Progress 1
Encyclopedia
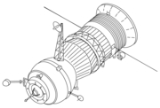
Progress 1 was a Soviet
unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1978 to resupply the Salyut 6
space station. It was the maiden flight of the Progress spacecraft, and used the Progress 7K-TG
configuration. It carried supplies for the EO-1
crew aboard Salyut 6, which consisted of Soviet cosmonauts Yuri Romanenko
and Georgi Grechko
. The cargo carried by Progress 1 also included equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres.
102. The Progress 7K-TG spacecraft was the first generation Progress, derived from the Soyuz 7K-T
and intended for unmanned logistics missions to space stations in support of the Salyut programme. The spacecraft were also used on some missions to adjust the orbit of the space station.
The Progress spacecraft had a dry mass of 6520 kilograms (14,374.1 lb), which increased to around 7020 kilograms (15,476.5 lb) when fully fuelled. It measured 7.48 metres (24.5 ft) in length, and 2.72 metres (8.9 ft) in diameter. Each spacecraft could accommodate up to 2500 kilograms (5,511.6 lb) of payload, consisting of dry cargo and propellant. The spacecraft were powered by chemical batteries, and could operate in free flight for up to three days, remaining docked to the station for up to thirty.
11A511U carrier rocket flying from Site 31/6 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome
in the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic. The rocket that launched it had the serial number
E15000-075. Following launch, Progress 1 was given the COSPAR designation 1978-008A, whilst NORAD assigned it the Satellite Catalog Number
10603.
Following launch, Progress 1 began two days of free flight. It subsequently docked with the aft port of the Salyut 6 space station at 10:12:14 UTC on 22 January. When the Progress spacecraft docked, the station's other docking port was occupied by the Soyuz 27
spacecraft.
On 6 February 1978, Progress 1 was catalogued in a low Earth orbit
with a perigee
of 324 kilometres (174.9 nmi) and an apogee
of 344 kilometres (185.7 nmi), inclined
at 51.6 degrees and with a period
of 91.21 minutes. Progress 1 undocked from Salyut 6 at 05:54 UTC on 6 February. It remained in orbit for two more days, finally being deorbited to a destructive reentry over the Pacific Ocean
at around 02:00 UTC on 8 February.
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1978 to resupply the Salyut 6
Salyut 6
Salyut 6 , DOS-5, was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth flown as part of the Salyut programme. Launched on 29 September 1977 by a Proton rocket, the station was the first of the 'second-generation' type of space station. Salyut 6 possessed several revolutionary advances over the earlier...
space station. It was the maiden flight of the Progress spacecraft, and used the Progress 7K-TG
Progress 7K-TG
Progress 7K-TG , was a Soviet unmanned spacecraft used to resupply space stations in low Earth orbit. Forty three flew, delivering cargo to Salyut 6, Salyut 7, and Mir...
configuration. It carried supplies for the EO-1
Salyut 6 EO-1
Salyut 6 EO-1 was a Soviet long duration space expedition, the first to dock successfully with the space station Salyut 6. The two person crew stayed were in space for a record setting 96 days, from December 1977 to March 1978...
crew aboard Salyut 6, which consisted of Soviet cosmonauts Yuri Romanenko
Yuri Romanenko
Yury Viktorovich Romanenko is a former Soviet cosmonaut, twice Hero of the Soviet Union . Over his career, Yury Romanenko spent a total of 430 days 20 hours 21 minutes 30 seconds in space and 18 hours in space walks. In 1987 he was a resident of the Mir space station, launching on Soyuz TM-2 and...
and Georgi Grechko
Georgi Grechko
Georgy Mikhaylovich Grechko is a retired Soviet cosmonaut who flew on several space flights among which Soyuz 17, Soyuz 26, and Soyuz T-14.Grechko graduated from the Leningrad Institute of Mechanics with a doctorate in mathematics. He was a member of Communist Party of Soviet Union...
. The cargo carried by Progress 1 also included equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres.
Spacecraft
Progress 1 was a Progress 7K-TG spacecraft. The first of forty three to be launched, it had the serial numberSerial number
A serial number is a unique number assigned for identification which varies from its successor or predecessor by a fixed discrete integer value...
102. The Progress 7K-TG spacecraft was the first generation Progress, derived from the Soyuz 7K-T
Soyuz 7K-T
The second generation of the Soyuz spacecraft, the Soyuz Ferry or Soyuz 7K-T, comprised Soyuz 12 through Soyuz 40 . Although still using the Igla system, these had no solar panels, employing batteries...
and intended for unmanned logistics missions to space stations in support of the Salyut programme. The spacecraft were also used on some missions to adjust the orbit of the space station.
The Progress spacecraft had a dry mass of 6520 kilograms (14,374.1 lb), which increased to around 7020 kilograms (15,476.5 lb) when fully fuelled. It measured 7.48 metres (24.5 ft) in length, and 2.72 metres (8.9 ft) in diameter. Each spacecraft could accommodate up to 2500 kilograms (5,511.6 lb) of payload, consisting of dry cargo and propellant. The spacecraft were powered by chemical batteries, and could operate in free flight for up to three days, remaining docked to the station for up to thirty.
Launch and docking
Progress 1 was launched at 08:24:40 UTC on 20 January 1978, atop a Soyuz-USoyuz-U
The Soyuz-U launch vehicle is an improved version of the original Soyuz LV. Soyuz-U is part of the R-7 family of rockets based on the R-7 Semyorka missile. Members of this rocket family were designed by the TsSKB design bureau and constructed at the Progress Factory in Samara, Russia....
11A511U carrier rocket flying from Site 31/6 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome
Baikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome , also called Tyuratam, is the world's first and largest operational space launch facility. It is located in the desert steppe of Kazakhstan, about east of the Aral Sea, north of the Syr Darya river, near Tyuratam railway station, at 90 meters above sea level...
in the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic. The rocket that launched it had the serial number
Serial number
A serial number is a unique number assigned for identification which varies from its successor or predecessor by a fixed discrete integer value...
E15000-075. Following launch, Progress 1 was given the COSPAR designation 1978-008A, whilst NORAD assigned it the Satellite Catalog Number
Satellite Catalog Number
The Satellite Catalog Number is a sequential 5-digit number assigned by USSPACECOM to all Earth orbiting satellites in order of identification. Before USSPACECOM, the catalog was maintained by NORAD...
10603.
Following launch, Progress 1 began two days of free flight. It subsequently docked with the aft port of the Salyut 6 space station at 10:12:14 UTC on 22 January. When the Progress spacecraft docked, the station's other docking port was occupied by the Soyuz 27
Soyuz 27
Soyuz 27 was a 1978 Soviet manned spacecraft which flew to the orbiting Salyut 6 space station, during the mission EP-1. It was the third manned flight to the station, and the second successful docking...
spacecraft.
Mission
Progress 1 was the first of twelve Progress spacecraft used to supply the Salyut 6 space station between 1978 and 1981. Its payload of 2300 kilograms (5,070.6 lb) consisted of 1000 kilograms (2,204.6 lb) of propellant and oxygen, as well as 1300 kilograms (2,866 lb) of food, replacement parts, scientific instruments, and other supplies. Whilst Progress 1 was docked, the EO-1 crew, consisting of cosmonauts Yuri Romanenko and Georgi Grechko, was aboard the station. Once the cosmonauts had unloaded the cargo delivered by Progress 1, they loaded refuse onto the freighter for disposal.On 6 February 1978, Progress 1 was catalogued in a low Earth orbit
Low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit is generally defined as an orbit within the locus extending from the Earth’s surface up to an altitude of 2,000 km...
with a perigee
Apsis
An apsis , plural apsides , is the point of greatest or least distance of a body from one of the foci of its elliptical orbit. In modern celestial mechanics this focus is also the center of attraction, which is usually the center of mass of the system...
of 324 kilometres (174.9 nmi) and an apogee
Apsis
An apsis , plural apsides , is the point of greatest or least distance of a body from one of the foci of its elliptical orbit. In modern celestial mechanics this focus is also the center of attraction, which is usually the center of mass of the system...
of 344 kilometres (185.7 nmi), inclined
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
at 51.6 degrees and with a period
Orbital period
The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of...
of 91.21 minutes. Progress 1 undocked from Salyut 6 at 05:54 UTC on 6 February. It remained in orbit for two more days, finally being deorbited to a destructive reentry over the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
at around 02:00 UTC on 8 February.
See also
- 1978 in spaceflight1978 in spaceflight1978 saw the launch of the Pioneer Venus missions launched by the United States, on 20 May and 8 August. The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe landed four spacecraft on the planet, one of which transmitted data for 67 minutes before being destroyed by atmospheric pressure...
- List of Progress flights
- List of unmanned spaceflights to Salyut space stations

