
Plethysmograph
Encyclopedia

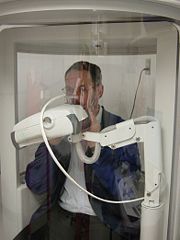
Organ (anatomy)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in structural unit to serve a common function. Usually there is a main tissue and sporadic tissues . The main tissue is the one that is unique for the specific organ. For example, main tissue in the heart is the myocardium, while sporadic are...
or whole body (usually resulting from fluctuations in the amount of blood or air it contains).
Lungs
Pulmonary plethysmographs are commonly used to measure the functional residual capacityFunctional residual capacity
Functional Residual Capacity is the volume of air present in the lungs, specifically the parenchyma tissues, at the end of passive expiration...
(FRC) of the lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s—the volume in the lungs when the muscles of respiration are relaxed—and total lung capacity.
In a traditional plethysmograph, the test subject is placed inside a sealed chamber the size of a small telephone booth with a single mouthpiece. At the end of normal expiration, the mouthpiece is closed. The patient is then asked to make an inspiratory effort. As the patient tries to inhale (a maneuver which looks and feels like panting), the lungs expand, decreasing pressure within the lungs and increasing lung volume. This, in turn, increases the pressure within the box since it is a closed system and the volume of the box compartment has decreased to accommodate the new volume of the subject.
Boyle's Law
Boyle's law
Boyle's law is one of many gas laws and a special case of the ideal gas law. Boyle's law describes the inversely proportional relationship between the absolute pressure and volume of a gas, if the temperature is kept constant within a closed system...
is used to calculate the unknown volume within the lungs. First, the change in volume of the chest is computed. The initial pressure and volume of the box are set equal to the known pressure after expansion times the unknown new volume. Once the new volume is found, the new volume minus the original volume is the change in volume in the box and also the change in volume in the chest. With this information, Boyle's Law is used again to determine the original volume of gas: the initial volume (unknown) times the initial pressure is equal to the final volume times the final pressure.
The difference between full and empty lungs can be used to assess diseases and airway passage restrictions. An obstructive disease will show increased FRC because some airways do not empty normally, while a restrictive disease will show decreased FRC. Body plethysmography is particularly appropriate for patients who have air spaces which do not communicate with the bronchial tree; in such patients gas dilution would give an incorrectly low reading.
Newer lung plethysmograph devices have an option which does not require enclosure in a chamber.
Limbs
Some plethysmograph devices are attached to armArm
In human anatomy, the arm is the part of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow joints. In other animals, the term arm can also be used for analogous structures, such as one of the paired forelimbs of a four-legged animal or the arms of cephalopods...
s, leg
Human leg
The human leg is the entire lower extremity or limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh and even the hip or gluteal region; however, the precise definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle.Legs are used for standing,...
s or other extremities and used to determine circulatory capacity.
In water plethysmography an extremity, e.g. an arm, is enclosed in a water-filled chamber where volume changes can be detected. Air plethysmography uses a similar principle but based on an air-filled long cuff, which is more convenient but less accurate.
Another practical device is mercury-filled strain gauges used to continuously measure circumference of the extremity, e.g. at mid calf.
Impedance plethysmography is a non-invasive method used to detect venous thrombosis
Venous thrombosis
A venous thrombosis is a blood clot that forms within a vein. A venous thrombosis is a blood clot that forms within a vein. A venous thrombosis is a blood clot that forms within a vein. (Thrombosis is a medical term for blood clotting (Haemostasis) occurring in the wrong place, i.e...
in these areas of the body.
Genitals
Another common type of plethysmograph is the penile plethysmographPenile plethysmograph
Penile plethysmography , or "phallometry", refers to measurement of bloodflow to the male genital. The most commonly reported methods of conducting penile plethysmography involve the measurement of the circumference of the penis with a mercury-in-rubber strain gauge, or the volume of the penis with...
. This device is used to measure changes in blood flow in the penis
Penis
The penis is a biological feature of male animals including both vertebrates and invertebrates...
. Although some researchers use this device to assess sexual arousal
Sexual arousal
Sexual arousal, or sexual excitement, is the arousal of sexual desire, during or in anticipation of sexual activity. Things that precipitate human sexual arousal are called erotic stimuli, or colloquially known as turn-ons. There are many potential stimuli, both physical or mental, which can cause...
and sexual orientation
Sexual orientation
Sexual orientation describes a pattern of emotional, romantic, or sexual attractions to the opposite sex, the same sex, both, or neither, and the genders that accompany them. By the convention of organized researchers, these attractions are subsumed under heterosexuality, homosexuality,...
, the data are usually not admissible in court cases in the United States. An approximate female equivalent to penile plethysmography is vaginal photoplethysmography, which optically measures blood flow in the vagina.
Use in preclinical research
Plethysmography is a widely used method in basic and preclinical researchPre-clinical development
In drug development, pre-clinical development is a stage of research that begins before clinical trials can begin, and during which important feasibility, iterative testing and drug safety data is collected....
to study respiration. Several techniques are used:
Respiratory parameters from conscious freely moving animals: whole-body plethysmography
Whole-body plethysmography is used to measure respiratory parameters in conscious unrestrained subjects, including quantification of bronchoconstrictionBronchoconstriction
Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Bronchoconstriction can also be due to an accumulation of thick mucus....
.
The standard plethysmograph sizes are for the study of mice, rats and guinea pigs. On request, larger plethysmographs can also be manufactured for other animals, such as rabbits, dogs, pigs, or primates.
The plethysmograph has two chambers, each fitted with a pneumotachograph
Spirometry
Spirometry is the most common of the pulmonary function tests , measuring lung function, specifically the measurement of the amount and/or speed of air that can be inhaled and exhaled...
. The subject is placed in one of them (subject chamber) and the other remains empty (reference chamber).
The pressure change is measured by a differential pressure transducer with one port exposed to the subject chamber and the other to the reference chamber.
Respiratory parameters from conscious restrained animals: double-chamber / head-out plethysmography
The double-chamber plethysmograph (dcp) measures respiratory parameters in a conscious restrained subject, including airway resistanceAirway resistance
Airway resistance is a concept used in respiratory physiology to describe mechanical factors which limit the access of inspired air to the pulmonary alveoli, and thus determine airflow....
and conductance. Different sizes of plethysmograph exist to study mice, rats or guinea pigs.
The head-out configuration is identical to the standard configuration described above except that there is no head chamber.
Of course the collar seal is still applied, so that the body chamber remains airtight. With only a thoracic signal, all parameters can be obtained except for specific airway resistance (SRaw) and specific airway conductance (Sgaw).
Resistance/compliance from sedated animals
In anesthetized plethysmography, lung resistance and dynamic compliance are measured directly because the subject is anesthetized.Depending on the level of sedation, the subject may be spontaneously breathing (SB configuration) or under mechanical ventilation (MV configuration).
A flow signal and a pressure signal are required to calculate compliance and resistance.
Further reading
- Glaab T, Taube C, Braun A, Mitzner W (2007) Invasive and noninvasive methods for studying pulmonary function in mice. Respiratory Research 8:63 (free full text article)
See also
- Optoelectronic plethysmographyOptoelectronic plethysmographyOptoelectronic Plethysmography is a method to evaluate ventilation through an external measurement of the chest wall surface motion.This method has been developed at the Bioengineering Department of the Politecnico di Milano university....
- Body plethysmographyBody plethysmographyBody plethysmography or "Body Box" for short, is a very sensitive lung measurement used to detect lung pathology that might be missed with conventional pulmonary function tests. This method of obtaining the absolute volume of air within one's lungs may also be used in situations where several...
- PhotoplethysmographPhotoplethysmographA photoplethysmogram is an optically obtained plethysmogram, a volumetric measurement of an organ. A PPG is often obtained by using a pulse oximeter which illuminates the skin and measures changes in light absorption...
- Respiratory inductance plethysmographyRespiratory inductance plethysmographyRespiratory Inductance Plethysmography is a method of evaluating pulmonary ventilation by measuring the movement of the chest and abdominal wall....

