
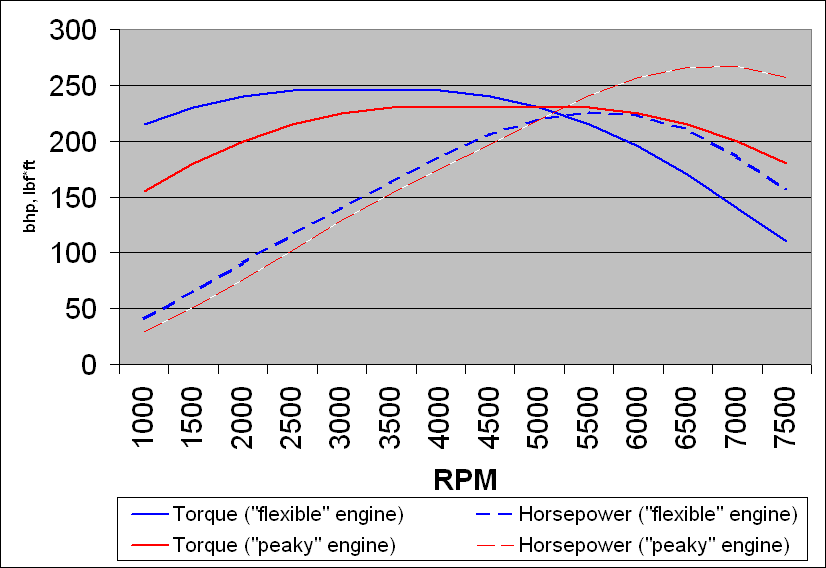
Power band
Encyclopedia
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
or electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
refers to the range of operating speeds under which an the engine or motor is able to operate efficiently. While engines and motors have a large range of operating speeds, the power band is usually a much smaller range of engine speed, only half or less of the total engine speed range (electric motors are an exception - see Electric Motors below).
Specifically, power band is defined by the range from peak torque to peak horsepower (or sometimes to redline). For example: combustion engines typically generate maximum torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
at perhaps 2500 RPM. The peak horsepower
Horsepower
Horsepower is the name of several units of measurement of power. The most common definitions equal between 735.5 and 750 watts.Horsepower was originally defined to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses in continuous operation. The unit was widely adopted to measure the...
might be 5000 RPM. Such an engine would have a power band of 2500 to 5000 RPM, in which the engine would be very efficient.
Applications
Since engines produce the highest power over a relatively narrow range of speeds, a power-splitting device such as a clutchClutch
A clutch is a mechanical device which provides for the transmission of power from one component to another...
or torque converter
Torque converter
In modern usage, a torque converter is generally a type of hydrodynamic fluid coupling that is used to transfer rotating power from a prime mover, such as an internal combustion engine or electric motor, to a rotating driven load...
is required to efficiently achieve a wide range of speeds.
A transmission
Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
with a selection of different gear ratios is designed to make satisfactory power and torque available over the full range of road speeds. The goal of a transmission is essentially to keep the engine operating in its powerband.
By careful gear selection, an engine can be operated in its power band, throughout all vehicle speeds. Such use prevents the engine from labouring at low RPMs or exceeding recommended operating speeds.
Gasoline Engines
A modern, well designed and engineered fuel injectedFuel injection
Fuel injection is a system for admitting fuel into an internal combustion engine. It has become the primary fuel delivery system used in automotive petrol engines, having almost completely replaced carburetors in the late 1980s....
, computer controlled
Electronic control unit
In automotive electronics, electronic control unit is a generic term for any embedded system that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a motor vehicle....
, multivalve (and optionally variable-valve timing
Variable valve timing
In internal combustion engines, variable valve timing , also known as Variable valve actuation , is a generalized term used to describe any mechanism or method that can alter the shape or timing of a valve lift event within an internal combustion engine...
equipped) gasoline engine using good fuel can achieve remarkable flexibility, with a near-flat torque output from 1500 to 6000 RPM, allowing easy cruising and forgiving low-speed road manners. However, achieving maximum horsepower for strong acceleration or high road speed still requires high RPM, as power is the product of torque multiplied by speed of rotation (analogous to force x speed). Though the literal power band covers most of the operating RPM range, particularly in 1st gear (as there is no lower gear to shift down to, and no powerless "flat spot" much above a medium jogging pace), the effective band whilst on the move changes in each gear, becoming the range spanned at the upper end by either the limiter, or a point roughly located between peak power and the redline/rev limiter where power drops off, and at the lower end whatever engine speed changing up from that point in the next lower gear lands you at.
Diesel Engines
A typical small diesel has a narrower band, generating peak torque at lower rpm (often 1500-2000 RPM) but also with a sharper fall-off below this, and reaching peak power around 3500-4500 RPM, again rapidly losing strength above this speed. Turbo diesel engines can display this characteristic very markedly as it combines with the turbo lag (narrowed, exaggerated power band) intrinsic to most turbocharged engines. Therefore the manufacturer's (or purchaser's/modifier's) choice of gearing, and appropriate use of the available ratios, is even more crucial to make best use of the available power and avoid being "bogged down" in flat spots.Electric Motors
Electric motorElectric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
s are unique in many ways, especially when it comes to the power band. The maximum power of an electric motor is reached almost instantly and stays at that level until just before the stall point of the motor. Therefore, the power band is nearly identical to the range of operating speeds of the motor. This means that electric motors generate near maximum torque throughout all operating speeds of the motor.
See also
- Engine tuningEngine tuningEngine tuning is the adjustment, modification or design of internal combustion engines to yield optimal performance, to increase an engine's power output, economy, or durability....
- OverdriveOverdrive (mechanics)Overdrive is a term used to describe a mechanism that allows an automobile to cruise at sustained speed with reduced engine RPM, leading to better fuel economy, lower noise and lower wear...
- Shift kitShift kitA Shift kit is an aftermarket component for automobiles to improve how well the car shifts between gears. Kits are mode for both automatic and manual transmissions.-Manual transmission kit:...
- Shift timeShift timeShift time refers to the time interval between gear changes in a transmission during which power delivery is interrupted. This is usually in reference to motor vehicles but can apply to any gearbox. Reducing shift time is important in performance vehicles or race cars because during shifting the...
- Continuously variable transmissionContinuously variable transmissionA continuously variable transmission is a transmission that can change steplessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratios between maximum and minimum values. This contrasts with other mechanical transmissions that offer a fixed number of gear ratios...

