
Pontecorvo–Maki–Nakagawa–Sakata matrix
Encyclopedia
In particle physics
, the Pontecorvo–Maki–Nakagawa–Sakata matrix (PMNS matrix), Maki–Nakagawa–Sakata matrix (MNS matrix), lepton mixing matrix, or neutrino mixing matrix, is a unitary matrixThe PMNS matrix is not unitary in the seesaw model
which contains information on the mismatch of quantum states of lepton
s when they propagate freely and when they take part in the weak interaction
s. It is important in the understanding of neutrino oscillation
s. This matrix was introduced in 1962 by Ziro Maki, Masami Nakagawa and Shoichi Sakata
, to explain the neutrino oscillations predicted by Bruno Pontecorvo
.
of leptons, the matrix can be written as: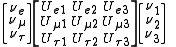 .
.
On the left are the neutrino fields participating in the weak interaction
, and on the right is the PMNS matrix along with a vector of the neutrino fields diagonalizing the neutrino mass matrix. The PMNS matrix describes the probability of a neutrino of given flavor α to be found in mass eigenstate i. These probabilities are proportional to |Uαi|2.
Various parametrization
s of this matrix exist, however due to the difficulties of detecting neutrino
s, it is much more difficult to determine the individual coefficients than in the equivalent matrix for the quarks (the CKM matrix). The matrix is most commonly parameterized by three mixing angles
(Θ12, Θ23 and Θ13) and a single phase. Experimentally, the mixing anfles were established to be approximately Θ12=45 degrees, Θ23=34 degrees, and Θ13<4 degrees.
As a starting point, one recent particle physics course provided the following
estimated values for the matrix (assuming the mixing angle Θ13=0, which is in good agreement with the experiment, and therefore no imaginary parameters in the matrix):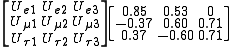 .
.
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
, the Pontecorvo–Maki–Nakagawa–Sakata matrix (PMNS matrix), Maki–Nakagawa–Sakata matrix (MNS matrix), lepton mixing matrix, or neutrino mixing matrix, is a unitary matrixThe PMNS matrix is not unitary in the seesaw model
Seesaw mechanism
In theoretical physics, the seesaw mechanism is a mechanism within grand unification theory, and in particular in theories of neutrino masses and neutrino oscillation, where it can be used to explain the smallness of observed neutrino masses relative to those of quarks and leptons.There are several...
which contains information on the mismatch of quantum states of lepton
Lepton
A lepton is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. The best known of all leptons is the electron which governs nearly all of chemistry as it is found in atoms and is directly tied to all chemical properties. Two main classes of leptons exist: charged leptons , and neutral...
s when they propagate freely and when they take part in the weak interaction
Weak interaction
Weak interaction , is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, alongside the strong nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity. It is responsible for the radioactive decay of subatomic particles and initiates the process known as hydrogen fusion in stars...
s. It is important in the understanding of neutrino oscillation
Neutrino oscillation
Neutrino oscillation is a quantum mechanical phenomenon predicted by Bruno Pontecorvowhereby a neutrino created with a specific lepton flavor can later be measured to have a different flavor. The probability of measuring a particular flavor for a neutrino varies periodically as it propagates...
s. This matrix was introduced in 1962 by Ziro Maki, Masami Nakagawa and Shoichi Sakata
Shoichi Sakata
was a Japanese academic and physicist who was internationally known for theoretical work on the structure of the atom. He proposed the Sakata model, which was an early precursor to the quark model....
, to explain the neutrino oscillations predicted by Bruno Pontecorvo
Bruno Pontecorvo
Bruno Pontecorvo was an Italian-born nuclear physicist, an early assistant of Enrico Fermi and then the author of numerous studies in high energy physics, especially on neutrinos. According to Oleg Gordievsky and Pavel Sudoplatov , Pontecorvo was also a Soviet agent...
.
The matrix
For three generationsGeneration (particle physics)
In particle physics, a generation is a division of the elementary particles. Between generations, particles differ by their quantum number and mass, but their interactions are identical....
of leptons, the matrix can be written as:
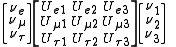 .
.On the left are the neutrino fields participating in the weak interaction
Weak interaction
Weak interaction , is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, alongside the strong nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity. It is responsible for the radioactive decay of subatomic particles and initiates the process known as hydrogen fusion in stars...
, and on the right is the PMNS matrix along with a vector of the neutrino fields diagonalizing the neutrino mass matrix. The PMNS matrix describes the probability of a neutrino of given flavor α to be found in mass eigenstate i. These probabilities are proportional to |Uαi|2.
Various parametrization
Parametrization
Parametrization is the process of deciding and defining the parameters necessary for a complete or relevant specification of a model or geometric object....
s of this matrix exist, however due to the difficulties of detecting neutrino
Neutrino detector
A neutrino detector is a physics apparatus designed to study neutrinos. Because neutrinos are only weakly interacting with other particles of matter, neutrino detectors must be very large in order to detect a significant number of neutrinos. Neutrino detectors are often built underground to isolate...
s, it is much more difficult to determine the individual coefficients than in the equivalent matrix for the quarks (the CKM matrix). The matrix is most commonly parameterized by three mixing angles
(Θ12, Θ23 and Θ13) and a single phase. Experimentally, the mixing anfles were established to be approximately Θ12=45 degrees, Θ23=34 degrees, and Θ13<4 degrees.
As a starting point, one recent particle physics course provided the following
estimated values for the matrix (assuming the mixing angle Θ13=0, which is in good agreement with the experiment, and therefore no imaginary parameters in the matrix):
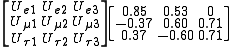 .
.

