also been proposed by Evertype
Michael Everson
Michael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
.
External links
- Ranjana script
- Newari/Ranjana script page on Omniglot
- Proposal for encoding Newari in Unicode
- Ranjana script
- Akṣara List of the Manuscript of Aṣṭasāhasrikāprajñāpāramitā, ca. the 11-12th Centuries, Collection of Sanskrit Mss. Formerly Preserved in the China Ethnic Library
- Akṣara List of the Sanskrit Inscriptions of Feilai peak, Hangzhou, China ( 1282-1292 CE)
- Lantsha script

