
Preload
Encyclopedia

Cardiology
Cardiology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the heart . The field includes diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology...
physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
, preload is the end volumetric pressure that stretches the right or left ventricle
Ventricle (heart)
In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
of the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
to its greatest geometric dimensions under variable physiologic demand. Passive filling of the (heart) ventricle
Ventricle (heart)
In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
and subsequent atrial contraction thus allows an echocardiographically volumetric measurement.
Preload is theoretically most accurately described as the initial stretching of a single cardiomyocyte prior to contraction. This cannot be measured in vivo
In vivo
In vivo is experimentation using a whole, living organism as opposed to a partial or dead organism, or an in vitro controlled environment. Animal testing and clinical trials are two forms of in vivo research...
and therefore other measurements are used as estimates. Estimation may be inaccurate, for example in a chronically dilated ventricle new sarcomere
Sarcomere
A sarcomere is the basic unit of a muscle. Muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells . Muscle cells are composed of tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as dark and light bands...
s may have formed in the heart muscle allowing the relaxed ventricle to appear enlarged. The term end-diastolic volume
End-diastolic volume
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume is the volume of blood in the right and/or left ventricle at end Load or filling in . Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, EDV is often used synonymously with preload, which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in...
is better suited to the clinic, although not exactly equivalent to the strict definition of preload. Atrial pressure is a surrogate for preload.
Calculation
Quantitatively, preload can be calculated as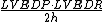
where LVEDP = Left ventricular end diastolic pressure, LVEDR = Left ventricular end diastolic radius (at the ventricle's midpoint), and h = thickness of the ventricle. This calculation is based on the Law of Laplace.
Factors affecting preload
Preload is affected by venous blood pressure and the rate of venous return. These are affected by venous tone and volume of circulating blood.Preload is related to the ventricular end-diastolic volume
End-diastolic volume
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume is the volume of blood in the right and/or left ventricle at end Load or filling in . Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, EDV is often used synonymously with preload, which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in...
; a higher end-diastolic volume implies a higher preload. However, the relationship is not simple because of the restriction of the term preload to single myocytes. Preload can still be approximated by the inexpensive echocardiographic measurement end diastolic volume or EDV.
Preload increases with exercise (slightly), increasing blood volume (overtransfusion, polycythemia) and neuroendocrine excitement (sympathetic tone).
An arteriovenous fistula
Arteriovenous fistula
An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arterial aneurysm....
can increase preload.
See also
- AfterloadAfterloadAfterload is the tension or stress developed in the wall of the left ventricle during ejection. Following Laplace's law, the tension upon the muscle fibers in the heart wall is the product of the pressure within the ventricle, multiplied by the volume within the ventricle, divided by the wall...
- Cardiac outputCardiac outputCardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min...
- Frank–Starling law of the heart
- Passive leg raising testPassive leg raising testIn medicine, the passive leg raising test is a bedside test to evaluate the need for further fluid resuscitation in critically ill patients.The test involves raising the legs of a patient , which causes gravity to pull blood from the legs, thus increasing circulatory volume available to the heart ...

