
Functional residual capacity
Encyclopedia
Expiration
Expiration is an independent feature film written, directed and starring Gavin Heffernan. It was the winner of the Grand Jury Prize and Best Film at the Canadian Filmmakers' Festival....
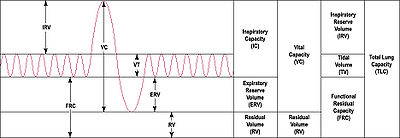
. At FRC, the elastic recoil forces of the lungs and chest wall are equal but opposite and there is no exertion by the diaphragm
Thoracic diaphragm
In the anatomy of mammals, the thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm , is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle that extends across the bottom of the rib cage. The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and performs an important function in respiration...
or other respiratory muscles.
FRC is the sum of Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) and Residual Volume (RV) and measures approximately 2400 ml in a 70 kg, average-sized male. It can not be estimated through spirometry
Spirometry
Spirometry is the most common of the pulmonary function tests , measuring lung function, specifically the measurement of the amount and/or speed of air that can be inhaled and exhaled...
, since it includes the residual volume. In order to measure RV precisely, one would need to perform a test such as nitrogen washout, helium dilution
Helium dilution technique
The helium dilution technique is the way of measuring the functional residual capacity of the lungs ....
or body plethysmography
Body plethysmography
Body plethysmography or "Body Box" for short, is a very sensitive lung measurement used to detect lung pathology that might be missed with conventional pulmonary function tests. This method of obtaining the absolute volume of air within one's lungs may also be used in situations where several...
.
A lowered or elevated FRC is often an indication of some form of respiratory disease
Respiratory disease
Respiratory disease is a medical term that encompasses pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange possible in higher organisms, and includes conditions of the upper respiratory tract, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleura and pleural cavity, and the...
. For instance, in emphysema
Emphysema
Emphysema is a long-term, progressive disease of the lungs that primarily causes shortness of breath. In people with emphysema, the tissues necessary to support the physical shape and function of the lungs are destroyed. It is included in a group of diseases called chronic obstructive pulmonary...
, the lungs are more compliant and therefore are more susceptible to the outward recoil forces of the chest wall. Emphysema patients often have noticeably broader chests because they are breathing at larger volumes.
The helium dilution technique
Helium dilution technique
The helium dilution technique is the way of measuring the functional residual capacity of the lungs ....
is a common way of measuring the functional residual capacity of the lungs.

