
Quantum beats
Encyclopedia
In physics
, quantum beats are simple examples of phenomena that cannot be described by semiclassical theory, but can be described by fully quantized calculation, especially quantum electrodynamics
. In semiclassical theory (SCT), there is an interference or beat note
term for both V-type and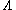 -type atoms. However, in the quantum electrodynamic (QED) calculation, V-type atoms have a beat term but
-type atoms. However, in the quantum electrodynamic (QED) calculation, V-type atoms have a beat term but 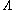 -types do not. This is strong evidence in support of quantum electrodynamics
-types do not. This is strong evidence in support of quantum electrodynamics
.
V-type and
There is a figure in Quantum Optics that describes V-type and 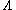 -type atoms clearly.
-type atoms clearly.
Simply, V-type atoms have 3 states: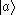 ,
, 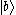 , and
, and 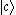 . The energy levels of
. The energy levels of 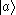 and
and 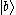 are higher than that of
are higher than that of 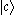 . When electrons in states
. When electrons in states 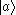 and :
and :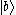 subsequently decay to state
subsequently decay to state 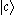 , two kinds of emission are radiated.
, two kinds of emission are radiated.
In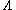 -type atoms, there are also 3 states:
-type atoms, there are also 3 states: 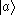 ,
, 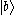 , and :
, and : . However, in this type,
. However, in this type, 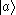 is at the highest energy level, while
is at the highest energy level, while 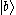 and :
and : are at lower levels. When two electrons in state
are at lower levels. When two electrons in state 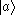 decay to states
decay to states 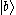 and :
and :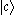 , respectively, two kinds of emission are also radiated.
, respectively, two kinds of emission are also radiated.
The derivation below follows the reference Quantum Optics
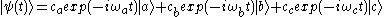 .
.
If the nonvanishing dipole
matrix elements are described by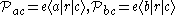 for V-type atoms,
for V-type atoms,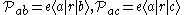 for
for 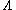 -type atoms,
-type atoms,
then each atom has two microscopic oscillating dipoles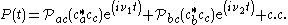 for V-type, when
for V-type, when 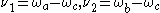 ,
,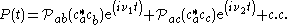 for
for 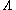 -type, when
-type, when 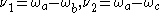 .
.
In the semiclassical picture, the field radiated will be a sum of these two terms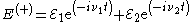 ,
,
so it is clear that there is an interference or beat note term in a square law detector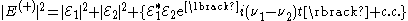 .
.
.
Let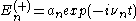 is a creation operator and
is a creation operator and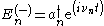 is an annihilation operator.
is an annihilation operator.
Then the beat note becomes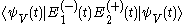 for V-type and
for V-type and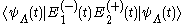 for
for 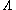 -type,
-type,
when the state vector for each type is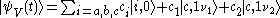 and
and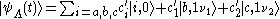 .
.
The beat note term becomes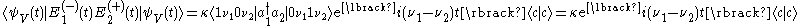 for V-type and
for V-type and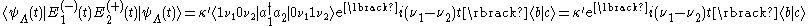 for
for 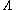 -type.
-type.
By orthogonality
of eigenstates, however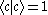 and
and 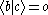 .
.
Therefore, there is a beat note term for V-type atoms, but not for -type atoms.
-type atoms.
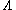 -type atoms do not. This difference is caused by quantum mechanical uncertainty
-type atoms do not. This difference is caused by quantum mechanical uncertainty
. A V-type atom decays to state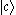 via the emission with
via the emission with 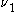 and
and 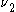 . Since both transitions decayed to the same state, one cannot determine along which path each decayed, similar to Young's double-slit experiment
. Since both transitions decayed to the same state, one cannot determine along which path each decayed, similar to Young's double-slit experiment
. However,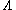 -type atoms decay to two different states. Therefore, in this case we can recognize the path, even if it decays via two emissions as does V-type. Simply, we already know the path of the emission and decay.
-type atoms decay to two different states. Therefore, in this case we can recognize the path, even if it decays via two emissions as does V-type. Simply, we already know the path of the emission and decay.
The calculation by QED is correct in accordance with the most fundamental principle of quantum mechanics
, the uncertainty principle
. Quantum beats phenomena are good examples of such that can be described by QED but not by SCT.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, quantum beats are simple examples of phenomena that cannot be described by semiclassical theory, but can be described by fully quantized calculation, especially quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved...
. In semiclassical theory (SCT), there is an interference or beat note
Beat (acoustics)
In acoustics, a beat is an interference between two sounds of slightly different frequencies, perceived as periodic variations in volume whose rate is the difference between the two frequencies....
term for both V-type and
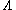 -type atoms. However, in the quantum electrodynamic (QED) calculation, V-type atoms have a beat term but
-type atoms. However, in the quantum electrodynamic (QED) calculation, V-type atoms have a beat term but 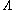 -types do not. This is strong evidence in support of quantum electrodynamics
-types do not. This is strong evidence in support of quantum electrodynamicsQuantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved...
.
V-type and 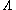 -type atoms
-type atoms
There is a figure in Quantum Optics that describes V-type and 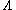 -type atoms clearly.
-type atoms clearly.Simply, V-type atoms have 3 states:
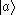 ,
, 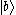 , and
, and 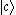 . The energy levels of
. The energy levels of 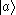 and
and 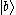 are higher than that of
are higher than that of 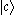 . When electrons in states
. When electrons in states 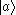 and :
and :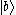 subsequently decay to state
subsequently decay to state 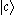 , two kinds of emission are radiated.
, two kinds of emission are radiated.In
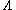 -type atoms, there are also 3 states:
-type atoms, there are also 3 states: 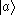 ,
, 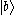 , and :
, and : . However, in this type,
. However, in this type, 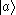 is at the highest energy level, while
is at the highest energy level, while 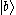 and :
and : are at lower levels. When two electrons in state
are at lower levels. When two electrons in state 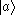 decay to states
decay to states 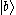 and :
and :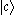 , respectively, two kinds of emission are also radiated.
, respectively, two kinds of emission are also radiated.The derivation below follows the reference Quantum Optics
Calculation based on semiclassical theory
In the semiclassical picture, the state vector of electrons is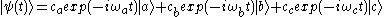 .
.If the nonvanishing dipole
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
matrix elements are described by
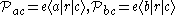 for V-type atoms,
for V-type atoms,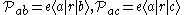 for
for 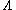 -type atoms,
-type atoms,then each atom has two microscopic oscillating dipoles
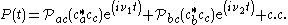 for V-type, when
for V-type, when 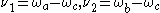 ,
,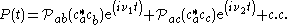 for
for 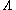 -type, when
-type, when 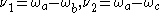 .
.In the semiclassical picture, the field radiated will be a sum of these two terms
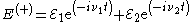 ,
,so it is clear that there is an interference or beat note term in a square law detector
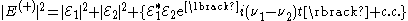 .
.Calculation based on quantum electrodynamics
For quantum electrodynamical calculation, we should introduce the creation and annihilation operators from second quantization of quantum mechanicsQuantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
.
Let
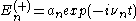 is a creation operator and
is a creation operator and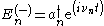 is an annihilation operator.
is an annihilation operator.Then the beat note becomes
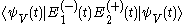 for V-type and
for V-type and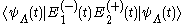 for
for 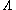 -type,
-type,when the state vector for each type is
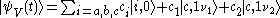 and
and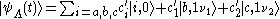 .
.The beat note term becomes
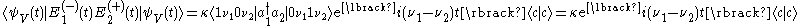 for V-type and
for V-type and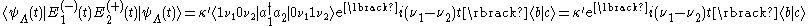 for
for 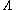 -type.
-type.By orthogonality
Orthogonality
Orthogonality occurs when two things can vary independently, they are uncorrelated, or they are perpendicular.-Mathematics:In mathematics, two vectors are orthogonal if they are perpendicular, i.e., they form a right angle...
of eigenstates, however
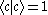 and
and 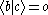 .
.Therefore, there is a beat note term for V-type atoms, but not for
 -type atoms.
-type atoms.Conclusion
As a result of calculation, V-type atoms have quantum beats but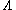 -type atoms do not. This difference is caused by quantum mechanical uncertainty
-type atoms do not. This difference is caused by quantum mechanical uncertaintyUncertainty
Uncertainty is a term used in subtly different ways in a number of fields, including physics, philosophy, statistics, economics, finance, insurance, psychology, sociology, engineering, and information science...
. A V-type atom decays to state
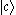 via the emission with
via the emission with 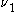 and
and 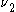 . Since both transitions decayed to the same state, one cannot determine along which path each decayed, similar to Young's double-slit experiment
. Since both transitions decayed to the same state, one cannot determine along which path each decayed, similar to Young's double-slit experimentDouble-slit experiment
The double-slit experiment, sometimes called Young's experiment, is a demonstration that matter and energy can display characteristics of both waves and particles...
. However,
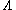 -type atoms decay to two different states. Therefore, in this case we can recognize the path, even if it decays via two emissions as does V-type. Simply, we already know the path of the emission and decay.
-type atoms decay to two different states. Therefore, in this case we can recognize the path, even if it decays via two emissions as does V-type. Simply, we already know the path of the emission and decay.The calculation by QED is correct in accordance with the most fundamental principle of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, the uncertainty principle
Uncertainty principle
In quantum mechanics, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle states a fundamental limit on the accuracy with which certain pairs of physical properties of a particle, such as position and momentum, can be simultaneously known...
. Quantum beats phenomena are good examples of such that can be described by QED but not by SCT.

