
Quality function deployment
Encyclopedia
Quality function deployment (QFD) is a “method to transform user demands into design quality, to deploy the functions forming quality, and to deploy methods for achieving the design quality into subsystems and component parts, and ultimately to specific elements of the manufacturing process.”, as described by Dr. Yoji Akao
, who originally developed QFD in Japan in 1966, when the author combined his work in quality assurance
and quality control
points with function deployment used in value engineering
.
QFD is designed to help planners focus on characteristics of a new or existing product or service from the viewpoints of market segment
s, company, or technology-development needs. The technique yields graphs and matrices
.
QFD helps transform customer
needs (the voice of the customer
[VOC]) into engineering
characteristics (and appropriate test method
s) for a product or service, prioritizing each product or service characteristic while simultaneously setting development targets for product or service.
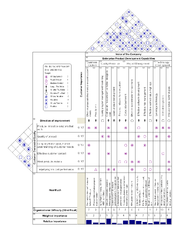 QFD is applied in a wide variety of services, consumer products, military needs (such as the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter), and emerging technology
QFD is applied in a wide variety of services, consumer products, military needs (such as the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter), and emerging technology
products. The technique is also used to identify and document competitive marketing strategies and tactics (see example QFD House of Quality
for Enterprise Product Development, at right). QFD is considered a key practice of Design for Six Sigma
(DFSS - as seen in the referenced roadmap). It is also implicated in the new ISO 9000:2000 standard which focuses on customer satisfaction.
Results of QFD have been applied in Japan and elsewhere into deploying the high-impact controllable factors in Strategic planning
and Strategic management
(also known as Hoshin Kanri
, Hoshin Planning,
Acquiring market needs by listening to the Voice of Customer (VOC), sorting the needs, and numerically prioritizing them (using techniques such as the Analytic Hierarchy Process
) are the early tasks in QFD. Traditionally, going to the Gemba
(the "real place" where value is created for the customer) is where these customer needs are evidenced and compiled.
While many books and articles on "how to do QFD" are available, there is a relative paucity of example matrices available. QFD matrices become highly proprietary due to the high density of product or service information found therein.
appeared in 1972 in the design of an oil tanker by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. Akao has reiterated numerous times that a House of Quality
is not QFD, it is just an example of one tool.
A Flash tutorial exists showing the build process of the traditional QFD "House of Quality
" (HOQ). (Although this example may violate QFD principles, the basic sequence of HOQ building are illustrative.) There are also free QFD templates available that walk users through the process of creating a House of Quality
.
Other tools extend the analysis beyond quality to cost, technology, reliability, function, parts, technology, manufacturing, and service deployments.
In addition, the same technique can extend the method into the constituent product subsystems, configuration item
s, assemblies, and parts. From these detail level components, fabrication and assembly process QFD charts can be developed to support statistical process control
techniques.
uses QFD to establish customer requirements and to identify important design requirements with a special emphasis on modularity.
process somewhat resembles Management by objectives
(MBO), but adds a significant element in the goal setting process, called "catchball". Use of these Hoshin techniques by U.S. companies such as Hewlett Packard have been successful in focusing and aligning company resources to follow stated strategic goals throughout an organizational hierarchy.
Since the early introduction of QFD, the technique has been developed to shorten the time span and reduce the required group efforts.
Yoji Akao
is a Japanese planning specialist recognized as the developer of Hoshin Kanri . With the late Shigeru Mizuno, he developed Quality Function Deployment...
, who originally developed QFD in Japan in 1966, when the author combined his work in quality assurance
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance, or QA for short, is the systematic monitoring and evaluation of the various aspects of a project, service or facility to maximize the probability that minimum standards of quality are being attained by the production process...
and quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
points with function deployment used in value engineering
Value engineering
Value engineering is a systematic method to improve the "value" of goods or products and services by using an examination of function. Value, as defined, is the ratio of function to cost. Value can therefore be increased by either improving the function or reducing the cost...
.
QFD is designed to help planners focus on characteristics of a new or existing product or service from the viewpoints of market segment
Market segment
Market segmentation is a concept in economics and marketing. A market segment is a sub-set of a market made up of people or organizations with one or more characteristics that cause them to demand similar product and/or services based on qualities of those products such as price or function...
s, company, or technology-development needs. The technique yields graphs and matrices
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
.
QFD helps transform customer
Customer
A customer is usually used to refer to a current or potential buyer or user of the products of an individual or organization, called the supplier, seller, or vendor. This is typically through purchasing or renting goods or services...
needs (the voice of the customer
Voice of the customer
Voice of the customer is a term used in business and Information Technology to describe the in-depth process of capturing a customer's expectations, preferences and aversions...
[VOC]) into engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
characteristics (and appropriate test method
Test method
A test method is a definitive procedure that produces a test result.A test can be considered as technical operation that consists of determination of one or more characteristics of a given product, process or service according to a specified procedure. Often a test is part of an experiment.The test...
s) for a product or service, prioritizing each product or service characteristic while simultaneously setting development targets for product or service.
Areas of application

Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
products. The technique is also used to identify and document competitive marketing strategies and tactics (see example QFD House of Quality
House of Quality
House of Quality is a diagram, resembling a house, used for defining the relationship between customer desires and the firm/product capabilities. It is a part of the Quality Function Deployment and it utilizes a planning matrix to relate what the customer wants to how a firm is going to meet...
for Enterprise Product Development, at right). QFD is considered a key practice of Design for Six Sigma
Design for Six Sigma
Design for Six Sigma is a separate and emerging business-process management methodology related to traditional Six Sigma. While the tools and order used in Six Sigma require a process to be in place and functioning, DFSS has the objective of determining the needs of customers and the business, and...
(DFSS - as seen in the referenced roadmap). It is also implicated in the new ISO 9000:2000 standard which focuses on customer satisfaction.
Results of QFD have been applied in Japan and elsewhere into deploying the high-impact controllable factors in Strategic planning
Strategic planning
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy. In order to determine the direction of the organization, it is necessary to understand its current position and the possible avenues...
and Strategic management
Strategic management
Strategic management is a field that deals with the major intended and emergent initiatives taken by general managers on behalf of owners, involving utilization of resources, to enhance the performance of firms in their external environments...
(also known as Hoshin Kanri
Hoshin Kanri
Hoshin kanri - is a method devised to capture and cement strategic goals as well as flashes of insight about the future and develop the means to bring these into reality."...
, Hoshin Planning,
Acquiring market needs by listening to the Voice of Customer (VOC), sorting the needs, and numerically prioritizing them (using techniques such as the Analytic Hierarchy Process
Analytic Hierarchy Process
The Analytic Hierarchy Process is a structured technique for organizing and analyzing complex decisions. Based on mathematics and psychology, it was developed by Thomas L...
) are the early tasks in QFD. Traditionally, going to the Gemba
Gemba
is a Japanese term meaning "the real place." Japanese detectives call the crime scene genba, and Japanese TV reporters may refer to themselves as reporting from genba. In business, genba refers to the place where value is created; in manufacturing the genba is the factory floor...
(the "real place" where value is created for the customer) is where these customer needs are evidenced and compiled.
While many books and articles on "how to do QFD" are available, there is a relative paucity of example matrices available. QFD matrices become highly proprietary due to the high density of product or service information found therein.
House of Quality
House of QualityHouse of Quality
House of Quality is a diagram, resembling a house, used for defining the relationship between customer desires and the firm/product capabilities. It is a part of the Quality Function Deployment and it utilizes a planning matrix to relate what the customer wants to how a firm is going to meet...
appeared in 1972 in the design of an oil tanker by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. Akao has reiterated numerous times that a House of Quality
House of Quality
House of Quality is a diagram, resembling a house, used for defining the relationship between customer desires and the firm/product capabilities. It is a part of the Quality Function Deployment and it utilizes a planning matrix to relate what the customer wants to how a firm is going to meet...
is not QFD, it is just an example of one tool.
A Flash tutorial exists showing the build process of the traditional QFD "House of Quality
House of Quality
House of Quality is a diagram, resembling a house, used for defining the relationship between customer desires and the firm/product capabilities. It is a part of the Quality Function Deployment and it utilizes a planning matrix to relate what the customer wants to how a firm is going to meet...
" (HOQ). (Although this example may violate QFD principles, the basic sequence of HOQ building are illustrative.) There are also free QFD templates available that walk users through the process of creating a House of Quality
House of Quality
House of Quality is a diagram, resembling a house, used for defining the relationship between customer desires and the firm/product capabilities. It is a part of the Quality Function Deployment and it utilizes a planning matrix to relate what the customer wants to how a firm is going to meet...
.
Other tools extend the analysis beyond quality to cost, technology, reliability, function, parts, technology, manufacturing, and service deployments.
In addition, the same technique can extend the method into the constituent product subsystems, configuration item
Configuration item
The term configuration item or CI refers to the fundamental structural unit of a configuration management system. Examples of CIs include individual requirements documents, software, models, plans, and people...
s, assemblies, and parts. From these detail level components, fabrication and assembly process QFD charts can be developed to support statistical process control
Statistical process control
Statistical process control is the application of statistical methods to the monitoring and control of a process to ensure that it operates at its full potential to produce conforming product. Under SPC, a process behaves predictably to produce as much conforming product as possible with the least...
techniques.
Pugh concept selection
Pugh Concept Selection can be used in coordination with QFD to select a promising product or service configuration from among listed alternatives.Modular Function Deployment
Modular Function DeploymentModular Function Deployment
Modular function deployment is a systematic method and procedure for company-supportive product modularization.-Five steps:MFD consists of five major steps. It starts with quality function deployment analysis to establish customer requirements and to identify important design requirements with a...
uses QFD to establish customer requirements and to identify important design requirements with a special emphasis on modularity.
Relationship to other techniques
The QFD-associated Hoshin KanriHoshin Kanri
Hoshin kanri - is a method devised to capture and cement strategic goals as well as flashes of insight about the future and develop the means to bring these into reality."...
process somewhat resembles Management by objectives
Management by objectives
Management by Objectives is a process of defining objectives within an organization so that management and employees agree to the objectives and understand what they need to do in the organization....
(MBO), but adds a significant element in the goal setting process, called "catchball". Use of these Hoshin techniques by U.S. companies such as Hewlett Packard have been successful in focusing and aligning company resources to follow stated strategic goals throughout an organizational hierarchy.
Since the early introduction of QFD, the technique has been developed to shorten the time span and reduce the required group efforts.

