
Plotkin bound
Encyclopedia
In the mathematics
of coding theory
, the Plotkin bound, named after Morris Plotkin, is a bound on the maximum possible number of codewords in binary code
s of given length n and given minimum distance d.
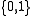 . In particular, if all codewords have a fixed length n, we
. In particular, if all codewords have a fixed length n, we
speak of a binary code of length n. Equivalently, we may consider in this case the codewords as elements of vector space
 over the finite field
over the finite field
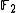 . Let
. Let 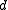 be the minimum
be the minimum
distance of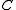 , i.e.
, i.e.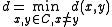
where is the Hamming distance
is the Hamming distance
between and
and 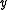 . The expression
. The expression 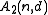 represents the maximum number of possible codewords in a binary code of length
represents the maximum number of possible codewords in a binary code of length  and minimum distance
and minimum distance  . The Plotkin bound places a limit on this expression.
. The Plotkin bound places a limit on this expression.
Theorem (Plotkin bound):
i) If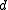 is even and
is even and 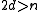 , then
, then

ii) If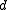 is odd and
is odd and  , then
, then
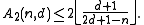
iii) If is even, then
is even, then
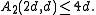
iv) If is odd, then
is odd, then
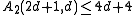
where denotes the floor function
.
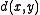 be the Hamming distance
be the Hamming distance
of and
and  , and
, and 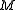 be the number of elements in
be the number of elements in 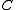 (thus,
(thus, 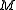 is equal to
is equal to  ). The bound is proved by bounding the quantity
). The bound is proved by bounding the quantity  in two different ways.
in two different ways.
On the one hand, there are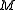 choices for
choices for  and for each such choice, there are
and for each such choice, there are 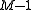 choices for
choices for 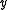 . Since by definition
. Since by definition 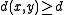 for all
for all  and
and 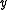 (
(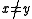 ), it follows that
), it follows that
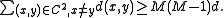
On the other hand, let be an
be an  matrix whose rows are the elements of
matrix whose rows are the elements of 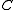 . Let
. Let 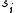 be the number of zeros contained in the
be the number of zeros contained in the 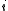 'th column of
'th column of  . This means that the
. This means that the 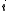 'th column contains
'th column contains 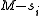 ones. Each choice of a zero and a one in the same column contributes exactly
ones. Each choice of a zero and a one in the same column contributes exactly 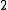 (because
(because 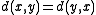 ) to the sum
) to the sum 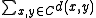 and therefore
and therefore
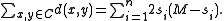
If is even, then the quantity on the right is maximized if and only if
is even, then the quantity on the right is maximized if and only if 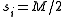 holds for all
holds for all  , then
, then
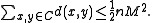
Combining the upper and lower bounds for that we have just derived,
that we have just derived,

which given that is equivalent to
is equivalent to

Since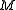 is even, it follows that
is even, it follows that
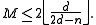
On the other hand, if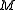 is odd, then
is odd, then 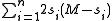 is maximized when
is maximized when 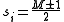 which implies that
which implies that
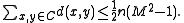
Combining the upper and lower bounds for , this means that
, this means that
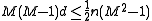
or, using that ,
,
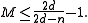
Since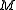 is an integer,
is an integer,
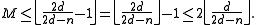
This completes the proof of the bound.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
of coding theory
Coding theory
Coding theory is the study of the properties of codes and their fitness for a specific application. Codes are used for data compression, cryptography, error-correction and more recently also for network coding...
, the Plotkin bound, named after Morris Plotkin, is a bound on the maximum possible number of codewords in binary code
Code
A code is a rule for converting a piece of information into another form or representation , not necessarily of the same type....
s of given length n and given minimum distance d.
Statement of the bound
We say a code is binary, if the codewords use symbols from the binary alphabet . In particular, if all codewords have a fixed length n, we
. In particular, if all codewords have a fixed length n, wespeak of a binary code of length n. Equivalently, we may consider in this case the codewords as elements of vector space
Vector space
A vector space is a mathematical structure formed by a collection of vectors: objects that may be added together and multiplied by numbers, called scalars in this context. Scalars are often taken to be real numbers, but one may also consider vector spaces with scalar multiplication by complex...
 over the finite field
over the finite fieldFinite field
In abstract algebra, a finite field or Galois field is a field that contains a finite number of elements. Finite fields are important in number theory, algebraic geometry, Galois theory, cryptography, and coding theory...
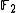 . Let
. Let 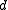 be the minimum
be the minimumdistance of
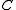 , i.e.
, i.e.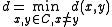
where
 is the Hamming distance
is the Hamming distanceHamming distance
In information theory, the Hamming distance between two strings of equal length is the number of positions at which the corresponding symbols are different...
between
 and
and 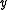 . The expression
. The expression 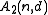 represents the maximum number of possible codewords in a binary code of length
represents the maximum number of possible codewords in a binary code of length  and minimum distance
and minimum distance  . The Plotkin bound places a limit on this expression.
. The Plotkin bound places a limit on this expression.Theorem (Plotkin bound):
i) If
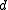 is even and
is even and 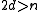 , then
, then
ii) If
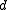 is odd and
is odd and  , then
, then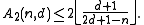
iii) If
 is even, then
is even, then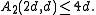
iv) If
 is odd, then
is odd, then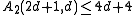
where denotes the floor function
Floor function
In mathematics and computer science, the floor and ceiling functions map a real number to the largest previous or the smallest following integer, respectively...
.
Proof of case i
Let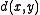 be the Hamming distance
be the Hamming distanceHamming distance
In information theory, the Hamming distance between two strings of equal length is the number of positions at which the corresponding symbols are different...
of
 and
and  , and
, and 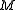 be the number of elements in
be the number of elements in 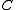 (thus,
(thus, 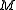 is equal to
is equal to  ). The bound is proved by bounding the quantity
). The bound is proved by bounding the quantity  in two different ways.
in two different ways.On the one hand, there are
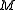 choices for
choices for  and for each such choice, there are
and for each such choice, there are 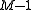 choices for
choices for 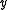 . Since by definition
. Since by definition 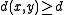 for all
for all  and
and 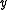 (
(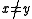 ), it follows that
), it follows that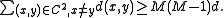
On the other hand, let
 be an
be an  matrix whose rows are the elements of
matrix whose rows are the elements of 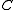 . Let
. Let 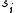 be the number of zeros contained in the
be the number of zeros contained in the 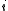 'th column of
'th column of  . This means that the
. This means that the 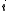 'th column contains
'th column contains 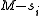 ones. Each choice of a zero and a one in the same column contributes exactly
ones. Each choice of a zero and a one in the same column contributes exactly 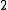 (because
(because 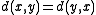 ) to the sum
) to the sum 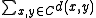 and therefore
and therefore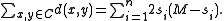
If
 is even, then the quantity on the right is maximized if and only if
is even, then the quantity on the right is maximized if and only if 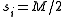 holds for all
holds for all  , then
, then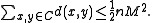
Combining the upper and lower bounds for
 that we have just derived,
that we have just derived,
which given that
 is equivalent to
is equivalent to
Since
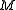 is even, it follows that
is even, it follows that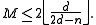
On the other hand, if
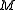 is odd, then
is odd, then 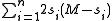 is maximized when
is maximized when 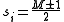 which implies that
which implies that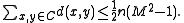
Combining the upper and lower bounds for
 , this means that
, this means that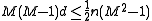
or, using that
 ,
,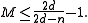
Since
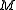 is an integer,
is an integer,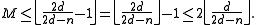
This completes the proof of the bound.
See also
- Singleton boundSingleton boundIn coding theory, the Singleton bound, named after Richard Collom Singleton, is a relatively crude bound on the size of a block code C with block length n, size r and minimum distance d.-Statement of the Bound:...
- Hamming boundHamming boundIn mathematics and computer science, in the field of coding theory, the Hamming bound is a limit on the parameters of an arbitrary block code: it is also known as the sphere-packing bound or the volume bound from an interpretation in terms of packing balls in the Hamming metric into the space of...
- Gilbert-Varshamov boundGilbert-Varshamov boundIn coding theory, the Gilbert–Varshamov bound is a bound on the parameters of a code . It is occasionally known as the Gilbert–Shannon–Varshamov bound , but the Gilbert–Varshamov bound is by far the most popular name...
- Johnson bound
- Griesmer boundGriesmer boundIn the mathematics of coding theory, the Griesmer bound, named after James Hugo Griesmer, is a bound on the length of binary codes of dimension k and minimum distance d.There is also a very similar version for non-binary codes....

