
Airway resistance
Encyclopedia
Airway resistance is a concept used in respiratory physiology
to describe mechanical factors which limit the access of inspired air to the pulmonary alveoli, and thus determine airflow.
Resistance is greatest at the bronchi of intermediate size, in between the fourth and eighth bifurcation.
Because airway resistance is dictated by the diameter of the airways and by the density of the inspired gas, the low density of heliox
reduces airway resistance, and makes it easier to ventilate the lungs.
Resistance can be calculated using Ohm's law
or Poiseuille's law. It can be estimated with body plethysmography
.

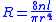
(rewrite)
Because of the fourth power in the denominator, resistance increases rapidly as diameter decreases.
Respiratory physiology
Respiratory physiology is the branch of human physiology focusing upon respiration.Topics include:-Volumes:* lung volumes* vital capacity* functional residual capacity* dead space* spirometry* body plethysmography* peak flow meter-Mechanics:...
to describe mechanical factors which limit the access of inspired air to the pulmonary alveoli, and thus determine airflow.
Resistance is greatest at the bronchi of intermediate size, in between the fourth and eighth bifurcation.
Because airway resistance is dictated by the diameter of the airways and by the density of the inspired gas, the low density of heliox
Heliox
Heliox is a breathing gas composed of a mixture of helium and oxygen .Heliox has been used medically since the 1930s, and although the medical community adopted it initially to alleviate symptoms of upper airway obstruction, its range of medical uses has since expanded greatly, mostly because of...
reduces airway resistance, and makes it easier to ventilate the lungs.
Resistance can be calculated using Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
or Poiseuille's law. It can be estimated with body plethysmography
Body plethysmography
Body plethysmography or "Body Box" for short, is a very sensitive lung measurement used to detect lung pathology that might be missed with conventional pulmonary function tests. This method of obtaining the absolute volume of air within one's lungs may also be used in situations where several...
.
Ohm's law

-
 = resistance
= resistance -
 = pressure
= pressure -
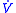 = airflow (the dot over the letter is used to denote rateRateIn mathematics, a rate is a ratio between two measurements, often with different units. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit time. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit time, or per unit of length or mass or...
= airflow (the dot over the letter is used to denote rateRateIn mathematics, a rate is a ratio between two measurements, often with different units. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit time. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit time, or per unit of length or mass or...
in respiratory physiologyRespiratory physiologyRespiratory physiology is the branch of human physiology focusing upon respiration.Topics include:-Volumes:* lung volumes* vital capacity* functional residual capacity* dead space* spirometry* body plethysmography* peak flow meter-Mechanics:...
.)
Poiseuille's law
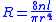
(rewrite)
- R = resistance
- n = viscosity
- l = length
- r = radius
Because of the fourth power in the denominator, resistance increases rapidly as diameter decreases.
Derived parameters
Airway resistance is generally given as Raw. Derived parameters include:- Specific airway resistance (sRaw), also called volumic airway resistance (Raw/V); calculated as Raw/FRCFunctional residual capacityFunctional Residual Capacity is the volume of air present in the lungs, specifically the parenchyma tissues, at the end of passive expiration...
. - Airway conductanceConductanceConductance may refer to:* Electrical conductance, the ability for electricity to flow a certain path* Fluid conductance, the ability for fluid to transmit through materials* Thermal conductivity, the ability for temperatures to transmit through materials...
(Gaw); calculated as 1/Raw. - Specific airway conductance (sGaw), also called volumic airway conductance (Gawaw/FRC.
See also
- turbulent flow
- laminar flowLaminar flowLaminar flow, sometimes known as streamline flow, occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers. At low velocities the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another like playing cards. There are no cross currents...
- Reynolds number
- Upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS)

